Category: construction Posted on 10/24/2019 Comments: Read: 3 min Views: Post Views: 4 274
Heating a house is a "vital" process, and therefore it is not surprising that there are many different ways, devices and technologies in order to practically and efficiently heat a home. Systems may differ in their technology and structure, but the main thing is that they provide efficient heating of the room.
Heating with a radiator is natural for the present. The system itself is subdivided into gravitational, in which circulation depends on the heat carrier, and forced, in which additional elements (pump) are needed for circulation.
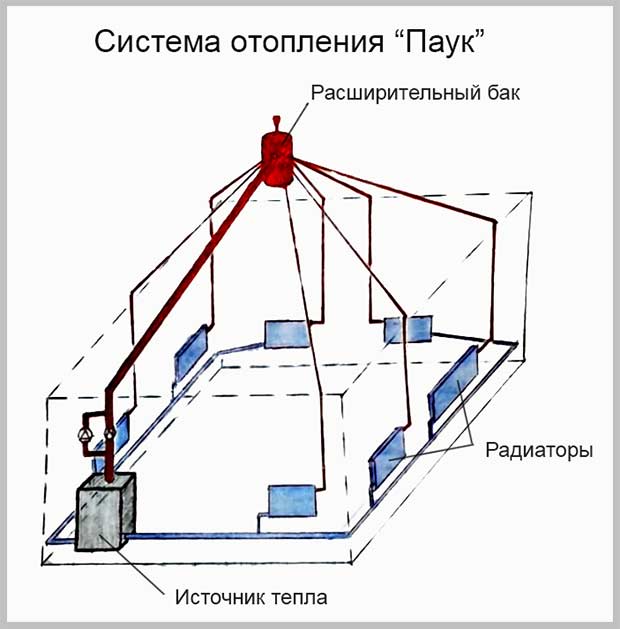
Some heating systems are gradually becoming obsolete and replaced by new ones. However, there are those who are returning to everyday life due to their practicality or economy. The Spider heating system is one of these. This system has been forgotten because modern heating systems are closed, and circulation pumps are widely used in them. However, for heating small private houses, it is still an excellent heating option.
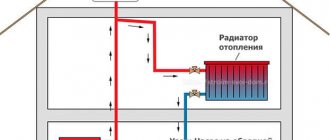
The "Spider" consists of a direct heat source (which can operate on any fuel), an expanded tank (it is fixed at the top), pipelines and the actual radiators. Due to its appearance (schematic) and location, the system got its name.
An expanded tank (reservoir) is installed in the attic of the building, which must be well insulated. Risers are suitable for it, which lead to a heat source and radiators. When the coolant cools down, it leaves cold through horizontally located pipes (mains).
Electric boilers for heating a private house - their main advantages and disadvantages
That is why an electric boiler is increasingly used in modern homes, the mention of which many associate with the very high cost of operating it.
It is quite reasonable that electric power is quite expensive today, but if there is no desire to fiddle with wood, coal or diesel fuel, and there is no natural gas, there is simply no other choice.
An electric boiler has the following advantages:
- it is easy to install, the requirements that accompany its installation are easy to fulfill, and there are not many of them, and most importantly, licensing of work is not required;
- low installation cost, and when used in rooms with short-term operation, heating can become even cheaper than gas;
- it is easier to operate, and maintenance does not require special knowledge, in addition, it is the most automated, which allows you to simply set the required heating mode;
- ensuring safety, during its operation, carbon monoxide hazardous to human health is not formed, and the possibility of an explosive gas-air mixture is excluded.
Heating a house with an area of 150 square meters requires about 15 KW / h, it is difficult to obtain this power outside the city, where 5 KW / h is already a great achievement.
And laying a three-phase line in terms of cost and the number of required permits is comparable to laying a gas pipe to a house.
This is the main disadvantage of electric boilers.
In economic terms, the choice of an electric heater as a heat source is very successful.
Direct electric heating is the most popular type of heating in Europe and the most promising in our country.
