- Room characteristics
- Thermal insulation of warehouses and hangars
- Warehouse heating methods
- Air heating systems
- Radiant heating systems
- Air-thermal curtains
- Water infrared panels
Send a quick request Heating of warehouses, hangars, storage facilities and other similar buildings differs significantly from heating, say, residential buildings - both the overall dimensions of the room and the special requirements for the conditions of the internal microclimate play an important role.
INTECH-Klimat is ready to implement professional solutions for climatic and other engineering equipment. We will perform a full cycle of turnkey works: design, selection, delivery, installation and maintenance. Call now: +7
... Submit your application
In particular, it is usually required to heat not the entire warehouse, but only certain working areas and places of cargo storage, moreover, the temperature and humidity level in such areas can be completely different. In this regard, the issue of heating the warehouse must be approached with the utmost responsibility - in order to be able to fully use the functionality of the premises.
Standard water heating, with which any of us are well familiar, is of little use for heating air in such a spacious room - the heated air masses will simply rise upward into unused areas. Accordingly, costs will rise significantly - with minimal useful return. So, what kind of warehouse heating system should you use?
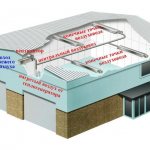
Room characteristics
When choosing a heating system, you should pay attention to some characteristics of the building. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the height of the ceiling and the area of the building. If the height from floor to ceiling is more than 3 m, then it is not recommended to use water systems, because they are unable to provide the required temperature in large rooms.
The second important indicator is thermal insulation. Insulated walls and ceiling will significantly save money spent on heating a workshop or warehouse. If it is not possible to avoid heat loss, it is recommended to use heat sources that heat certain work areas.
You should also take into account the technological temperature requirements for the storage of raw materials or products.
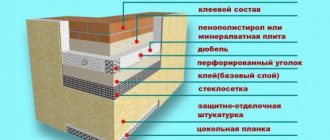
Thermal insulation of warehouses and hangars
The warehouse can be either a brick, block or concrete building, or a metal hangar. If in the first case insulation is not always required, then the hangar insulation is simply necessary. Without this, it will be cold in winter, and very hot in summer, even hotter than outside.
Heating the hangar should be done only after high-quality insulation, since the main task of heating is to replenish heat loss. The less heat loss, the cheaper heating costs. Therefore, you need to carefully select the material according to the characteristics and correctly calculate the insulation layer.
As a rule, warehouses are insulated from the inside. The speed of work is of great importance. The price of the event is also important. What parameters should the thermal insulation layer meet:
- minimum thermal conductivity;
- incombustibility;
- moisture resistance;
- speed of application;
- operation without finishing.
The lack of finishing will not affect the work of the warehouse in any way, beauty is not needed here, the main thing is practicality and reliability.
Taking into account all the above parameters, the thermal insulation of the warehouse with polyurethane foam will be an ideal option.
PPU is a polymer insulation with a closed-cell structure, and for a hangar, foamed polyurethane foam is generally the only option. It has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient in comparison with all modern heaters, which is 0.029 W / m * C. It does not allow steam to pass through and does not absorb moisture. The material does not burn, even if an open flame is directed at it; accordingly, it does not emit poisonous gases. PU foam has high adhesion to almost all materials, that is, it adheres firmly to any surface. The insulation is light, does not shrink, and is not afraid of rodents.
Thermal insulation of a PPU warehouse is carried out in one day, depending on the area, but often not more than a day. Insulation is applied by spraying using a special blow molding machine. Nobody conducts such work with their own hands, they hire contractors.
Autonomous gas heating of apartments is now the norm for new buildings. This is really very convenient.
With the help of the smart home system, heating is controlled remotely, only the Internet is needed.
Warehouse insulation
Warming a warehouse differs from the insulation of an ordinary residential building: it is both huge spaces and work at a height. In addition, not all companies can afford to suspend the activities of the warehouse for a while, and, therefore, work on the insulation of the premises must be carried out at night or directly during the operation of the enterprise.
Let's consider some types of warehouse insulation:
- Mineral wool. This is a classic method, quite cheap and therefore popular. Mineral wool is fireproof and does not rot. Its disadvantages are the high ability to absorb moisture and the high weight of the slabs, which can be dangerous for walls organized from thin galvanized steel (hangars).
- Sprayed polyurethane foam. Recently, this is a very popular method of warming warehouses. Polyurethane foam is non-flammable, has low thermal conductivity and high vapor barrier, it is easy and quick to apply, it forms a dense seamless coating without any "cold bridges". Its disadvantage is its rather high cost, and the impossibility of carrying out work with a functioning warehouse.
