The heating system provides for piping, today you can't get away from this. If recently the choice was limited to ferrous metal, now the assortment is wider. Therefore, before buying, you need to clearly understand what you want to get as a result.
There is a standard set of requirements for heating pipes:
- Durability. The service life of the product should be at least not less than the rest of the system;
- Strength. Most dwellings are connected to a forced heating system, so a safety margin must be required;
- Resistant to drop temperatures and water hammer;
- Aesthetics;
- Maintainability;
- Economic benefit. If the price of the pipe is high, then the rest of the characteristics must correspond to this.
You can choose a product for any wallet, and even the most budgetary options can now boast of reliability.
Types of pipes for heating
Let's take a look at the most popular options.
Steel
This material has been forgotten for a while, but thanks to modern joining systems, without welding, steel pipes are gaining popularity again.
Main characteristics:
- resistance to high temperatures (the pipe can withstand heating up to 1500 degrees without deformation);
- high thermal conductivity;
- low coefficient of linear expansion;
- large margin of safety.
Material advantages:
- The only way to ensure the natural circulation of the coolant is due to the ability to select a pipe of any diameter. This is especially true now, when solid fuel boilers are increasingly appearing in people's homes. Often the circulation pump is not used in this configuration;
- High resistance to water hammer allows you to feel calm with centralized communicationswhen it is impossible to control the fluid supply process;
- Affordable cost;
- Good thermal conductivity allows the use of the pipes themselves as a heating device.
Disadvantages:
- Corrosion susceptibility. Therefore, zinc or insulation is often used. Indoors, regular painting is required;
- Complexity of installation. Even without welding, certain skills are required for high-quality wiring;
- Large mass. Long spans need high-quality wall mountings;
- Rough inner surface. This fact leads to a narrowing of the internal space, especially due to the low quality of the coolant, which is ubiquitous in our country;
- Obligatory thermal insulation in an unheated room. High thermal conductivity is not only a plus, but also a minus.

Steel pipes are the only way to ensure natural circulation of the coolant due to the ability to select a pipe of any diameter
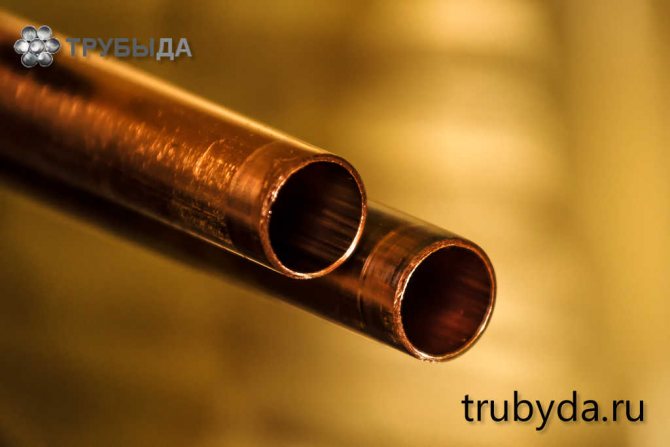
Copper
A relatively new material for heating, but perfectly suitable for these purposes. Main characteristics:
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- high pressure resistance;
- heating without consequences up to 300 degrees;
- plastic. This pipe is not afraid of negative temperatures, the frozen water inside will not cause harm.
Benefits:
- Durability. The minimum service life is from 50 years;
- Ease of installation;
- Do not develop on the walls microorganisms;
- Attractive appearance;
- Almost ideal for use in harsh climates. All the dangers of operating the pipe are not terrible due to their properties.
Disadvantages:
- High price;
- Susceptibility to electrochemical corrosion. Therefore, the presence of electrical wiring nearby requires insulation of the pipe with polymers;
- Lack of ability to combine with other metals (except for bronze). In the places of their contact, copper will collapse.
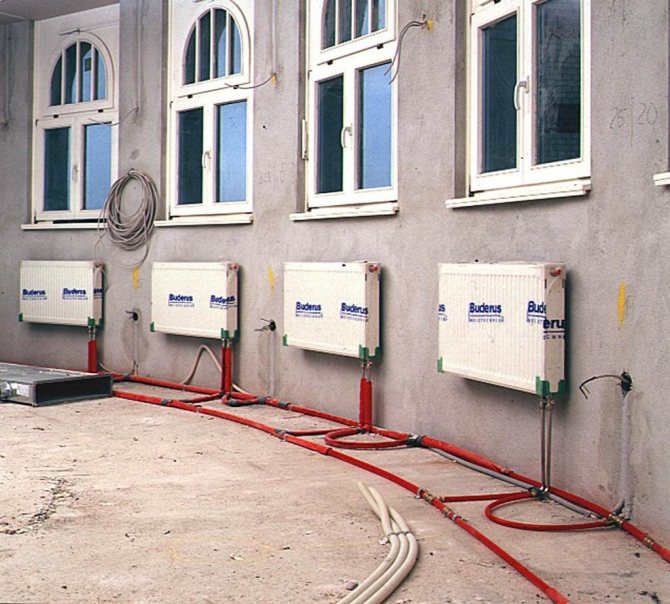