One-pipe and two-pipe heating systems - what are the similarities and differences
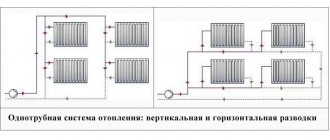
Before proceeding to consider the issues of similarities and differences between heating systems of a one-pipe scheme and a scheme based on the use of a pipe for supplying and removing a coolant, it is necessary to understand why it is called horizontal. In heating engineering, there are two main schemes for heating systems. The first is vertical, it is intended for use in multi-storey buildings and implies the placement of final heating devices on several tiers or floors. The horizontal system implies the use of final heating devices - radiators located within one floor. Actually, these are all the main differences.
Theoretically, in multi-storey buildings where there is a centralized boiler room, a horizontal scheme can be used as a local version located on one floor or as a branch for a separate apartment. Moreover, this scheme has the same advantages and disadvantages as the usual scheme in an individual one-story house.
One-pipe wiring diagram
A single-pipe horizontal heating distribution system is the most primitive heating system. Schematically, it can be represented as a ring made of a pipe filled with a coolant. When the coolant is heated at one end of this looped pipe, the liquid begins to expand and is gradually pushed out of the heating zone, pushing the cold liquid to the heating element. After the liquid passes a certain distance along the ring and from the place of heating, it began to gradually cool. But since the heating process is ongoing, the circulation process will be maintained. The principle of a one-pipe heating system allows you to provide a large number of heating devices, while the coolant, passing through the cavities of the radiators, heats them unevenly. The one closest to the boiler will be as hot as possible, because the liquid immediately after leaving the boiler heat exchanger has a high temperature, but as it moves through the system, it will cool down. Therefore, in the last radiator, the temperature will be the lowest.
A single-pipe horizontal heating system, despite this specificity, still has many positive aspects:
- Its cost is much lower due to the small number of connecting pipelines, and the small laboriousness of installation;
- Compared to other systems, it is easier to install - it is just a set of pipes and radiators connected in series with a minimum number of taps and valves;
- Compared to other options, the service life of the equipment is much longer than in other systems - there is simply nothing to break down and the risk of clogging is minimal;
- A single-pipe scheme allows you to ensure coverage of the entire building or floor along the perimeter, which in turn makes it possible to warm up the room thoroughly.
Alas, with so many positive qualities, the model also has negative points that must be taken into account when designing a room heating system:
- The system is not designed to accommodate temperature control devices on each individual radiator or battery. Most likely, to create a comfort zone, you will have to move furniture, since it is almost impossible to disconnect the battery in the room with such a connection;
- During operation, you must be very careful - the breakdown of one device threatens the failure of the entire system. With a serial connection of radiators, to repair one, you will have to turn off the entire system and drain the coolant.
Well, one more point to which you need to pay attention - the farther from the heating source of the coolant, the larger the radiator should be. Here, everything is just the battery closest to the boiler, with a small size, will give off heat more than a similar one installed at the end of the line. That is why, in order to even out the balance of heat transfer, the dimensions of the battery increase with distance from the heater.
Two-pipe heating system wiring diagram
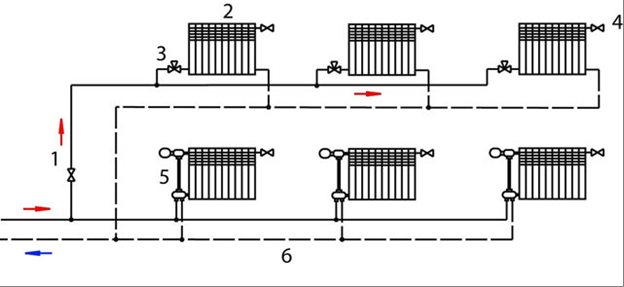

A horizontal heating system assembled according to a two-pipe scheme has undoubtedly great capabilities in terms of regulating heat transfer from radiators and fuel economy. The reason for this is the very scheme of building the system. In principle, this can be represented in the form of two rings of pipes - the first of which is intended for supplying hot coolant, and the second for removing the cooled one. The first circuit is constantly fed from a heat source - a heating boiler, the second is directed to the boiler and supplies the cooled heat carrier to the heat exchanger. These circuits are connected by radiators, in which the coolant is cooled. From the point of view of heating technology, this system is more complex than a one-pipe system, but it is also more efficient, since heat is equally uniformly supplied to all radiators with minimal losses.
