Is it possible to install a socket in the bathroom
In buildings built back in Soviet times, it was almost not provided for the installation of sockets in the bathrooms. The main reason was weak wiring, small area of premises, lack of electrical appliances that require connection. All available means of switching - sockets and switches - were installed outside, not far from the door.
Such a connection scheme created certain inconveniences, since all electrical appliances had to be connected from the outside, and the door to the bathroom did not close at the same time. Many owners were forced to use extension cords, which is strictly prohibited by the requirements and provisions of the PUE.

Modern apartments are distinguished by large areas for furniture, a bathroom, especially where the bathroom is combined with a toilet. An additional internal space has appeared, where, in addition to small household appliances, it is possible to place powerful equipment - washing machines, a boiler, heated towel rails and other types of electrical installations. Many rooms are equipped with underfloor heating systems that require a separate connection.
Before installing sockets in the bathroom, you should determine their exact number, in accordance with the planned connection of consumers. Among them, a division should be made into equipment that is permanently connected to the network and devices that are used only occasionally. Devices permanently connected to the network can be connected not to the outlet, but through the terminal block directly to the home electrical panel.
Installation in a protective casing
If a socket with a protection class below IP4 is used, it must be installed in a protective casing (shield). The protection class of the latter must also be at least IP4.


But, this option is permissible only if it is not possible to buy waterproof sockets or when installing additional electrical components in the dashboard, for example, to connect a warm floor or built-in lighting.


Instructions on how to move the outlet to another place: detailed step-by-step instructions on how to transfer and mask the outlet (135 photos and videos)

How to choose a circuit breaker for a house and an apartment: advice on choosing and calculating the parameters of a current machine. Which machine is better - a review of leading manufacturers (175 photos + video)


How to check the voltage in the outlet with a multimeter: a step-by-step description of how to measure the main parameters of the current in the network (120 photos + video)


In general, it is not difficult to install outlets in the bathroom. But, it is important to comply with all the above requirements in order to ensure the required level of electrical safety. Therefore, first of all, you need to correctly design the wiring diagram and choose the appropriate sockets.


Division of the room into separate zones
When choosing an installation site, it is necessary to follow the rules and be guided by the PUE, while all distances, including the installation height of the sockets, must be observed. It is recommended to arrange the sockets so that in the event of a breakdown, they are easily accessible for replacement or repair.In order to avoid violations of the installation rules, the entire bathroom is conditionally divided into several zones.
According to regulatory documents, the entire territory of the bathroom is conditionally divided into several zones. They determine the degree of safety and allow you to most optimally develop a plan for the placement of electrical appliances and equipment, to lay the wiring to each point in the shortest possible way.
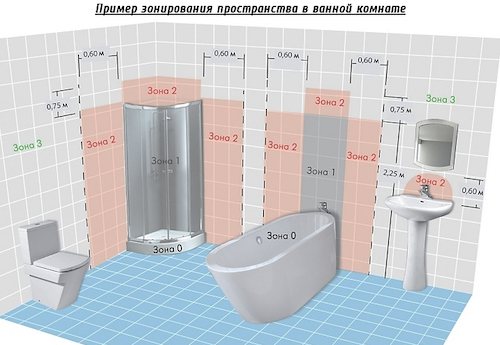

The conditional division of the bathroom includes the following zones:
- Zone 0. Grips the inside of the shower tray and the inside of the bath. It is impossible to place any waterproof electrical equipment in this place.
- Zone 1. Located directly above the shower tray, bathtub, washbasin or sink, at a height of 2.5 m from floor level.
- Zone 2. Located up to 60 cm in all directions horizontally from cabinets, shower tray, bathtub or sink. The height from the floor is up to 2.25 m. It covers the area above the 1st zone at a height of 3 m from the floor.
- Zone 3. Overlaps the 2nd zone by 2.4 m, keeping the height from the floor 2.25 m. The height above the 2nd zone is up to 3 m. Based on these parameters, the height of the sockets in the bathroom is also determined.
Waterproof: what type of outlet can I use
The appearance, the location of the connection points are regulated by the relevant requirements of GOST, as well as the PUE (rules for electrical installations). All products are marked with the letter code of the international quality standard - IP and two digits from 0 to 8. The first number is most often absent - dustproofness does not play such an important role as the ability to resist moisture.
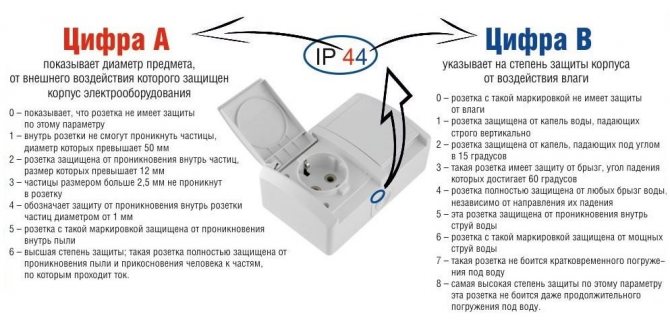

Using this table, you can select the desired outlet parameters
If the number eight on the device, it is intended for a device that can be immersed a meter or more under water. Zero is the least secure option. In bathrooms, it is allowed to use sockets of IP4 category, perfectly resisting splashes, water drops from any side. Typically, the structure is supplied with a spring-loaded (hermetically self-closing) lid.


