Flammability properties are of decisive importance for the fire safety of substances and materials. In this respect, all known compositions are divided into flammable and non-flammable. These terms define their flammability. Based on this quality of materials, it is possible to calculate in advance the optimal option for fire protection of a structure even at the stage of its design. Which materials are non-combustible and which are prone to rapid ignition can be calculated with great accuracy at the preliminary stage of construction.
What materials are non-flammable?
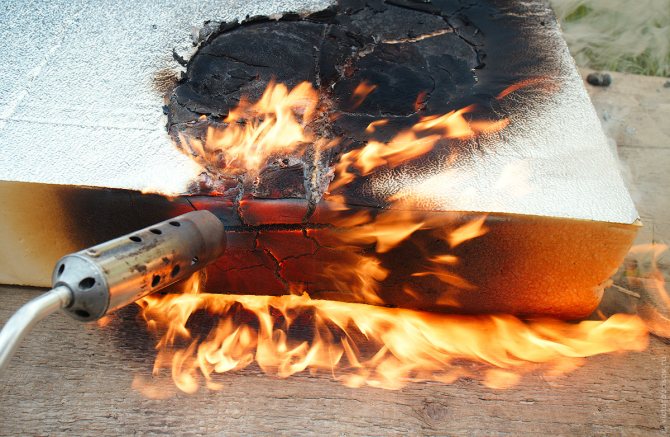
The group of non-combustible materials includes those that, in the process of exposure to an open flame, retain their original state. At the same time, they do not ignite, do not char, do not smolder and do not contribute to the spread of fire.
The Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements of 2008 acts as a regulatory source that classifies substances according to the degree of fire hazard. The main material on this issue is contained in article 12 of this document. Additional information on fire and explosion hazard is contained in GOST 12.1.044-89.
In accordance with these regulations, the flammability group refers to the parameters that determine the combustion of materials under different conditions. It should be noted that:
1.
The category of non-combustible substances includes compounds that are incapable of burning in a normal environment.
2.
There is a group of non-flammable substances that, when in contact with air or water, become explosive and fire hazardous. This group also includes compounds with the chemical properties of powerful oxidizing agents. To accurately determine the properties of materials and assess their fire resistance, it is necessary to find out their composition, what characteristics the substances of which they are composed have.
In the course of certification activities and expertise, the working and chemical properties of the test substances are precisely established. The results obtained are taken as a basis for the development of GOSTs, technical conditions for the operation of enterprises, the issuance of a certificate, and the development of fire-prevention measures at the facility.
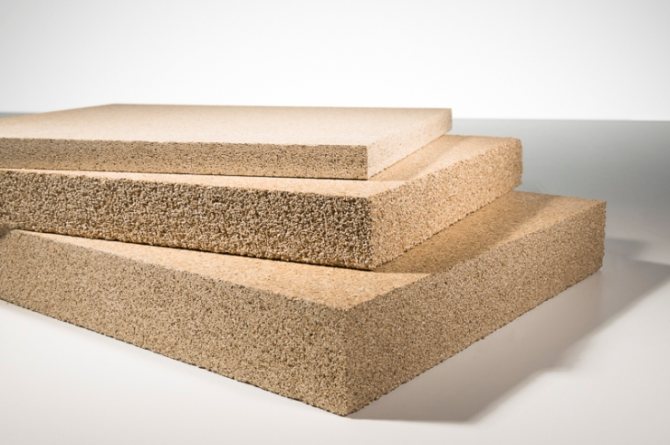
Liquid non-combustible insulation
The class of these heaters includes mainly synthetic-based materials that have excellent thermal insulation properties. The most famous representative of this type is liquid polyurethane.

This is a modern, absolutely non-combustible and environmentally friendly insulation. When using polyurethane for walls, ceilings and floors, you can be sure that the insulation will last for a long time. Polyurethane also has high adhesive properties, reliably seals the smallest cracks and crevices, completely preventing the formation of cold bridges.
Advantages:
- excellent heat-conducting qualities;
- high efficiency, safety.