Copper pipes are almost ideal for use in harsh climates
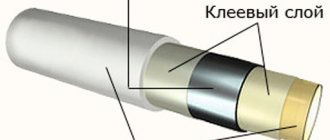
Metal-plastic
Popular material consisting of 5 layers, including polyethylene, glue, aluminum foil. Combines the positive characteristics of plastic and metal.
Characterized by:
- good temperature indicators (acceptable for systems with a coolant up to 110 degrees);
- flexibility - bends easily even by hand;
- durability;
- resistance to temperature and pressure changes;
- lack of corrosion.
Positive sides:
- Ease of installation. To distribute pipes to rooms, it is not at all necessary to invite a specialist; a person with minimal construction skills will cope with the work;
- Acceptable service life (up to 25 years old);
- Small linear expansion (slightly more than copper) in the presence of thermal conductivity;
- Chemical neutrality allows lay a network inside walls, floors;
- Smooth inner surface.
Negative sides:
- Expensive fittings;
- Destruction during defrosting, in connection with which the outer gasket is excluded;
- Small gap inside. You can't get away from this, fittings are made the only way.
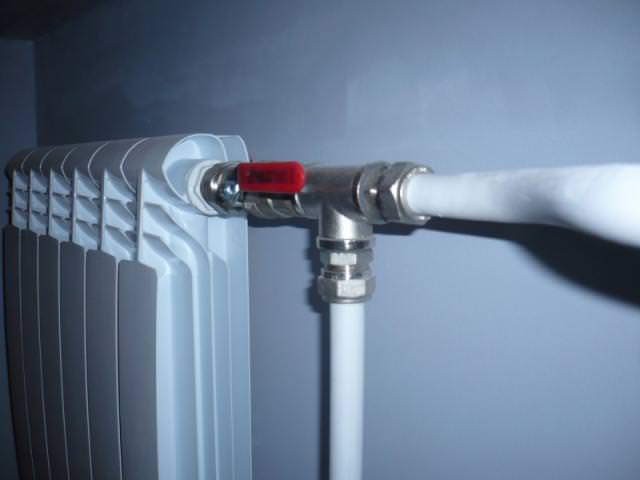


It is not at all necessary to invite a specialist to distribute the pipes to the rooms; a person with minimal construction skills will cope with the work.
Polypropylene
A completely new material that has rapidly conquered a large niche in the heating pipe market. For the passage of the coolant, a reinforced version is used, which excludes thermal expansion, and therefore sagging.
Main characteristics:
- mechanical resistance;
- lack of corrosion;
- durability;
- resistance to water hammer, temperature drop;
- low thermal conductivity.
Benefits:
- Ease of installation. This will require a special soldering iron and little skills in working with it. At the same time, it is not necessary to buy a device, many hardware stores lease it for little money;
- Affordable price;
- Huge service life (up to 100 years old);
- Neat appearance;
- Light weight;
- No corrosion allows you to safely use the material when laying inside walls and floors;
- Low thermal conductivity does not require thermal insulation when passing in basements and attics;
- Not afraid of negative temperatures, a defrosted system will not lead to the destruction of the structure.
Disadvantages:
- Media temperature limits. In most cases, this is 80 degrees. So in northern latitudes or in the immediate vicinity of a boiler room with central heating, it can be dangerous to use this type of pipes;
- Can't be repaired. If a certain area is damaged, you need to either cut out a piece and weld a new one with the fittings, or change the span completely from fitting to fitting;
- Even a small deviation from the horizontal during installation requires the use of a special fitting. Operation, even when slightly bent, is prohibited.


For the passage of the coolant, a reinforced version is used, which excludes thermal expansion, and therefore sagging
Scopes of copper pipes
Copper communications are most popular in Europe, where they have been recognized for over 60 years. For a while, they were supplanted by cheap steel, then plastic, but now everything is returning to normal. New technologies make it possible to install from them pipelines for drinking and technical water supply, heating, systems for liquid and gaseous fuels, waste water.


The use of copper pipes for plumbing is classic. The bactericidal properties improve the quality of the supplied water, and the matt sheen of the visible areas gives the interior a sophisticated look. Not only freezing, but also boiling are not terrible for such a water supply, the elasticity of copper dampens all shocks. Brazing is required in this case.
It is ideal to use copper pipes in surface heating systems, the coefficients of thermal expansion of them and of the screed are equal. Liquid fuel in such communications is safe, it cannot ignite due to its complete tightness.
It is also safe to carry out gas distribution with these pipes in an apartment building, it is the tightness that saves lives here. Having spent money once, you can get a reliable and durable pipeline that can serve for more than a century - this is the best quality characteristic.
How to choose the right pipe
First you need to clearly understand the initial data, namely the main criteria for choosing:
- type of system - most accurate (natural) or compulsory;
- the maximum possible temperature of the coolant;
- limiting pressure in the system;
- laying method - external (along the walls), internal (warm floors), external (open air);
- the complexity of the configuration;
- budget;
- self-assembly or hiring specialists.
Practice has shown which material is more appropriate in the most common cases:
- Steel. Due to the ability to select a large diameter and high heat transfer, it is appropriate to use it in the most accurate heating system of a private house or summer cottage. All corners and secluded places will warm up with high quality even without a radiator (for example, a long corridor or storage room). Wiring around the apartment is still considered a very outdated option;
- Copper. Great for a private large house. Leaks due to corrosion are excluded, while all the positive aspects of the metal are preserved. However, the high cost and limitation on the material of the radiator are forced to take a very responsible approach to the choice;
- Metal-plastic. It is successfully used for apartments and houses both with a boiler with a pump and with a centralized heat supply system. But destruction during defrosting imposes some restrictions - the system must be in good shape during the entire period of cold weather;
- Polypropylene. Many apartment buildings are initially provided with a pipe system made of this material. A budget and reliable option for almost any user. But with a large number of corners and turns, installation can be extremely difficult.
There is no ideal material for heating pipes, there are pros and cons everywhere.
Copper pipe parameters
A copper pipe is best suited for individual heating, the characteristics of which prevent rupture during a pressure surge inside the system and its freezing. Plastic metal can withstand the expansion of water during freezing, a country house with a copper heating system is not afraid of any frost and utility accidents.