Experts recommend sockets marked for both parameters at least 4, but better than 5 or 6
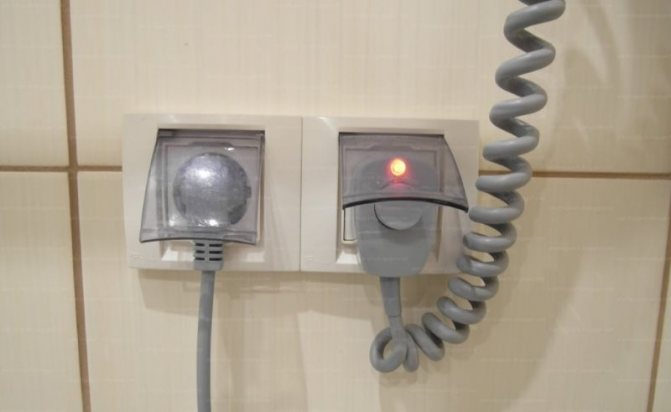


In the process of choosing and buying, as well as after installing the outlet, it will not be superfluous to make sure that it is in good working order - there should be no cracks on the case, the lid should fit snugly, and open with little effort
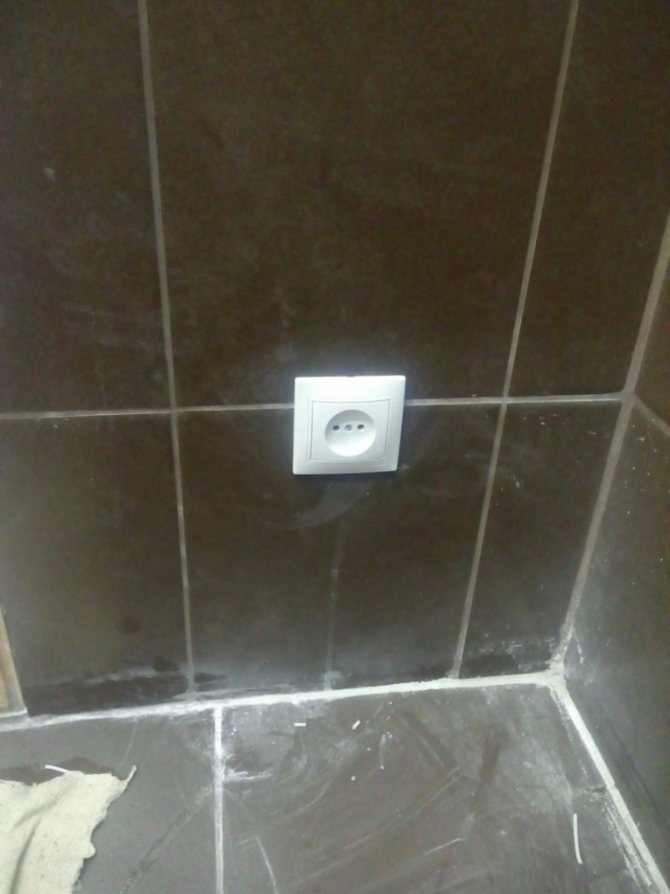
Installation of connection points in the bathroom is done after finishing the walls. A built-in, surface-mounted structure is mounted or protective covers are used. The electrical cables must be pulled in advance.
Where is it allowed to install sockets
After the bathroom is conditionally divided into several zones, you can calculate how many sockets there should be and choose a place for placing sockets for electrical equipment. At the same time, you should follow the rules and regulations established for each site.
The zero zone, as already noted, is not intended for the installation of any devices. The only exceptions are devices used directly in the bath. They operate on a voltage of no higher than 12 V, and the supplying step-down transformers are placed outside the boundaries of this section.
In the first zone, you can install a shower and an instant heating water heater. Also, it is allowed to install an individual electric shower equipped with a pump with high-quality waterproofing. There are also wires connecting these devices.