Disadvantages:
- high price;
- the complexity of the application.
Scope of application
The main purpose of determining the degree of flammability of substances lies in the practical field. The results of these activities are usually used in the construction and landscaping industry. The combined use of flammable and non-flammable substances will ensure high fire safety in combination with a moderate value of production costs.
The materials used in the construction industry make it possible to make the safe operation of buildings after the completion of the construction. Non-combustible materials for the bath can reduce the risk of fire to acceptable values.An example is the active use of hollow materials in construction.
Especially often a brick with voids inside the structure is used in this capacity. In addition, it is used as a non-combustible material for stoves in low-rise structures. It should be remembered that the contact points of chimneys and stoves docked with combustible structures must be insulated with fire retardants: mastic, plaster, sealant.
Non-combustible material for the chimney must be insulated at the junction with flammable elements. In the construction industry, hazardous materials are actively changing to formulations that are stable and resistant to fire. The traditional wooden floor structure is almost completely replaced by a conventional screed combined with floor ceramics or non-combustible linoleum. Non-combustible materials for walls and ceilings are widely used both in low-rise construction and in apartment buildings.
Materials based on wood and wood shavings are consistently being replaced from the construction industry. Usually, these materials are changed to block elements, for example, tuff blocks or foam concrete products. As finishing panels, both internal and external, non-combustible sheet material is used.


For the insulation of walls, ceilings, floors, roll and sheet material based on basalt and other mineral fibrous compositions is used. These products are characterized by high fire safety and are used:
- for thermal insulation of technical openings for windows and doors;
- to ensure thermal insulation of the outer floors, roof structures, floor of the room;
- for insulation of upper superstructures and attic floors;
- in order to ensure thermal insulation of pipelines for various purposes, including water pipelines, gas pipes, wastewater discharge system, cylindrical structures or roll samples are used as heat-saving elements;
- fibrous mineral compounds are also used for sound insulation in premises for various purposes.
Various metal structures also have a high degree of fire safety. This number includes:
1.
Cast iron and steel used to create pipe products, industrial and construction equipment, fittings for pipelines. From these metals casings are cast for machine tools and equipment for various purposes, they are used for the production of engineering equipment.
2.
Conventional steel is actively used for the production of fittings for structural fittings. Elements of supporting structures for structures for various purposes are created from steel.
3.
Copper, aluminum and various alloys based on them are used as conductive materials in the energy sector.
Chimney thermal insulation
Bath chimneys are subject to mandatory thermal insulation. This is especially important where the pipe crosses the ceiling and the thickness of the roofing cake. In these places, ceiling-throughput units (PPU) are equipped, i.e. a box formed by non-combustible materials - metal, LSU, etc.
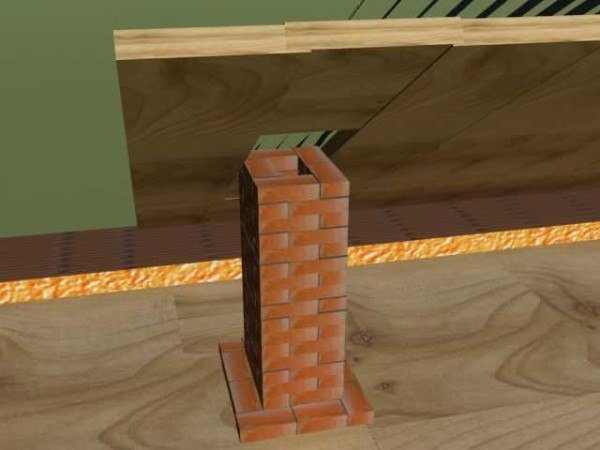

Thermal insulation of the chimney is also carried out in the attic volume when a living space is being set up in the attic of a bathhouse or when they seek to minimize the formation of condensation. The lightest option is rock wool, which is secured around the pipe with wire.
When equipping a living room around the pipe, you can surround it with a brick "sarcophagus", which, playing a protective role, will become an excellent source and accumulator of heat. If the construction of the bath is not able to withstand the mass of bricks, then the box can be mounted from sheet materials such as SKL and LSU.