The metal is used for the manufacture of products of the highest quality, sometimes products are covered with a layer of polyvinyl chloride to reduce heat loss. The dimensions of copper pipes depend on whether they are hard or soft. Rigid ones are produced in lengths from 3 to 5 meters, soft ones are rolled into coils with a length of 25 to 50 m. The weight of a copper pipe depends on the diameter and wall thickness, the theoretical weight of 1 mm is calculated according to special tables. These calculations are especially important when laying gas pipelines.
Blitz Tips
Using pipes made of various materials, you need to know some of their features:
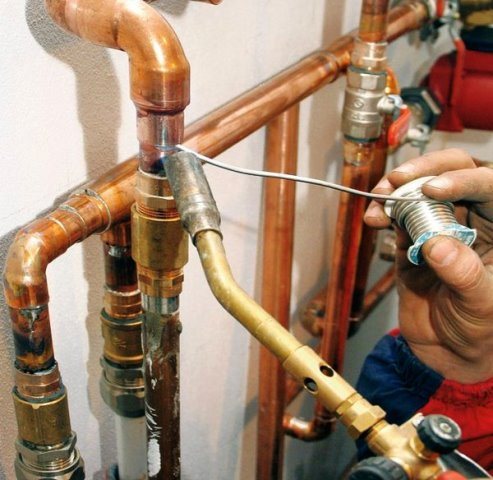
- Copper pipe can be welded by low temperature and high temperature methods, which is more reliable. But when exposed to high temperatures, copper darkens and loses its attractiveness. So you need to be prepared to mask the seam;
- The place of the weld on the copper is stronger than the rest of the surface. Therefore, it can burst anywhere, just not at the seam;
- When installing metal-plastic products, it is better to use a fitting with a press sleeve, then the connection point will never bother you. Otherwise, the nut will have to be tightened from time to time;
- Even a beginner can weld polypropylene, but heating below normal will lead to leakage, and overheating will narrow the gap. The material maintainability is zero, so it is better to entrust the installation of the system to a professional.
Quality project - comfortable operation
- Graphic and working part. The first is presented in the form of a sketch, the second contains the technological nuances of the work.
- Technical characteristics of construction materials: diameter of polypropylene pipes, type - simple, reinforced. The parameters affect the media's ability to circulate well and the temperature thresholds.
- Heating unit and piping diagram. The angles of slopes and transitions of the contours are indicated. This is true if the residential building has several floors. In such facilities, DIY heating from polypropylene is impossible without the operation of the circulation pump.
- Methods of fastening and connecting the pipeline to the boiler unit, the number of fittings and other components.
When the project is received and the meaning of the detailed explanatory note is clear, it is possible to install heating with plastic pipes with your own hands - not earlier.
What is a heat exchanger?
In the broadest sense of the word, a heat exchanger is an apparatus in which heat exchange takes place between two media of different temperatures. The history of the device goes back to antiquity. The principle of heat exchange between environments was used in ancient Greece in the baths - Thermes. Later, the knights heated the water with their armor. First, they were placed on hot coals, and then dipped into barrels of water.
A modern heat exchanger is technically more advanced. The device is built on the principle of a pipe in a pipe. Inside the wide pipe there is a bundle of thin ones, which are washed by the flow of the heating coolant. Thin tubes should be made of material with excellent thermal conductivity. The ideal option is copper tubes for heat exchangers.
Fittings for polypropylene pipes
Fittings for polypropylene pipes are selected in accordance with its diameter. It is impossible to combine a pipe and a fitting of different diameters. The main types of fittings for polypropylene pipes:
- corners - can be entirely made of polypropylene or with metal threads (for example, for a radiator) on one side, bending angles 45 ° and 90 °;
- tees and crosses - designed for routing pipes in different directions;
- coupling - allows you to connect long pipe sections;
- detachable coupling, or American - designed for detachable connection of the pipe connection to the radiator, thanks to it you can remove the radiator for flushing;
- adapters - allow you to switch from one pipe diameter to another, for example, when changing from a riser to a piping to a radiator.