In zone 2, the location of all devices permitted in zone 1 is allowed. On the same site, lighting and water heaters with a protection class of at least 2, equipped with basic and additional insulation, are installed. It is prohibited to install junction boxes and controls in all of the zones listed, from 0 to 2.
The third zone is considered the most remote from dangerous places. Firstly, they must be connected via an RCD with a trip current of up to 30 mA. In the case of using a group line, the pickup current is set to 10 mA. The second condition or option is to connect the sockets using an isolation transformer, but in practice this method is very rarely used. The distance from the outlet to the pipeline must be at least 50 cm, and from the doors of the shower stall - 60 cm or more.
PUE requirements and other standards
The bathroom is divided into zones that indicate the permissibility or inadmissibility of installing electrical equipment in them. The figure below shows briefly schematically these zones and distances to the elements of the bathroom - bathroom, sink, etc. Read more about them in GOST R 50571.11-96 (IEC 364-7-701-84) Electrical installations of buildings. Part 7. Requirements for special electrical installations. Section 701. Bathrooms and showers.
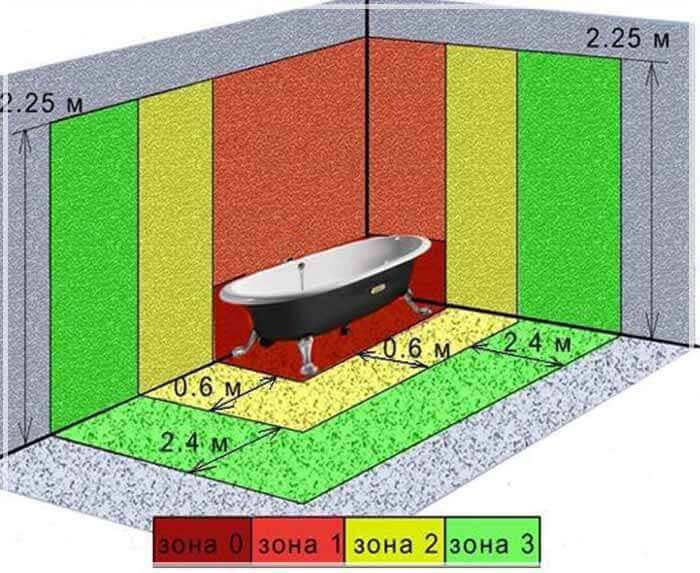

Bathroom areas for electrical safety:
- 0 is directly where there is water (sink, shower tray, etc.).
- 1 - Surrounds the previous area, usually adjacent walls.
- 2 - located at a distance of 60 cm, and for a shower cabin and similar containers not rectangular in a radius of 60 cm from the edges of zone 0.
- 3 - conditionally safe. It is located outside the second, that is, more than 60 cm from sinks and other things.
A more detailed description can be found in the above mentioned GOST. And what do the requirements of the PUE tell us? To do this, let's move on to paragraph 7.1 of the PUE, and consider some excerpts from the text:
7.1.40 describes the wiring requirements. It says that both open cabling and hidden wiring are permissible. The permissible temperature of their insulation must be at least 170 ° C.
7.1.47 describes the permissibility of installing certain products in the bathroom, in the corresponding zones (the table is compiled according to the text from the original):
Zone Security class What can be used 0 IPX7 electrical appliances with voltage up to 12 V, and the power supply must be located outside this zone; 1 IPX5 water heaters only 2 IPX4 (IPX5 for public places) water heaters and lamps of protection class 2 3 IPX1 (IPX5 for public places) Everything else
* in zones 0, 1 and 2, junction boxes, switchgear and control devices are not allowed.
7.1.48 is considering installing wall outlets in the bathroom in general. It says that sockets cannot be installed in public shower rooms, but in bathrooms of apartments or hotel rooms they can be installed only in zone 3, in accordance with GOST R 50571.11-96. At the same time, they must be connected through isolation transformers (which is not convenient and expensive in most cases), or through RCDs and difavtomats with an operating current of no more than 30 mA. Also, wiring accessories are installed at a distance of at least 0.6 meters from the doors of the shower stall.
So, let's summarize, where to install the sockets in the bathroom and how to connect according to GOST?
According to the norms of PUE and GOST, they must be connected through an RCD with an operating current of no more than 30 mA, be located no further than 60 cm from the doors of the shower stall and is located in zone 3. In this case, the wiring can be hidden and open. Place the junction boxes at the same distance, or even better outside the bathroom.


It also follows that the location of the electric points is selected only according to the zones. At the same time, it is not regulated at what height from the floor or what distance from the ceiling is permissible. Install them so that it is convenient to connect and disconnect electrical appliances. Also provide for the possibility of splashes or streams of water on electrical appliances and their connectors for connection - it should be excluded.
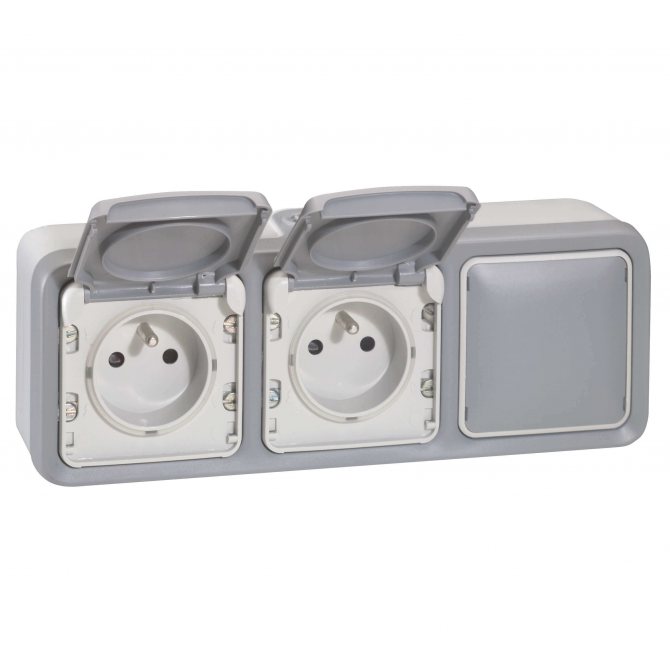
This means that the installation of sockets is also prohibited at the washbasin in the bathroom. You need to take them out to zone 3, i.e.60 cm from it, and if closer, then use the product in this case with IPx4 protection, that is, with a protective shutter. An excellent example is the Legrand Plexo series of quality surface-mounted wiring products:


Even such protected products should not be installed above or under the sink, since you cannot foresee where the water will flow if the water supply elements are damaged somewhere. Compliance with the requirements of the PUE is your safety.
You can find out more about the degree of IP protection by going to the article we linked to.
Choice of sockets for the bathroom
Choosing the right waterproof outlets for your bathroom is a snap. Despite the large number of design solutions, from a technical point of view, these products cannot be classified as diverse. When classifying them, only two main features are used - the power and the number of consumers connected at the same time.


The quantitative indicator, as a rule, does not raise any special questions. When choosing outlets, the main focus is on the power indicator. For example, washing machines and other powerful equipment are connected to sockets with a rating of 16 A. Appliances with lower parameters may melt due to overload and cause a short circuit. Low-power sockets, including those with a cover, are used to connect hair dryers, electric shavers and other similar devices, for which a rating of 8 A is quite enough.
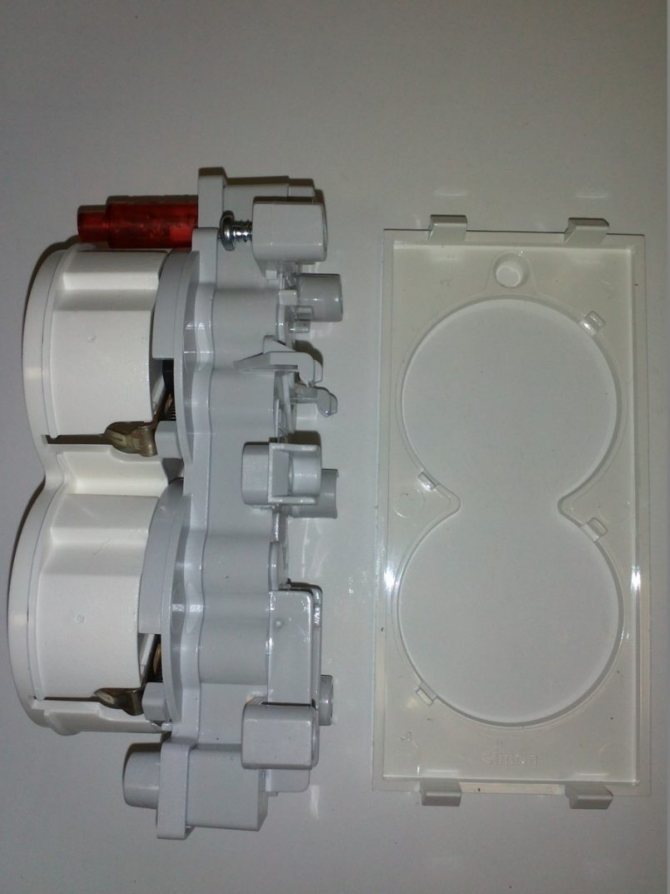
The main difference between products intended for bathrooms is their protection from moisture and the presence of a spring-loaded cover that protects against direct ingress of water. All distinguishing features are indicated in the markings on the case, including the two-digit IP symbols.
The digital designation characterizes the ability to counteract various types of external intrusions. The first number corresponds to the dust protection class, and the second to moisture. The degree of moisture resistance is indicated by numbers from 0 to 8. The lowest class is considered to be class zero, and the highest is class 8, at which the product can be operated being completely immersed in water to a depth of more than 1 m. In bathrooms, it is recommended to use sockets with protection class 4 and above, providing protection against dripping and splashing in all directions.