Classification of materials
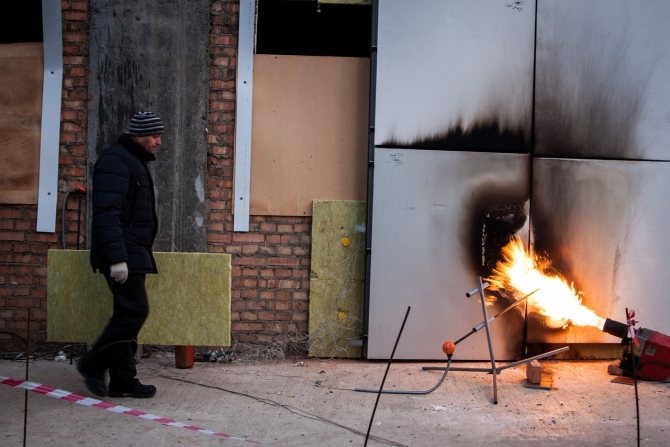
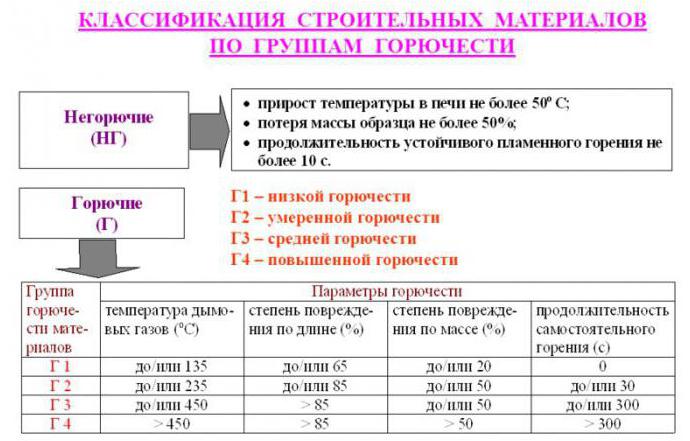
GOST 30244-94 is the main document that defines the methods for classifying materials by flammability classes.This normative act sets out the methods for testing materials and identifies two groups:
- non-combustible "NG";
- combustible "G".
The group of non-combustible includes compounds that withstand tests, which are as follows:
- reduction in the mass of the tested substance - no more than 50%;
- the temperature should rise by no more than 50%;
- time of stable burning with open fire - up to 10 seconds.


All types of materials that participated in the tests and did not pass even one of the criteria are classified as combustible. Differ in fire resistance and construction objects. Among this category, two types of buildings can be distinguished:
1.
All construction details are made of non-combustible compounds. The main bearing elements have an extreme degree of fire resistance, which allows them to withstand up to 2 hours of exposure to an open flame.
2.
The difference in the second category is the use of metal structures that have not been treated with fire protection. Metal elements should be used when creating openwork elements of trusses, beams and other patterns in the area of the roof of the building. In this case, the fire resistance limit will be 1.5 hours.
Objects that meet the above fire resistance requirements to the greatest extent meet fire safety standards. As an additional classification of non-combustible compounds used in the construction, reconstruction and repair of structures, several types of division are used.
Depending on the type of products manufactured, substances are divided into:
- produced in the form of a roll, tile, technological sheet;
- in the form of a free-flowing substance;
- in the form of rigid elements such as metal trusses or reinforced concrete slabs.
Depending on the purpose of the product:
- decorative finishing materials, for example, tiles for various purposes or wall panels;
- finished building structures, for example, slabs, bricks, floors;
- bulk materials for various purposes, heat-insulating and sound-insulating molded products.
Thermal conductivity and moisture absorption of thermal insulation materials
Thermal conductivity is the main operational characteristic of any insulation. Thermal conductivity does not depend on the density of the material, therefore, when choosing a heater, you should pay attention to this fact. The lower the thermal conductivity, the warmer the building or room protected by such insulation will be.
