Hello dear readers! How are you feeling? Are you ready for the cold? Have you insulated yourself?
Today I came across an article that puzzled me, to put it mildly. It said that this winter will be very vigorous. That is, frosty and snowy. Well, what can I say? There are advantages and disadvantages to this. On the positive side - perky entertainment - sledges, skates, skis, snowballs. And negative - heating the house will cost a pretty penny. In order not to be speechless, looking at the amount in the receipt, it is recommended to insulate the "nest". Fortunately, there are a lot of materials for warming the room.
I decided to see what the manufacturing organizations offer today. My attention was drawn to the "old new" raw material - foam glass. Why "old new"? Well, how can I explain to you? The old one is 86 years old, and the new one is improved. However, let's study the material in more detail. So, here's a topic for you - foam glass: disadvantages, advantages, production, cost and much more. Let's start? Go!
Cellular glass: product features
A bit of history
The foam glass was invented by the honored worker of technology and science Isaak Ilyich Kitaygorodsky. The professor specialized in glass production technology, since he considered it the material of the future. The professor's invention was improved by US specialists in the 40s. Initially, foam glass was used as a floating material. But it soon became clear that it demonstrates excellent heat and sound insulation properties, easily glued, and easily processed. Therefore, it was decided to use it in construction.
Thus, in Canada, there was a building created from concrete slabs with a layer made of aerated glass. This event happened back in 1946. The experiment was very successful. The material received well-deserved recognition. But, to the great regret of the inventor, in the Soviet countries he did not gain popularity, since the cost was high, and the production technology was not worked out. It was made in the USSR, but the quality of the products left much to be desired, which led to the closure of factories.
But at the present time the manufacture of this product is in full swing!
Concept
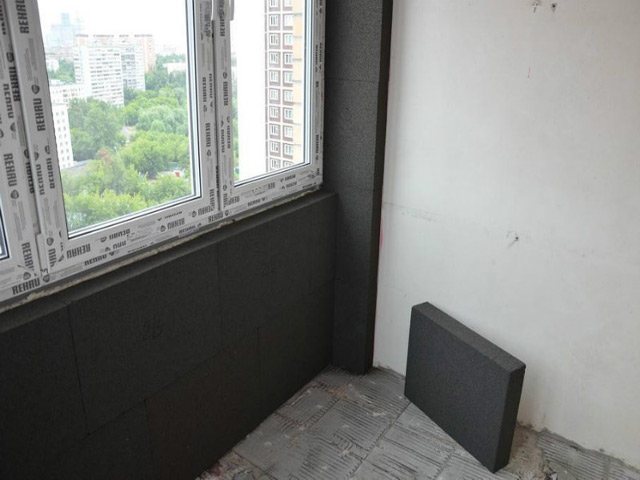


Thermal insulation of the balcony
Foam glass is a heat-insulating material made of silicate glass and raw materials that contribute to the formation of gas. Insulation is often called foamed or honeycomb glass because it has a honeycomb structure. Due to which it can boast of the most unique properties.
Production
Heat-insulating raw material - foam glass is made using powder technology. The process is quite simple but time consuming. It consists of the following steps:
- broken silicate glass is crushed;
- the crumb is thoroughly mixed with substances that form gas;
- charge (homogeneous mass) is placed on a conveyor belt or in molds and sent to the oven;
- glass softens, turning into a liquid but viscous mixture;
- under the influence of gases, the gruel foams;
- the mixture cools slowly;
- blocks, plates (sheets) or granules are formed from the product;
- the product is processed according to the requirements;
- plates, granules or blocks of foam glass are packed.
We can say that ordinary glass, which is used in everyday life, and the cellular product are twins, since they are identical in composition, the only difference is the pores filled with gas in the foamed product.
Only high quality materials and innovative equipment are used for the production of blocks, granules or slabs. In addition, the products undergo control, which is carried out by experts in accordance with European quality standards.
Advantages and disadvantages