- Sandwich panels. The prefabricated panels are very beautiful, strong enough and do not require additional processing. The disadvantage of sandwich panels is the laboriousness of their installation and high weight, which can create additional stress on the walls and foundation.
- Styrofoam. A very cheap way, foam plates are easy to install even with a working warehouse. The disadvantage is the highly flammable material.
An example of how a warehouse is insulated with polyurethane foam:
For some more examples of such insulation, see here.
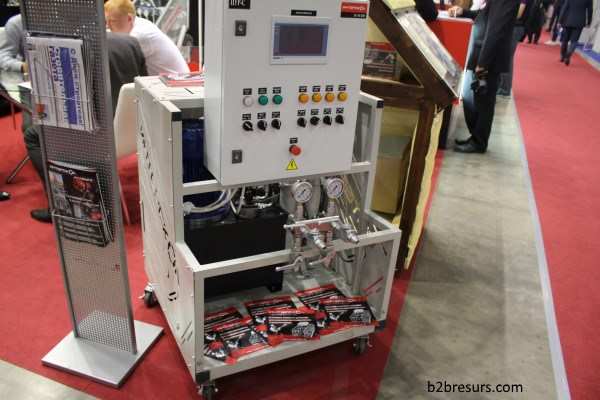

Interskol high pressure unit for polyurethane spraying.
Additionally: how to insulate a warehouse gate is a "narrow" moment.
Warehouse heating methods
The following heating systems are used to heat the air in the warehouse:
- centralized water;
- air;
- radiant.
In the first case, heating occurs due to hot water moving through the water pipe system and heating the radiators. The water comes from the central heating system; depending on the storage conditions, heating in the boiler room is possible, if any, as well as when using special electrical appliances.


It is used only in small warehouses with low ceilings due to the reasons already described above; Also, this system is not very popular due to the complexity of installation, as well as the large amount of occupied space, which does not allow using the warehouse area with maximum efficiency (this mainly concerns retail warehouses and bases where rack structures are used).
Air heating
Air heating was one of the first types of heating systems. And until now, such a system is popular due to its effectiveness. Air heating has the following advantages:
In order to save money, it is better to use combined air heating for industrial premises. Such a heating system consists of mechanical and natural air induction.
With natural intake, warm air will be drawn from the environment. It will be warm even in severe frosts outside. Mechanical induction - intake of cold air by an air duct for heating and supply to the room.
Air heating is the most optimal for heating large industrial premises. And in chemical plants, it is allowed to use only air as a heating system.
Air heating systems
Much more popular is the air heating of the warehouse, which was first used in the seventies of the last century and is being effectively improved to this day. These systems do not interact with any external sources, and the heating of the air in the room is provided by the operation of heat generators and heaters - water and steam.
The heated air enters through the box-shaped collectors to those rooms where it is necessary to maintain a certain temperature regime. To reduce or increase the air flow, special adjustable flaps or louvers are used.
This method also has some disadvantages, although there are fewer of them than the previous system. However, the air system is one of the most commonly used warehouse heating systems due to its ease of installation and relatively low cost of equipment.
Choosing a heating system for warehouses
When designing a heating system for warehouses, it is necessary to take into account the requirements of SNiP (Building Norms and Rules), namely SNiP 2.04.05-91. Here are some excerpts from it:
- 3.11. Heating systems for buildings should be designed to ensure uniform heating of indoor air, hydraulic and thermal stability, explosion safety, and accessibility for cleaning and repair.
- 3.9. In rooms of categories A and B (categories of explosion and fire hazard of premises), as a rule, air heating should be designed.
- 3.57. In rooms of categories A, B, C and pantries of combustible materials or in places designated in workshops for storing combustible materials, heating devices should be fenced with screens made of non-combustible materials, providing access to them for cleaning.
Heating of warehouses - this is an important function, the design of which should be considered carefully, taking into account the categories of fire hazard of the warehouse. In addition, the equipment used in the warehouse heating system should be easily accessible for the necessary repairs and cleaning.