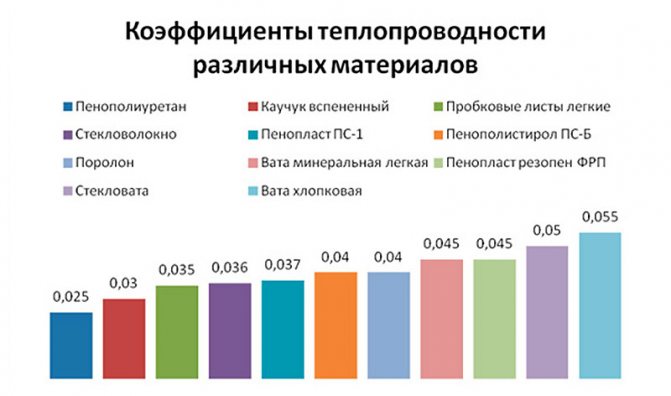

Coefficients of thermal conductivity of different thermal insulation materials
The next important parameter is moisture absorption. There is always water vapor in the atmosphere, and at a certain concentration in the insulation, they can turn into condensate, which will immediately reduce the properties of thermal conductivity. To prevent the formation of condensation, vapor barrier layers are used, for example, if it is a heater for a bath, where the humidity will always be high.
Fire resistance is the ability to resist open fire. This parameter is important for the chimney, for stoves and chimneys, as well as for other elements of the heating system that are exposed to strong heating. In such risk areas, heat-resistant insulation should always be used - mineral wool, slag wool and similar materials.
The table shows the types of insulation that have high heat-resistant characteristics:
| Properties | Slag wool | Glass wool | Mineral wool | Btv | BSTv |
| Maximum temperature, 0С | ≤ 250 | -60/+450 | ≤ 300 | -190/+700 | -190/+1000 |
| Ø, μm | 4,0-12,0 | 4,0-12,0 | 4,0-12,0 | 5,0-15,0 | 1,0-3,0 |
| Moisture absorption per day, ≤% | 1,95 | 1,75 | 0,095 | 0,035 | 0,025 |
| Prickly | there is | there is | Not | Not | Not |
| Bonding agents for surface attachment | there is | there is | there is | there is | Not |
| Thermal conductivity of the material, W / (m • K) | 0,40-0,48 | 0,038-0,046 | 0,077-0,12 | 0,038-0,046 | 0,033-0,038 |
| The volume of binders in the insulation,% | 2,5-10 | 2,5-10 | 2,5-10 | 2,5-10 | – |
| Flammability class (NG / G) | Non-flammable material | Non-flammable material | Non-flammable material | Non-flammable material | Non-flammable material |
| Evaporation of toxins | there is | there is | there is | If a binder is used | Not |
| Heat capacity, J / kg • K | 1000 | 1050 | 1050 | 500-800 | 800-1000 |
| Vibration resistance | Not | Not | Not | Not | there is |
| Compressive strength,% | – | – | 40 | 40 | 31,2 |
| Elasticity,% | – | – | 60 | 71 | 75,5 |
| Deformation temperature, 0С | 250-300 | 450-500 | 600 | 700-1000 | 1100-1500 |
| Fiber length, mm | 16,0 | 15,0-50,0 | 16,0 | 20,0-50,0 | 50,0-70,0 |
| Noise absorption coefficient | 0,75-0,82 | 0,75-0,92 | 0,75-0,95 | 0,75-0,95 | 0,95-0,99 |
| Chemical resistance (weight reduction),% in an aqueous medium | 7,85 | 6,25 | 4,55 | 1,65 | 1,65 |
| Chemical resistance (weight reduction),% in an alkaline medium | 7,05 | 6,05 | 6,45 | 2,75 | 2,75 |
| Chemical resistance (weight reduction),% in an acidic environment | 68,75 | 38,95 | 24,05 | 2,25 | 2,25 |

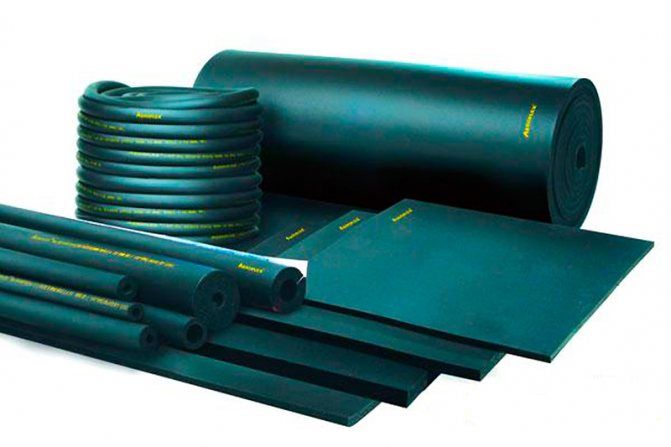
Soft heat-resistant insulation
Mineral wool thermal insulation material is a non-combustible insulation that goes on sale in the form of rolls and mats. It is easier to insulate the roof, floor surfaces and walls with a slab of mineral wool. Mats are used to insulate pipelines and curved surfaces, industrial equipment and elements of building structures.