Pros and cons
Describing the properties of the material, we can conclude that foam glass is almost an ideal material for insulation. However, it is not. It has advantages and disadvantages that fully characterize it.
Pros:
- safety for humans;
- ecological cleanliness;
- antiseptic properties guarantee high protection against bacteria;
- long service life;
- multifunctionality;
- can be used in the construction of various buildings;
- easily connects with other materials;
- do not lend themselves to attacks from rodents or insects;
- reflects moisture, ultraviolet and infrared rays;
- resistance to mechanical deformation;
- absolute neutrality towards acids;
- does not burn;
- ease of processing.
Not without drawbacks, which also gathered a significant number. Foam glass has the following disadvantages:
- high material cost due to the complexity of manufacturing using the latest developments;
- high brittleness, which can lead to cracks if improperly installed;
- low vapor permeability, which can lead to the accumulation of condensation on the surface adjacent to other material that is not so resistant to moisture;
- sensitivity to alkalis that can destroy the structure of the material;
- heavy weight;
- durability may be absolutely useless if the remaining layers deteriorate, since the re-use of foam glass is not provided;
- during transportation, it is necessary to protect the material from impacts, since even a small blow can destroy the block;
- even slightly damaged material can no longer be repaired, since its mechanical properties change instantly.
The material turned out to be far from ideal. And many people are still wary of using it in their designs. However, compliance with the rules of transportation, installation and operation will eliminate almost all the disadvantages.
Views
Today there are two types of foam glass - granular and block.
In addition, there are three types of granular insulation:
- foam glass gravel;
- foam glass crushed stone;
- foam glass sand.
And there are also three types of block insulation:


- plates (sheet foam glass);
- blocks;
- shells (shaped foam glass).
If we compare the thermal properties of granular and block glass, of course, gravel, crushed stone and sand are inferior to slabs, shells and blocks. But, nevertheless, granular insulation is more popular due to its relatively low price.
Scope of application
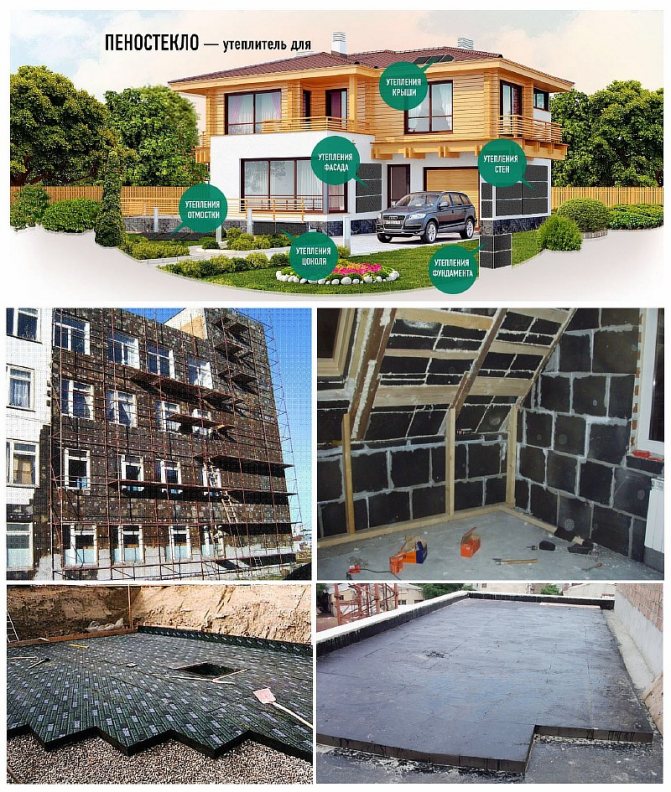
Foam glass, due to its properties, is used for insulation:


- private houses;
- outbuildings;
- sports complexes;
- underground structures;
- industrial buildings;
- medical institutions;
- educational institutions;
- office objects;
- recreational facilities - (for example, for baths, water parks, etc.).
The scope of application of the material is very wide, since the heat-insulating material is flawless:
- for insulation of the ceiling: the floor of the attic is filled with a cement-sand mortar, and then the slabs are laid, after which a reinforcing screed is made;
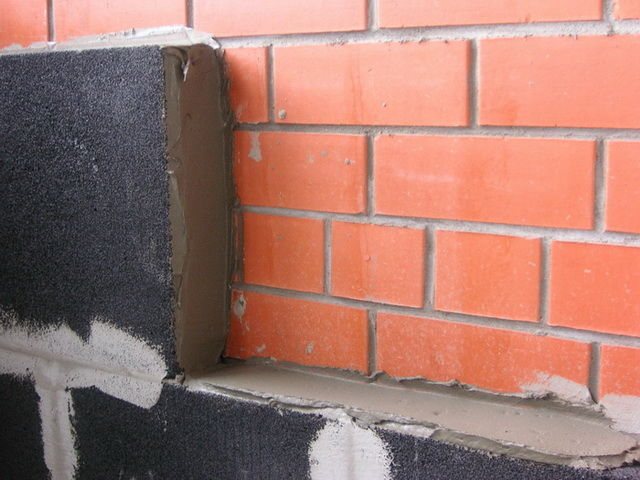
- for walls: the surface is prepared, special glue is applied, the product is applied, pressed tightly and covered with plaster;
- for the floor: a layer of sand (3-5 cm) is poured, thermal insulation is laid or filled in, joints are closed, a screed is made, a covering is mounted;
Yes, the material is popular due to its good technical characteristics.
Properties
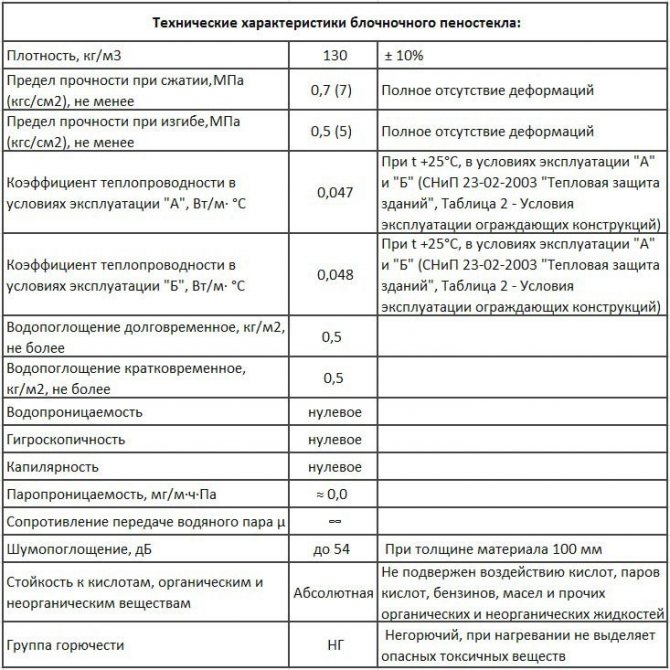
Cellular glass is famous for the following properties:
- noise absorption - 56 dB;
- water absorption - 0–5%;
- vapor permeability - 0–0.005 mg / m * h * PA;
- thermal conductivity - 0.04–0.08 W / (m * K);
- humidity (sorption) - 0.2–0.5%;
- bending strength - 0.4–0.6 MPa;
- compressive strength - 0.7–4 MPA;
- effective operating temperature - –260 - + 400 ° С;
- real operating temperature - –260 - + 230 ° С;
- deformation temperature - + 450 ° С.
Based on this data, recognized advantages and disadvantages can be identified.
Foam glass - characteristics and scope of this heat-insulating material
Foam glass - modern heat-insulating material obtained by processing silicate glass and a blowing agent (usually coal, anthracite, coke, soot) at high temperatures, about 1000 ○ С.
The foaming process is accompanied by an increase in the volume of glass 14 ... 15 times, compared with the original. In European countries, foam glass materials have long been recognized and one of the most effective heat-shielding building materials.
Thermal insulation material - foam glass: characteristics and scope
The thermal insulation properties of foam glass are due to the presence in its structure of a huge number of closed bubbles filled with air or carbon dioxide. Foam glass materials consist only of glass and gas (air, carbon dioxide) and their chemical composition is identical to the composition of ordinary glass we use in everyday life:
- silicon oxide;
- calcium oxide;
- magnesium oxide;
- potassium oxide;
- sodium oxide;
- aluminium oxide.
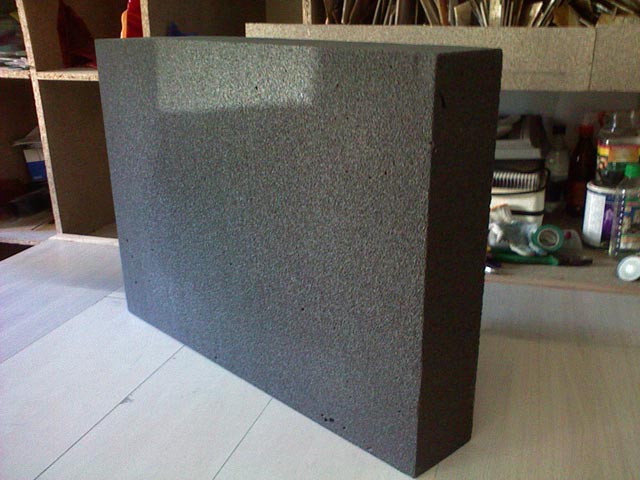
The structure of the foam glass looks like a honeycomb (photo 1), which ensures a relatively high strength of the material, taking into account the small size of the bubbles and the thickness of their walls (the average diameter of the bubbles is 2000 µm, and the thickness of the walls of the bubbles is 20 ... 100 µm).