Radiant heating systems
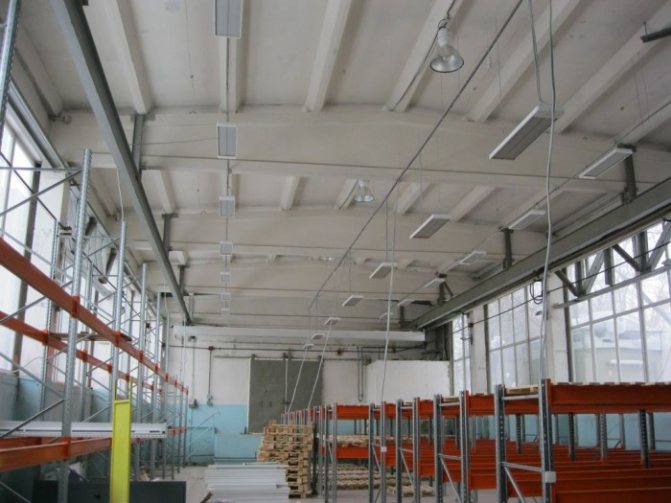
Radiant heating is even more economical and easy to install and use than air heating. Infrared heaters do not generate dust and do not dry the air. The principle of operation of such a system is extremely simple - like the rays of the sun, the elements of this system do not heat the air, but the objects at which they are directed - the floor, walls, objects - and these, in turn, give off part of the heat received to the environment.
This is most convenient in cases where heating of a certain small area is required; the luminaires themselves are easily mounted at a height of 1.5-2 meters from the floor, and the concentration of emitted heat particles can be adjusted.
Depending on the microclimate maintained inside the warehouse, "light" and "dark" infrared heaters are used. The release of heat in them is facilitated by natural or liquefied gas.Heaters can either be installed directly into walls or wall niches, or be part of entire radiant panels located along the entire length of the building. Portable models are also available that are used in conditions of impossibility of installing the heating system. Depending on their dimensions, they can be either manual or placed on special wheeled units.
"Light" infrared heaters are characterized by extremely high temperatures - the surface of the burner can heat up to 900 degrees. "Dark" ones provide less heating - only up to 500 degrees - but at the same time they are equipped with special reflectors that allow dissipating heat particles and, thereby, providing heating of much larger areas. They also differ in design - the former are solid ceramic tiles (it heats up and produces infrared radiation), while the latter are a pipe structure with an external heat-resistant coating, inside which the gas combustion process takes place.
The most versatile type of infrared heaters are radiant panels, which are widespread in most standard storage warehouses and are standard fire safety codes. It is also convenient to use them for air conditioning - when connecting a steam generator. At the same time, steam can be heated up to almost 200 degrees, which contributes to a significant increase in the rate of air exchange inside the room.
Thus, we can say that today radiant heaters of both types are the best options for heating systems - efficient, economical and convenient. However, the following restrictions on the use of these units should be mentioned:
- inability to use heating panels at a height below 4 meters. Otherwise, the heating temperature of the area will be too high - moreover, such intense radiation will have a bad effect on the health of people passing under them;
- in rooms with increased fire safety requirements. This applies to warehouses of fuels and lubricants and other flammable liquids, petroleum products, oils, etc .;
- in rooms where goods are stored, sensitive to infrared radiation.
Air autonomous heating of a warehouse
The most ancient type of heating, which appeared in time immemorial. Modern air systems do not need radiators and pipes - air ducts are installed instead. Despite the lower heat capacity than water, it provides a higher efficiency factor, since heat is distributed everywhere, along the entire room.
More on the topic: Warehouse heating methods
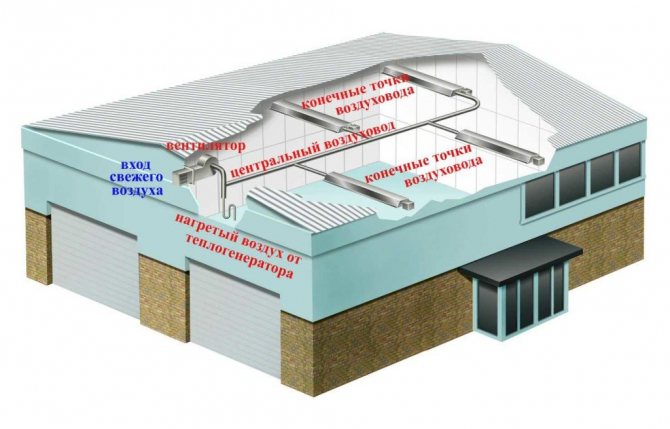

Air autonomous heating of a warehouse
Usually, an air heating system is combined with ventilation, which replaces the heated air with clean air, thereby purifying it and creating a feeling of freshness.
There are three types of air heating: natural, mechanical and combined. With natural heating, the system absorbs warm air currents from the environment and distributes them inside the building. With mechanical, cold air is taken - it heats up before being fed through the air ducts. The combination of the two types is the most rational solution and is suitable for any, even the coldest environment.