Refractory mineral wool is made from broken glass, quartz sand, soda ash and other additives that form fibers when melted. Heat-resistant fiber wool is impregnated with resins and gets under the press. Insulation must have high heat resistance, mineral wool is an excellent non-combustible material, since its sintering occurs at a temperature of ≥ 1000 ° C. Because of this high parameter, the refractory material is effective for insulating saunas and baths, heat-resistant walls and partitions, for the chimney of stove pipes, etc.
The most effective parameters that non-combustible mineral wool has:
- Small coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- High sound absorption coefficient;
- High vapor permeability coefficient.
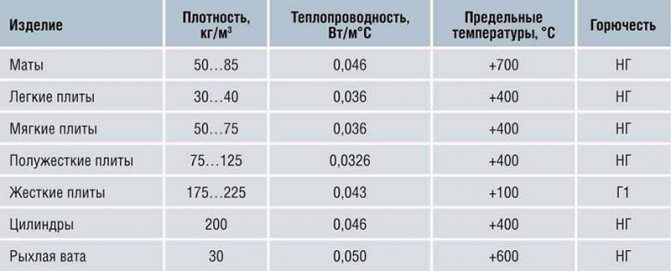

Parameters of products from mineral wool
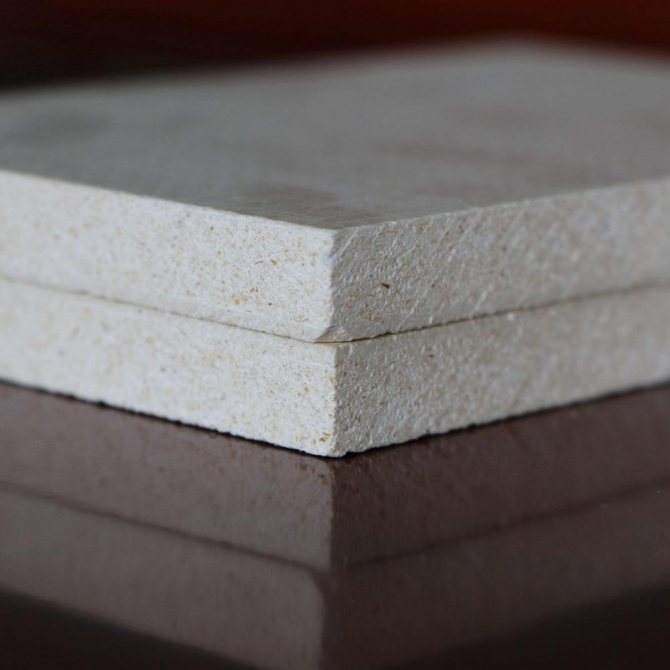
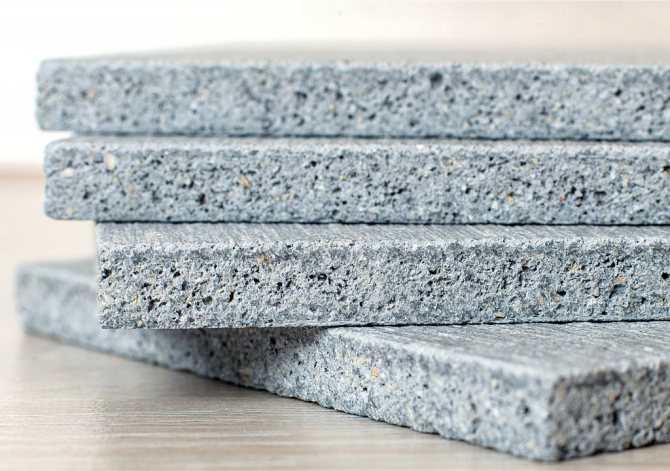
Foam glass is an environmentally friendly refractory material with a high melting point (≥ 450 ° C), non-combustible. Foam glass production options:
- Blocks (slabs) have a width of 650 x 450 mm, 600 x 600 mm, 600 x 500 mm, a thickness of 30-120 mm, they are used to insulate vertical planes. Fastened to cement mortar with an offset, in the same way as fireclay or silicate bricks;
- Granular foam glass is used as a free-flowing insulating material;
- Foam glass in the form of crushed stone, crumbs or breakage of different fractions is also used as backfill.
Foam glass granules or crushed stone are effective for floor and attic insulation. The table shows the main characteristics of the material:
| Characteristics and properties | Value | |
| Dimensions (length, width), mm | 475 x 400, 400 x 200, 400 x 250, 400 x 125 | 600 x 450 |
| Thickness, mm with a step of 10 mm | 60, 80, 100, 110 | 30-160 |
| Density, 10%, kg / m3 | 170-190 | 130 |
| Thermal conductivity of dry insulation, W (m • K) | 0,08 | 0,046 |
| Thermal conductivity of condition "A", W (m • K) | 0,08 | 0,046 |
| Thermal conductivity of condition "B", W (m • K) | 0,09 | 0,046 |
| Water vapor permeability, mg / (m • h • Pa), ≤ | 0,03 | 0,0005 |
| Compressive strength, MPa | 0,7 | 1,67 |