Foam glass structure
Foam glass, as a heat-insulating material, has been developed for a long time and has been industrially produced since the 50s ... 60s of the last century. Initially, due to its high cost, this material was not widely used. Only after the improvement of the production technology, the reduced cost of foam glass gave it a "second wind", although now its cost is not cheap either. Foam glass possesses high physical and chemical properties, which lead to a constant growing demand.
Here are the main characteristics of foam glass
- thermal conductivity of foam glass - 0.045 ... 0.060 W / m ∙ K;
- material density - 120 ... 140 kg / m3 (relatively light heat-insulating material);
- the material is airtight;
- water absorption - no more than 2.5 ... 5% or surface absorption - no more than 0.5 kg / m2;
- water insoluble material;
- ultimate compressive strength - 0.4 ... 1.2 MPa, and some blocks of foam glass can have a strength of 4 ... 24 MPa (depending on the brand of foam glass);
- the material is vapor-tight;
- modulus of elasticity - 800 MN / m2;
- noise absorption - up to 60 dB (it is determined that a wall thickness of 10 cm from foam glass is able to isolate a room from a noise volume of up to 56 dB);
- operating temperature range of foam glass material - from -200 ○ С to + 500 ○ С;
- foam glass is a non-combustible material (in the middle of the last century, roofs and ceilings of very important buildings were insulated from foam glass: NPP buildings, high-class hotels, which were subject to particularly high fire safety requirements);
- insulation resistant to chemicals;
- ecological material (non-toxic), does not emit harmful substances, including at high temperatures in the event of a fire;
- bio-resistant material (not food and shelter for rodents, insects, insects), the material does not rot;
- low coefficient of thermal expansion (0.9 · 10-6 K);
- the material does not shrink;
- the material is not hygroscopic (does not get wet when in a humid environment);
- has high adhesion to most building materials: plaster mortars, concrete, bituminous mastics, etc.;
- high durability (over 100 years).
The main feature of foam glass consists in the fact that this material possesses unchanged high heat-engineering properties, which do not change practically throughout the entire period of its operation. So tests of building materials made of foam glass after 50 ... 60 years of operation have shown that its characteristics have not changed at all, which cannot be said about many other heat-insulating materials.
In practice, this material has no drawbacks, except for one - high cost (in comparison with other heat-insulating materials).
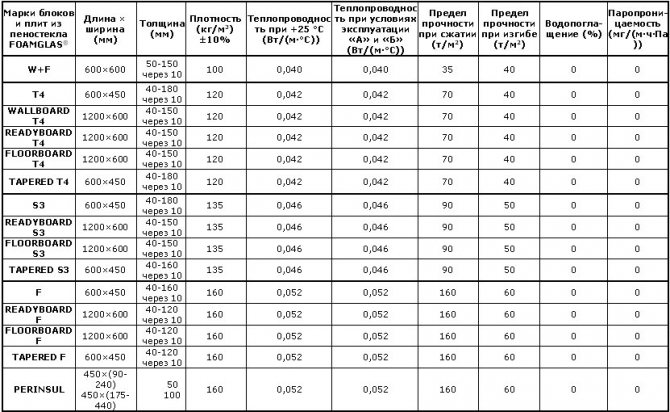
Foam glass building materials are made in the form of:
- slabs with dimensions: width - 450 mm, length - 600 mm, thickness - 60, 80, 100, 120 mm;
- blocks of size: 125 ÷ 450 × 125 ÷ 550 mm, thickness 20 ÷ 120 mm;
- crumbs (spherical granules).
Thermal insulation blocks and foam glass plates - area of application