Boris Damchuk
auto RU
Air heating is most preferable for large rooms with high ceilings, since they do not require a large number of communications and heat the air in the building everywhere. In warehouses of toxic substances, this type of heating is the only possible way to maintain a comfortable microclimate for work.
We recommend to buy
Air-thermal curtains
Air curtains are required to separate zones with different temperature conditions.The equipment is mounted in the aperture of doors, windows, gates. The curtain is formed by the movement of a high-speed air flow. It is a kind of invisible barrier that does not allow warm air to escape and does not let cold air in from outside. In addition, the air curtain isolates the warehouse from exhaust gases, dust and other negative phenomena without interfering with the movement of special vehicles.
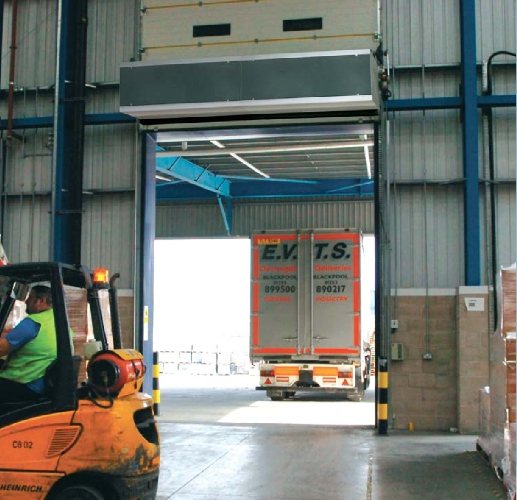


The curtain width is 0.6-2.5 meters. In wider openings, several devices are mounted close to each other. When calculating the heat curtain, the following factors are taken into account:
- the maximum temperature of the supplied air is 50 ° С at the entrance;
- temperature of air entering from outside 5-14 ° С;
- air speed no more than 8 m / s at the entrance and no more than 25 m / s at technological openings and gates;
- installation of thermal curtains is justified for entrance doors without vestibules, opening five or more times a day or for 40 minutes per shift.
Steam systems
The heat carrier is dry saturated steam with a temperature not exceeding 130 ° С. The system can be open-loop, when the condensate is transferred to the heat exchanger by a pump, or closed, when the condensate moves by gravity. Main advantages:
- minimal heat loss in heat exchangers;
- fast heating of radiators and other heating devices;
- low inertia;
- the possibility of heating multi-storey buildings;
- compactness of equipment;
- low hydrostatic pressure in the system.

Disadvantages:
- high heat losses in steam lines, as a result - a decrease in efficiency;
- noisiness;
- you cannot make the temperature of the coolant below 100 ° C;
- intensive corrosion of the metal elements of the circuit.
Steam heating is permitted for terminals with non-flammable and non-toxic dust, non-flammable and non-flammable vapors and gases. Steam lines are installed separately from the ventilation and air conditioning system.
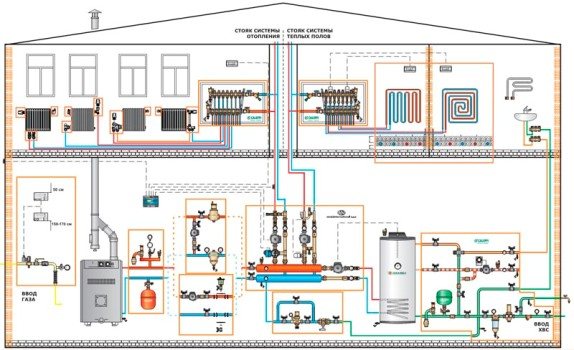
Types of heating systems with different heat carriers
By the type of coolant, steam, air and water are distinguished. warehouse heating... In some cases, the systems are combined, arranging steam-air, steam-water or water-air heating. Everything in order.
Steam systems
The heat carrier is dry saturated steam with a temperature not exceeding 130 ° С. The system can be open-loop, when the condensate is transferred to the heat exchanger by a pump, or closed, when the condensate moves by gravity. Main advantages:
- minimal heat loss in heat exchangers;
- fast heating of radiators and other heating devices;
- low inertia;
- the possibility of heating multi-storey buildings;
- compactness of equipment;
- low hydrostatic pressure in the system.

Disadvantages:
- high heat losses in steam lines, as a result - a decrease in efficiency;
- noisiness;
- you cannot make the temperature of the coolant below 100 ° C;
- intensive corrosion of the metal elements of the circuit.
Steam heating is permitted for terminals with non-flammable and non-toxic dust, non-flammable and non-flammable vapors and gases. Steam lines are installed separately from the ventilation and air conditioning system.