| Flexural strength, MPa | – | 0,5 |
| Moisture permeability for short-term and partial immersion, ≤ | 5% | 0.5 kg / m2 |
| Long-term immersion moisture permeability, kg / m2, ≤ | 5% | 0.5 kg / m2 |
| Working temperature 0С | -30/+400 | -260/+480 |
| Flammability group | NG (non-combustible material) | NG (non-combustible material) |


Foam glass
Types of substances
It is customary to distinguish between three main types of non-combustible substances of various origins. The first type includes solid materials presented in various structural and aggregate states. It can be free-flowing substances, and structures, and individual piece products.
This number includes:


- various samples of rocks, both rocky and softer, including limestone, dolomite, marble;
- concrete and reinforced concrete products;
- loose rocks, including gravel, sand, crushed stone;
- binders - chalk, clay, cement, gypsum, lime, plasters, mortars;
- cast iron and steel products of various types and designs - corners, channels, beams;
- non-ferrous metals, including bronze, copper, brass, aluminum alloys;
- mineral fibers such as basalt;
- various types of textile materials, including asbestos fabric, basalt fiber;
- ordinary and fire resistant glass.
Liquid substances:
- foaming agents and detergents;
- all types and conditions of water, from the source of drinking and ending with the use as a heat carrier;
- synthetic fluids that are incapable of burning;
- acids, alkalis, salts in the form of an aqueous solution.
Gaseous substances:
- carbon dioxide;
- nitrogen;
- freon;
- argon.
Types, classification and purpose
Refractory materials are produced on a mineral basis, a distinctive feature of which is the ability to maintain their normal functionality when exposed to high temperatures (more than 1580 degrees).
There are several classifications of refractories.
By size and shape
- Shaped refractory materials made in the form of large blocks, as well as simple, complex and particularly complex elements;
- Wedge-shaped and straight refractories of various sizes;
- Specialized refractory materials designed for laboratory and industrial use.