Thermal insulation blocks and foam glass plates
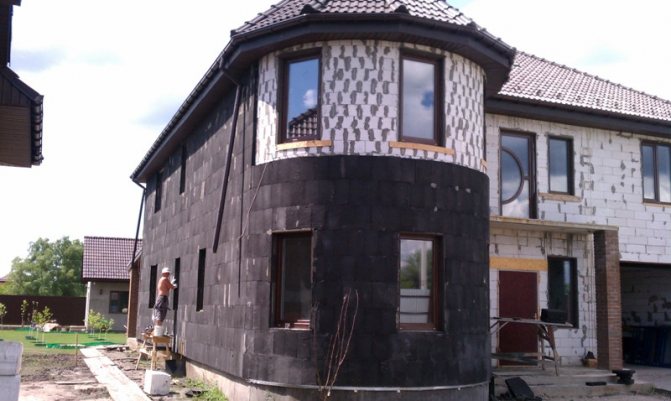
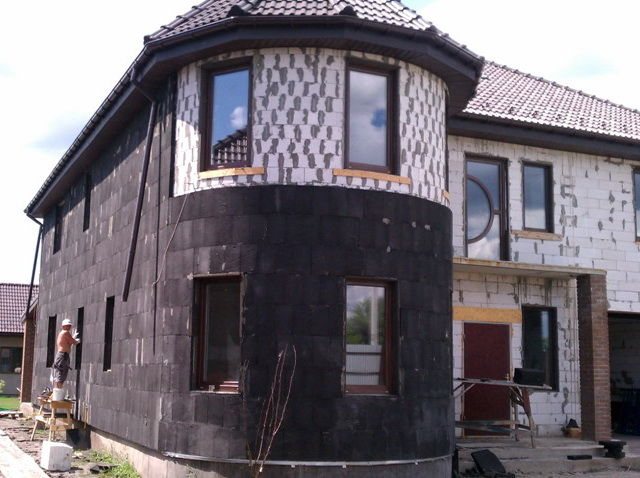
With the help of foam glass slabs and blocks, they perform sound and thermal insulation of plinths, blind area, foundations, various underground structures, insulate the facade, internal and external walls of high-rise buildings and structures, roofs (flat, pitched), photo 3.