Installation of sockets with a lower degree of protection is also allowed. However, such products cannot be mounted open. They must be installed in a special protective casing with the required tightness. In addition, any outlet intended for the bathroom must be equipped with a grounding contact.
Types of sockets according to the level of moisture resistance
Even if the outlet is located in the desired area and according to all the rules, it can still be sprayed with water or condensed, which will inevitably occur in the bathroom. Based on this, it is necessary to select waterproof sockets for the bathroom, the conductive parts of which are protected from water at a sufficient level.


sockets IP54
On any outlet, the manufacturer is obliged to affix the IP-XY standard marking, in which, instead of XY, the numbers from 0 to 8 will be put down. The first of the numbers shows the protection of the mechanism from various objects falling into it, and the second shows the level of its protection from moisture:
- 0 - Contacts are not protected by anything - even from accidental splashes.
- 1 - The contacts will not be sprayed from above.
- 2 - Protection against drizzling rain when the slope of the spray does not exceed 15 °
- 3 - The device can withstand heavy rain with a splash slope of up to 60 °
- 4 - The contacts are splash-proof from all directions.
- 5 - This device can be watered with a hose.
- 6 - Protection for devices that can be affected by the wave.
- 7 - Protection against short-term immersion to a depth of one meter.
- 8 - Completely waterproof device.
The bathroom requires sockets and other electrical appliances with an IP-x4 or higher protection class.
Line installation in the bathroom
Wet walls and floors in rooms with high humidity create an environment that conducts electricity well. Therefore, the laying of wires in the bathroom should be done according to certain rules:
- The wires are laid in a hidden way, under the finish in a corrugated pipe.
- Indoors, it is prohibited to install junction boxes, various twists and connections. The wires are laid in one piece and pulled from the outside of the box.
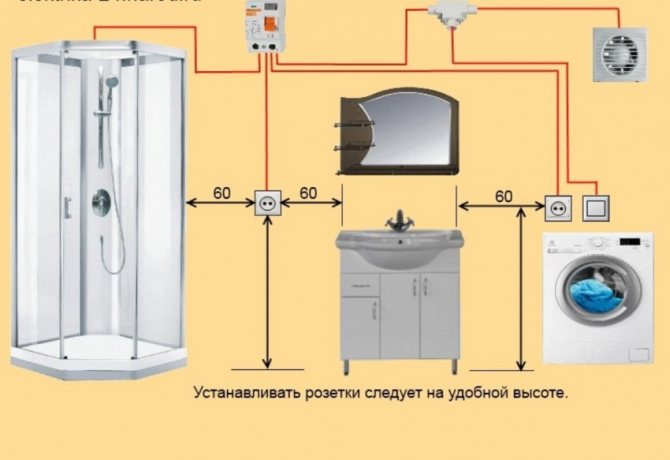
- Determining how many sockets are needed - most often, no more than 2-3 pieces.
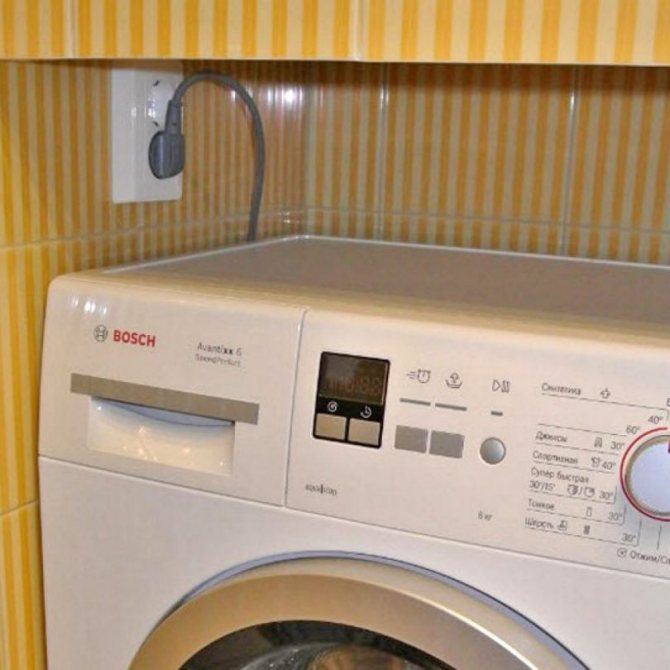
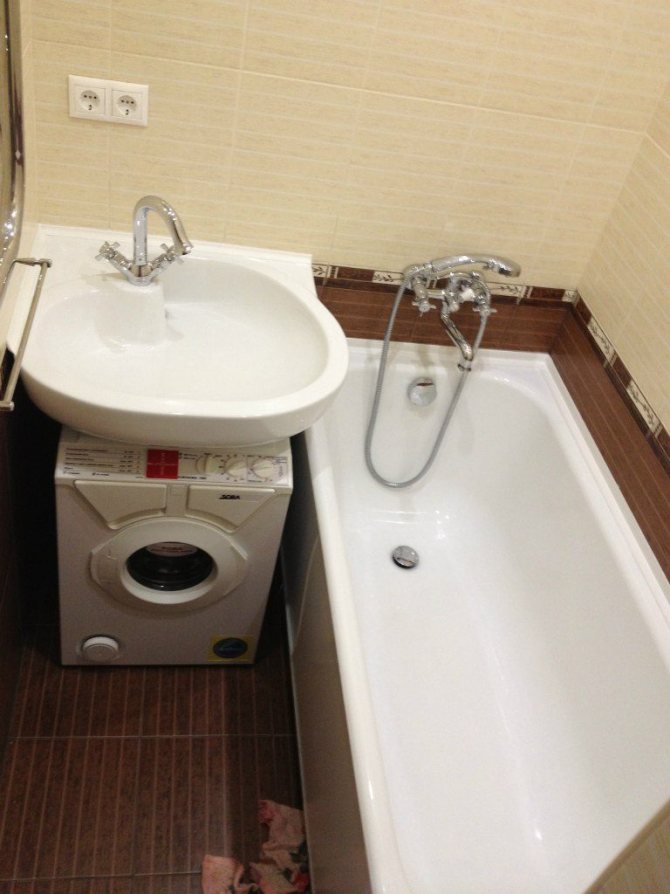
- There must be a separate socket in the bathroom for the washing machine and water heater. Installation of the switch is carried out outside the room.
- Each group of devices or dedicated line is equipped with a circuit breaker.
- The wiring lines should be drawn strictly vertically and horizontally, at what height is required in specific places. The wires themselves must be with copper conductors with a cross section of at least 2.5 mm2, enclosed in triple insulation. Used wires with a large number of bends or with damaged insulation are not allowed for use.
It is recommended to replace the old wiring, installed a very long time ago and never changed. This will allow during operation to avoid such malfunctions as overheating, short circuits, sparking, fire, accompanied by constant tripping of the circuit breaker. Often you have to solve the problem of how to move the outlet.