By operating temperature
The main ranges are subdivided into:
- 1580-1800 degrees;
- 1800-2000 degrees;
- 2000-3000 degrees;
- Over 3000 degrees.
By molding method
- Cast refractories created from a liquid slip base;
- Made of plastics. They are made by the method of initial machine molding, followed by pressing;
- In the form of cuts of natural mountain materials;
- Refractories created by the method of electric melting;
- Hot pressing;
- Thermoplastic pressing;
- Created from a powder base.
By structure
- Special density (open porosity is less than 3%);
- High density (open porosity 3-10%);
- Dense (open porosity 10-16%);
- Condensed (16-20%);
- Medium density (20-30%);
- Low density (total porosity 30-45%);
- Refractories with high porosity (45-75%);
- Ultra-porous refractory materials (> 75%).
By composition
By chemical composition, refractory materials it is customary to subdivide into 3 groups:
Neutral, made on the basis of aluminum and chromium oxides... These include:
- Carbonaceousused for the manufacture of piece furnace elements;
- Graphite... On their basis, crucibles are made for melting metal products;
- Chromite... They are used as an insulating layer in a refractory cake of sour and basic products.
Acidic (based on silicon dioxide)... Materials that belong to this group:
- Quartz sandused in the repair and welding of furnace elements;
- Dinas brickthat can be used for stove masonry;
- Quartz clay materialsused for the lining of furnace structures operating in a relatively low temperature regime.
Basic (on magnesium and calcium oxide):
- Chromomagnesite, is used for laying furnace structures operating in a mode of sharp temperature changes;
- Dolomite (powder material);
- Magnesite (in the form of masonry bricks or lining powder).
A separate classification category includes refractory thermal insulation materials.
They can significantly increase the efficiency of furnaces, since, due to their high porosity, they reduce heat loss through the wall elements.
Refractory insulation boards are manufactured 3 methods:
- Chemically, in which dolomite powder or limestone, dissolved in sulfuric acid, is introduced into the refractory base. In the course of a chemical reaction, foam is formed, which, when solidified, takes the form of a porous material.
- Implementation into a refractory base of carbonaceous elements (mainly small wood materials), which burn during firing, thereby forming voids in the starting material.
- With help soap foaming additives.
A little more about the types of fire resistant materials on the market:
Requirements for fire safety of materials
The modern regulatory framework is not limited to one document regulating the fire safety of substances and materials. The list of basic documents includes: 1.
GOST 30244-94 contains information on the procedure for testing building materials subject to fire. The norms of the document do not apply to paints and varnishes, granules, bulk substances, solutions used in construction.
2.
GOST 4640-2011 regulates the conditions for the production of mineral wool from rocks of various origins, slag waste from metallurgy, silicate materials. The main area of application of fibers is construction.
3.
NPB 244-97 contains standards for finishing and facing materials, waterproofing, roofing samples, floor coverings.
4.
GOST 32313-2011 regulates the quality condition of products of various shapes made of mineral wool, made in the form of plates, mats, cylinders with and without metal. Used in industry and construction to provide thermal insulation properties.
5.
GOST 21880-2011 defines the technical conditions for the production of mats used for thermal insulation of housing and communal services and industry. The products are manufactured using stitching technology.
6.
GOST 32603-2012 regulates the production of metal panels using mineral wool-based insulation.
7.
GOST 32314-2012 contains information on products made on the basis of mineral wool. The scope of application of the products is the construction industry.
The norms contained in these regulations do not limit the requirements for materials to a single fire resistance. The documents also contain other characteristics of the compositions used in the production area:
- resistance to various deformations after heating or exposure to water;
- moisture resistance and hygroscopicity;
- heat-conducting qualities;
- the ability to withstand mechanical stress, including rupture and bending;
- specific viscosity of the substance.
Non-combustible substances and materials in a cold state demonstrate completely different qualities than under the influence of an open flame. It is important to establish the suitability of a particular structure for use as a reliable link capable of withstanding design loads, including exposure to open flames.