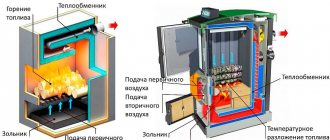
Air systems
Air heating systems for warehouses are the most common today. The heat carrier is air that heats up when passing through the generating set. The heated air is distributed evenly throughout the storage volume through a duct system. The units are mounted on the roof and along the walls. The system is well suited for heating large high-rise buildings.
Main advantages:
- the possibility of combining the heating circuit with ventilation for the flow of fresh air into the room;
- high efficiency up to 95%;
- rapid heating of the air due to the absence of an intermediate heat carrier;
- the ability to automate the heating system, adjust the exact parameters.
Warm air outlets are designed so that there are no massive building structures in the path of the air flow. At a warehouse height of less than 8 meters, the release is carried out with covering jets, at a height of more than 8 meters - with non-covering jets. The air jet, when the air is discharged, is applied to the ceiling at a height equal to 0.85 times the height of the terminal (H). Non-overlapping jets are formed at a height of 0.35-0.65 N from the floor. The distance between the diffusers when installed in a row is no more than three room heights.
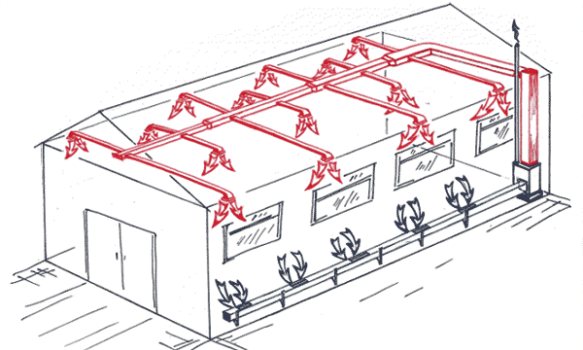

Air heating of a warehouse is economical in operation, pays off quickly, can be installed with or without air ducts. The system works effectively in terminals with high ceilings, it allows you to evenly heat the entire volume of air. Combining heating with ventilation and air conditioning reduces the financial costs of the project.
If there is no need for constant heating of warehouses, but a strong drop in temperature cannot be allowed, heat guns are used as more compact devices. The equipment is placed around the perimeter of the terminal and connected to the thermostat sensors. When the temperature drops to the set value, the equipment turns on and starts generating heat. The device of such heating does not require drawing up a project, it allows you to quickly warm up the room. But after turning off the heat gun, the air cools down just as quickly.
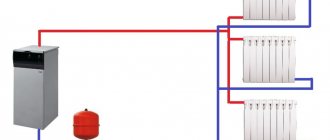
Water systems
The heating medium in the water heating system can be water or water-based antifreeze. For small rooms, arrange a circuit with natural circulation. The pipes are angled so that the water moves by gravity. For warehouses of a large area, such a solution will not be effective; installation of pumps is required. Forced circulation systems are highly efficient but require electricity.


Water heating is often chosen by warehouse owners as the most optimal option. In places where there is the possibility of connecting to the central network, the task is simplified. In the absence of such an opportunity, the calculation of heating the warehouse should include the choice of a boiler and the device of a separate room for the boiler room. As a disadvantage of such a system, the aesthetic component is indicated - the pipes along the walls do not decorate the warehouse.
The advantage of water systems over steam systems is uniform heating of heating devices, the air does not dry out, and optimal conditions for goods are maintained. But such heating is not recommended for storage terminals higher than five floors. This is because warm air rises and collects at the top, increasing heat leakage through the roof and leaving areas of the ground floor cold. In warehouses with high tops and hot water heating, specialists install ceiling fans to increase efficiency. The rotation of the propellers in winter allows warm air to circulate throughout the warehouse, while in summer it provides some coolness.
Water infrared panels
To date, there is another very profitable way that can be used to equip the heating of a hangar or any other large utility room - the use of water IR panels.
In this case, the heat transfer fluid is heated to 160 ° C and enters the radiating tubes located under the ceiling. The infrared radiator effectively dissipates heat throughout the entire volume of the heated room. Thus, the equipment operates not on the convective, but on the radiant principle.
The uniqueness of such equipment lies in the fact that the air in the room is not heated. Various types of surfaces are subject to heating, including the surface of equipment, goods, shelving, walls, floors, ceilings, and even people in the room.
With the help of IR water panels, it is possible to effectively organize the heating of the workshop, in which welding, carpentry and other production work is carried out.
In this case, the purpose of the method is not to heat the room itself or raw materials, but to provide heat to the working personnel.