After marking the lines, wires and cables are laid in their places. The gasket can be made in the voids between the wall and the decorative covering using corrugated sleeves. In the second version, the wires are laid directly in the walls, for which strobes are made in advance according to the marking. After laying, the wires are fixed with staples, and then the strobes are covered with a solution of stucco.
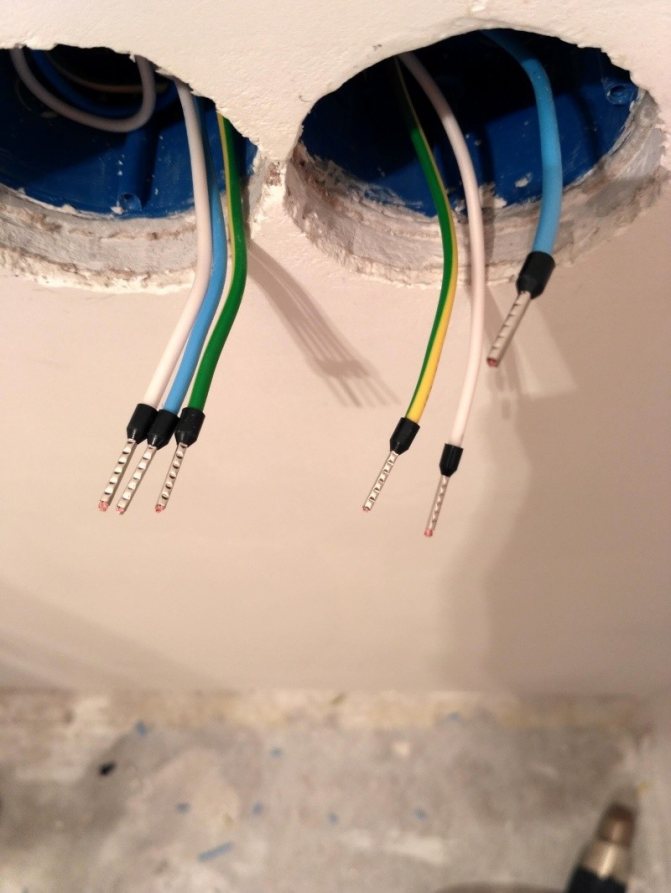
Further, in the places where the sockets are installed, socket boxes are mounted, fixed with alabaster. They lead wires with three cores, of which two are phase and zero, and one is ground.
Benefits of installing waterproof outlets
If a couple of years ago, sockets were not installed in a room with high humidity. They were taken out for installation outside. The advent of modern moisture resistant appliances has changed the situation. Now there is no fear of passing the cord through the doors, because it had to be laid across the floor to the outlet from the same washing machine. The door of the room closes, and the working equipment does not make noise for the whole house.
In this case, not just a separate point is installed, a whole block of devices plus a switch is mounted. This allows several household units to be switched on at once. For example, a washing machine starts up, a hairdryer turns on, at the same time a water boiler (powered by the mains) heats up the water.
Ensuring safe operation
One of the elements of electrical safety is a protective grounding device - RCD. Previously, when two-wire wiring was used, a separate heavy-gauge cable was led from the bathroom to the switchboard and connected to the ground bus. Thus, the question of how to make grounding was solved. In modern wires, three cores are initially provided, one of which performs the function of grounding. It must be connected to the grounding pin of the waterproof outlet, and then also goes to the distribution board.
Additional electrical safety is provided by a residual current device. These devices are mandatory for use in electrical wiring lines to bathrooms. The RCD is located in the home electrical panel and cuts off the power in case of current leaks.