Scope of foam glass
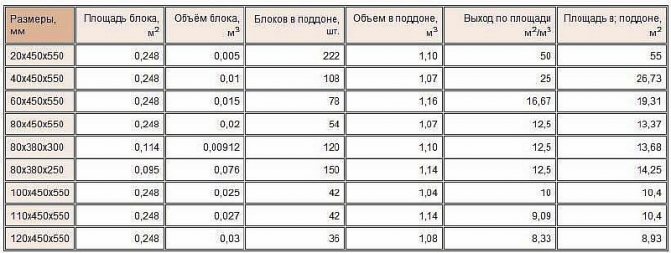
Table 1 presents useful data on the size of foam glass blocks, their mass and volume.
Geometric and shipping characteristics of foam glass blocks

Foam glass crumb - scope
Crumb is produced from the same raw materials as blocks or slabs in the form of granules of various fractions: 0 ... 5 mm; 5 ... 7 mm; 7 ... 20 mm.
The crumb is produced directly, or is formed by cutting large foam slabs into blocks. The crumb is used as a bulk thermal insulation material, in the construction of external walls with an interlayer and insulation of old houses. Also, with the help of foam glass crumbs, they insulate floors and roofs, photo 4, 5.


Foam glass crumb


The use of foam glass chips for insulation of walls and floors
Foam glass is also used to insulate pipelines with a diameter of up to 1420 mm, transitions, tees, with a heating temperature of up to 500 ○ C, photo 6.
Thermal insulation material made of foam glass for insulation of pipelines and their parts
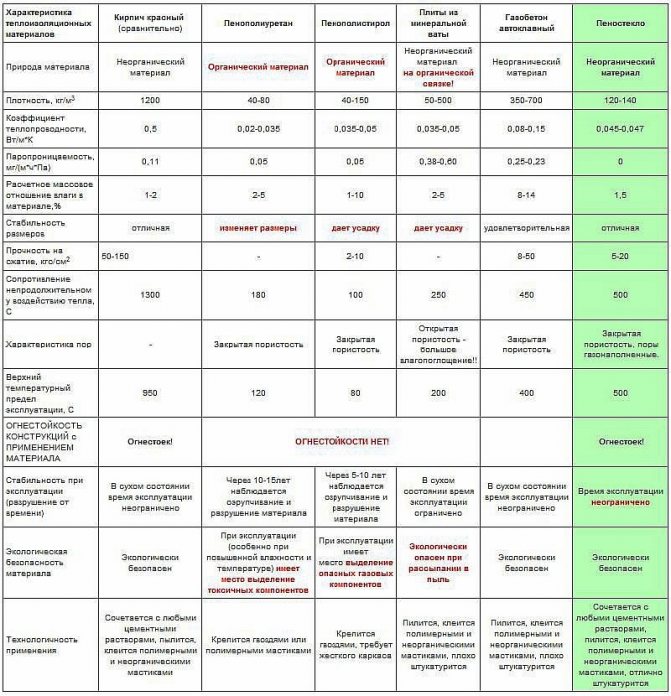
And in conclusion, instead of a conclusion, we will give comparative characteristics of some heat-insulating materials and foam glass in order to truly appreciate this unique material (see Table 2).
Comparative characteristics of building thermal insulation materials

The author of the publication is an expert of GIDproekt
Alexander A. Konev
Dignity
The material has many advantages. Let's consider the main ones.
- Safety. Does not contain substances harmful to the human body.
- Environmental friendliness. Produced from environmentally friendly raw materials.
- Hygiene. It has antiseptic properties.
- Durability. Service life - over 100 years.
- Versatility. It is used for insulation of any buildings.
- High adhesion. Combines with a lot of building materials.
- Biological passivity. He is not afraid of rodents, insects and microorganisms.
- Resistance to the negative effects of climatic factors. He is not afraid of temperature drops, precipitation, UV, etc.
- Resisting mechanical factors. It does not deform and does not lose its properties, since it can withstand impacts and high loads.
- Not susceptible to the influence of chemical factors. Does not react to acid.
- Resistant to thermal factors. Foam glass is absolutely non-combustible insulation.
- Ease of processing. Perfectly cut with a regular hacksaw.
The material is worthwhile, but there are drawbacks and there are many of them, unfortunately.