Posted: 19/05/2020
Aerated concrete blocks for wall insulation
Non-combustible insulation with high fire resistance parameters is aerated concrete with low density. Aerated concrete blocks with a density ≤ D 400 are required for thermal insulation of walls, ceilings, floors and attics.
There are two negative points when using such products:
- A layer of insulation will be required more than usual. For example, the thickness of mineral wool can be two times less than a layer of aerated concrete for the same quality of insulation. Therefore, the use of aerated concrete can have critical consequences when insulating small buildings or premises;
kg / m 3
Dry blocks
Blocks with a moisture content of 4%
The accuracy of the geometric parameters of products in width - 0.7 mm, in length and height - 0.8 mm
Additional insulation of a layer of aerated concrete is carried out with mineral wool - it is attached to the frame or layer by layer using dowels with wide caps. The disadvantage of such thermal insulation is that the mineral wool will have to be protected with decorative finishing materials - siding, clapboard, etc.
To determine the likelihood of a flame, the flammability of substances and various materials is of prime importance. This characteristic determines the category of fire hazard of structures, premises, industries; allows you to choose the right means to eliminate foci.
The combustibility group of all material components of the object determines the success of fighting a fire, minimizes the likelihood of casualties.
Refractory material for rooms with different heating elements
Sauna protective materials
In order for the walls of the bath to acquire fireproof properties, they are produced finishing with heat-resistant materials... These include:
- A cake made from a layer of thermal insulation and a metallic reflective coating;
- Fire resistant drywall sheets;
- Minerite slabs;
- Superisol sheets;
- Stainless steel sheets (relatively expensive option);
- Magnesite glass plate with increased moisture resistance;
- Calcium silicate sheet materials. Possesses all the properties of LSU plates, however, in comparison with them, such sheets are less durable;
- Terracotta tiles.
There are 2 types of LSU boards on the building materials market - with and without a laminated coating.
For facing the fireplace
The main sheet material for fireplaces is fire-resistant plasterboard.
However, fire-resistant tiles are more commonly used. In addition to its protective properties, it has excellent decorative properties, due to which you can achieve aesthetics and a sense of comfort in room.
Types of fireplace tiles:
- Terracotta... The numerous positive qualities of this material include a high ability to give off heat, which is an excellent indicator of a finishing fireplace material;
- Tiles... The properties are similar to terracotta. The main difference is the complex decorative pattern on the front surface of the piece element, which is often applied by hand;
- Clinker tiles... Differs in ease of installation and maintenance;
- Porcelain stoneware... Has increased resistance to cracking. Its characteristics are similar not only to clay materials, but also to granite;
- Majolica... It is based on terracotta tiles, which are covered with an additional layer of glaze during production.
The main selection rules suitable fireproof tiles for the fireplace:
- The material must be moisture resistant;
- Resistant to sudden temperature changes;
- The minimum number of pores will allow the tiles to last longer;
- The optimum thickness of the piece element is 8 mm;
- Tiles marked "A" are of higher quality than "B" -elements.
Blast Furnace Lining Materials
Blast furnace lining is an internal refractory shell that protects the main body from overheating.
Done using kaolin board vermiculite boards or paper.
In addition to sheet material, linings can be found using the following materials:
- Fireclay brick;
- Basalt fiber;
- Hewn stone (quartz, sandstone, conglomerate);
- Fireclay or mullite solutions.
Instructions for laying refractory bricks in the kiln:
Wall decoration for a boiler
The following are used for cladding wall structures near the heating boiler sheet materials:
- Fireproof drywall;
- Sheets with xylolite fiber backing.
Wall decoration for the oven
Manufactured using the following sheet materials:
- Metal screens;
- Reflective skins made of rolled stainless steel sheets;
- Minerita;
- Fire resistant gypsum plasterboard;
- Glass-magnesium plate material.
Ensuring the protection of wall structures from the harmful effects of high temperatures - obligatory event, which can be produced in a great variety of ways. Installation of piece and sheet elements will not take too much time and money, however, it will allow the heated room to last much longer.