A separate RCD with a rating exceeding the rated current of the circuit breaker is installed on the sockets in the bathroom. If this condition is not met, then the circuit with the protective device will simply not function normally.
Simultaneously with the RCD, automatic switches are installed to protect the line from overloads and short circuits. They protect individual power outlets or groups of outlets. The rating of the protective equipment is selected in accordance with the expected load.
What equipment and how to connect
Bathroom sockets are commonly used:
- for connecting a washing machine;
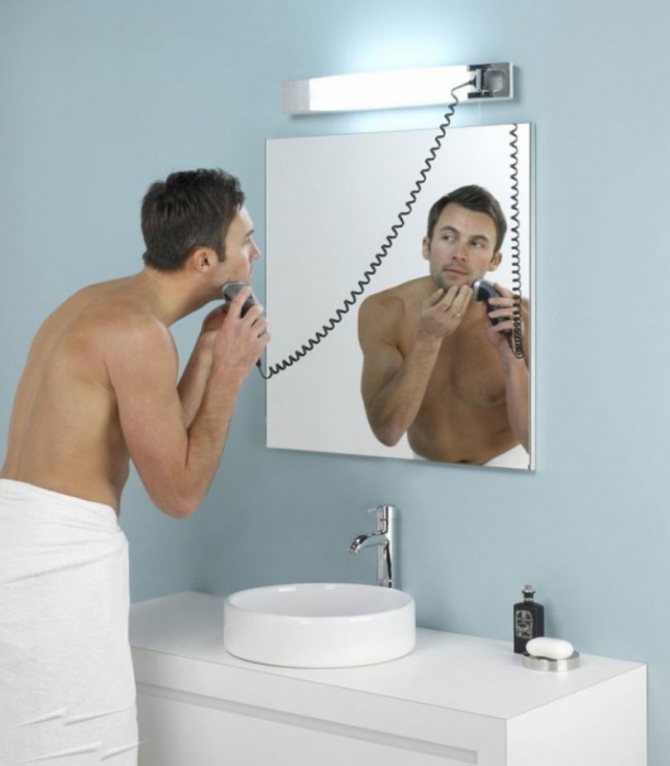
- hair dryer;
- for a razor;
- for illuminated mirrors;
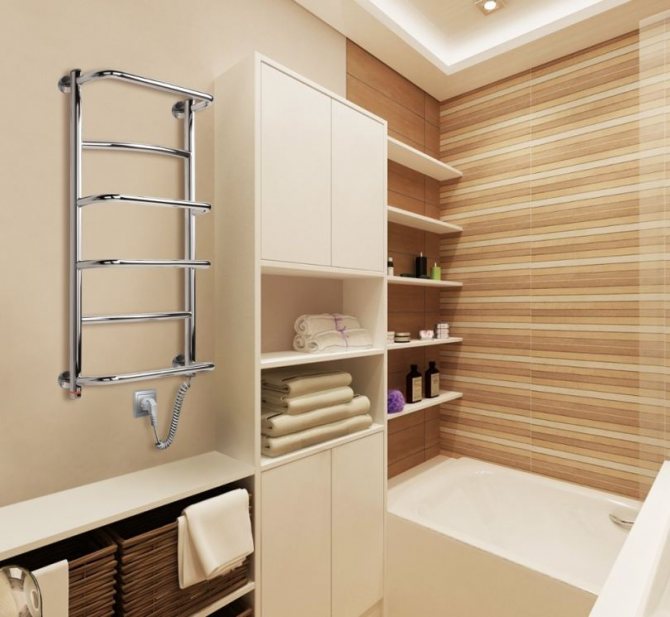
- for a water heating tank;
- for a heated towel rail and so on.
Powerful consumers, such as instantaneous water heaters with a capacity of over 3.5 kW, should be connected to the network directly from a separate machine and through a residual current device (RCD). Or through a difavtomat with an actuation current of no more than 30 mA. This is a normalized value and where it comes from, we will describe below.
In the figure below you can see an example of an electric heater connection diagram:
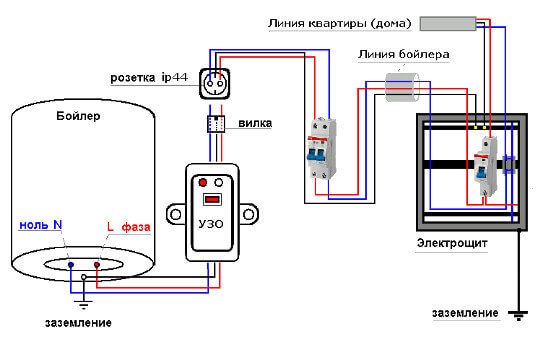