roof insulation with foam glass
Insulation opinions
Reviews of people who used the material note the following points:
- manufacturers give a guarantee for foamed glass for 50-100 years;
- during the operation of the house, the foam glass does not fall apart;
- blocks, slabs are not compatible with brickwork;
- the material is absolutely not vapor permeable.
In home construction, foam glass insulation, as noted by reviews, is relevant with constant temperature fluctuations in the region.
Low level of heat transfer, speed of installation, resistance to fires and environmental safety ensure the use of foam glass as an insulating material for all types of buildings.
disadvantages
Of course, every raw material has negative points. Foam glass is no exception. Before purchasing material, it is necessary to scrupulously study the negative points.
- High price. For the production of raw materials, innovative high-tech equipment is required, which leads to its rise in price. And also the manufacture of foamed glass requires high energy costs.
- Fragility. Raw materials, despite their strength, are very fragile, which leads to cracking if you ignore the installation recommendations.
- Lack of steam permeability. Foam glass, as it was said, is not exposed to the destructive effects of biological factors, but the surface under it is easy.
- Fear of alkalis and hydrofluoric acid. Cellular glass, like an aspen leaf, trembles at the "sight" of alkalis and hydrofluoric acid, since they are capable of destroying it.
- Severity. The raw materials are relatively heavy, which negatively affects the building structure.
- Durability. Of course, a long service life is a plus. But the materials used to build the facility are unlikely to last more than 100 years. This means that the structure needs to be repaired periodically, and the cellular glass is not intended to be reused. Which exit? Replacement of insulation.
- Low impact resistance. Cellular glass does not withstand even light blows. Mechanical influence is the “death” of the material. Of course, if the insulation is in the structure, it is not afraid of blows. He is afraid of them when transporting, unloading and installing.
- Impossibility of "resuscitation". If the glass is damaged, it can be taken to landfill. It is impossible to glue or cover up the cracks.
The properties have played a cruel joke with honeycomb glass, turning a huge number of advantages into disadvantages.
Price
The cost of foam glass bites. Prices, of course, vary, since they depend on many factors, but on average, you can buy blocks for $ 120-400 per cubic meter. You can buy plates and shells by paying $ 110-350, and you can get a granular version by spending $ 35-100 per cubic meter.
What can you say? Foam glass insulation is a very dubious and costly undertaking, since the material has a lot of serious drawbacks, and, moreover, is incredibly expensive. But, as they say, the owner is a master. Maybe it's not for nothing that they call it the raw material of the future. To buy or not to buy? That is the question! The choice is yours, dear readers.
Warmth and comfort to your home, dear friends! See you on other blog pages!
Quote of Wisdom: Reading is the best teaching (A.S. Pushkin).
Application of foam glass


High service life and resistance to aggressive environments, high humidity allow for thermal insulation using foam glass in residential, industrial, commercial buildings. Foam glass slabs and blocks are selected according to the requirements for wall protection. Thick materials prevent increased heat transfer and maintain the temperature regime created in the building. Ideal for wooden buildings (do not cause wood to rot).


In detailed photos on thermal insulation with foam glass, you can see the ways of using raw materials: for walls, plinths, basements and premises, roofs (from the attic or attic).

Granular building material is commonly used to protect flat roofs.It is used together with bituminous and cement mixtures and steam and moisture insulating materials. The grain composition of the raw material is selected according to the design and shape of the roof.