Connecting a heated towel rail to an outlet is not always appropriate and aesthetically pleasing, so it makes sense to also connect it directly to the circuit breaker, although its power is usually not as high as that of flow heaters.
How many outlets should there be? If the washing machine is located in another room, usually more than 1-2 pieces are not installed, and if the machine is in the same room and there is a boiler in addition to it, 3-4 pieces are installed.
Additional safety measures in bathrooms
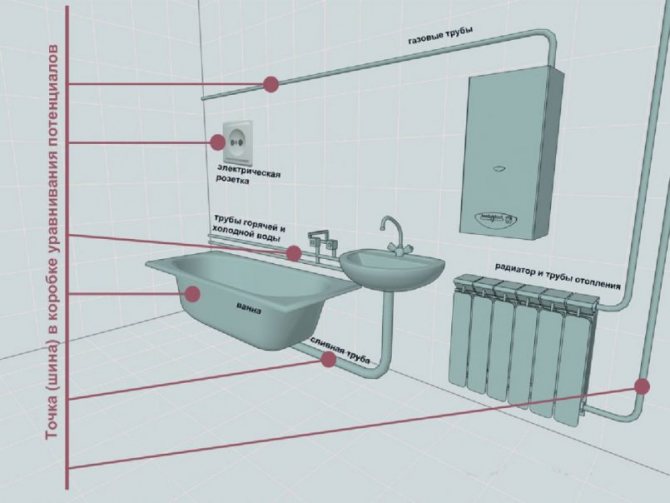
Additional electrical safety in the bathroom is provided by creating an equipotential bonding system in the bath.
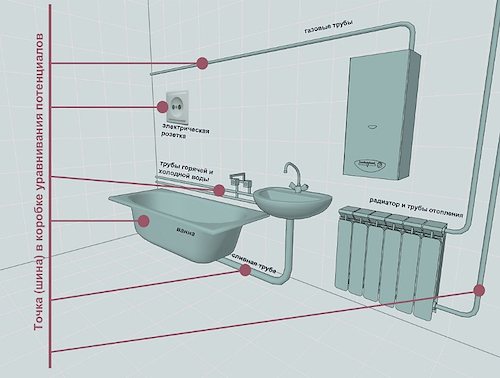

In this case, the electrical connection of the conductive parts is performed, consisting of:
- Main protective conductor (trunk).
- Main ground wire (trunk) or special grounding clamp.
- Utilities consisting of steel pipes inside and outside the building.
- Metal elements of building structures, lightning protection systems and other suitable networks.
In accordance with the Rules for the Installation of Electrical Installations, all stationary equipment and other conductive parts are connected to the potential equalization system, as well as zero protective conductors with which open contact and touching open places are possible. The same list also includes a wall outlet for the bathroom.
This system must be installed in rooms with high humidity, even in the absence of any electrical equipment. All components are connected to a common wire, which in turn is connected to the PE bus, which is located at the input or in the switchboard.
Accommodation requirements
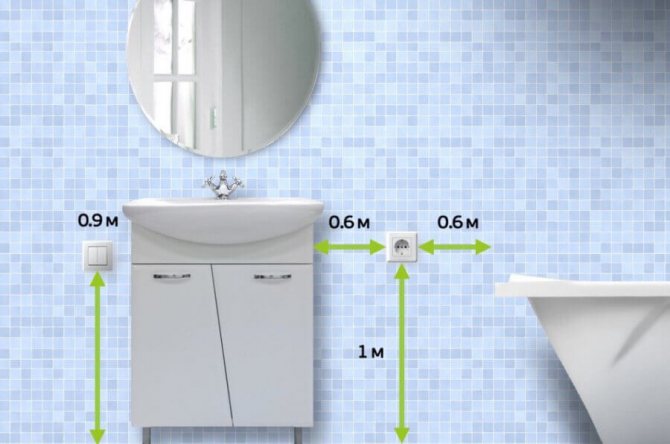
To properly install your washing machine, in addition to using the correct equipment, it is important to choose the right outlet location. In this survey, it is not the proximity to the household appliance that will be connected to it that matters, but the distance from water sources and the height above the floor level. As a rule, there are only 1-2 safe places in the bathroom for installing the socket.


To determine where to lead the cable from the switchboard, the following factors must be taken into account:
- In the bathroom, electrical outlets for connecting household appliances are installed at a height of at least 60 cm from the floor. This requirement must be observed in order to safeguard the life of household members and protect expensive equipment from damage. If the installation height is less than 60 cm, if there are heavy leaks or pipe breaks, the water can come into contact with electricity, provoking an emergency.
- In rooms with high humidity, the sockets are placed no closer than 60 cm from objects that are sources of splashes or water sources.This arrangement reduces the risk of moisture entering electrical equipment, making it safer to use household appliances.
Interesting! When designing wiring in the bathroom, this room is conventionally divided into 4 zones. The zero or red zone is located around the bath or shower, no electrical equipment should be installed there.
The first zone practically coincides in location with the zero, but here you can install equipment with a power of up to 12 V, which is necessary for the functioning of plumbing. The second or yellow zone is placed every 0.6 m, water heaters are installed in it. In the green zone, at a distance of 2.4 m from the spray source, sockets and other household appliances powered from the mains are located.