A two-pipe horizontal heating system has a number of advantages over a one-pipe system:
- The coolant is supplied to all radiators at approximately the same temperature, this allows for quick and high-quality heating of the room;
- The system is completed with a large number of taps, gate valves, shut-off and control valves. This makes it possible to adjust the room temperature independently of other radiators;
- The system is more protected from unforeseen situations, such as water hammer and a rapid increase in pressure in the system;
- Thanks to the large number of regulating devices, it is possible to quickly find the airlock and quickly bleed the air formed in the system.
- The system is very maintainable - it is very simple to turn off one radiator without shutting down the entire system - just shut off the water supply and drainage taps and the radiator can be removed and repaired;
- The scheme allows you to use it both as the main type of heating in an apartment or on a separate floor, and to use it in parallel when connecting a collector with other options, for example, a "warm floor" system.
But in fairness, it must be said that the two-pipe scheme also has its own specific drawbacks. In order to properly configure the system, you need to spend a lot of time and effort. To maintain the balance correctly, it is necessary to know and understand how the adjustment is made and where the regulating devices are installed.
Two-pipe manifold heating circuit
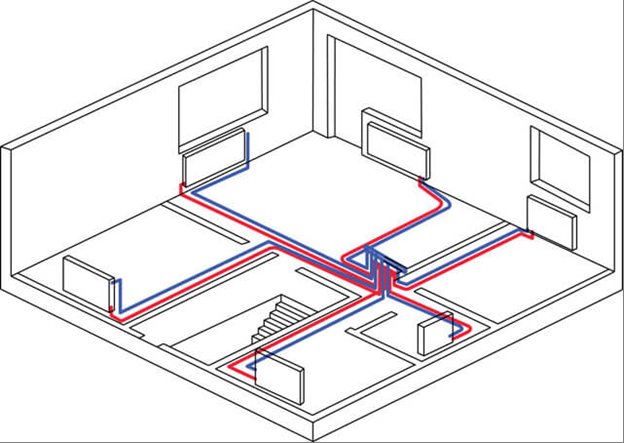

Another option for constructing a heating system for a multi-storey apartment building is a horizontal heating system with a collector parallel system.
Conventionally, this system can be represented as several branches of a conventional two-pipe heating circuit connected at one point. When entering the floor, a collector is installed, to which the rays of the directions of the construction of the heating system are connected. Each direction has a two-pipe system and several radiators are installed in a separate room or several rooms. This scheme allows the use of both steel and polymer pipes, which significantly reduces the cost of both the system itself and its laying.
The second point to which attention is paid is the possibility of simple adjustment of the temperature of the coolant and accounting for the consumed thermal energy. On the collector itself, control equipment and metering devices are installed, which makes it possible to control heating from one place.This scheme is especially convenient for those who install a new generation of devices that can be controlled through the smart home system.
The advantage of the collector principle of construction is the ability to save money first on installation, and then on operation, because laying pipes is cheaper than with a simple two-pipe scheme. And in the heating season, you can reduce heat consumption by switching off or minimizing the consumption of the heat carrier in the premises.
Horizontal heating, made according to the collector scheme, allows you to connect any objects, which is also important for ease of use and cost savings.
Summing up all of the above, it must be said that the collector circuit provides good performance only in the presence of good pressure or a circulation pump. Otherwise, the advantages of a two-pipe collector circuit can be represented by the following list:
- The arrangement of the system does not require large expenditures;
- All elements can be installed using the method of hidden piping;
- Allows you to combine several elements into a single system;
- Suitable for heating both small and large areas;
- The equipment includes protective devices that block end devices in the event of a water hammer;
As for the shortcomings, it is worth remembering that this scheme includes complex nodes, without which its performance is impossible, which means:
- That it is necessary to attract professionals for installation;
- It is necessary to correctly calculate all the elements, from ordinary taps to the diameter of the pipes and the thickness of the heat-insulating layer.
Direct electric heating of a private house
Electric heating systems for private houses are extremely popular today.
They operate on the most expensive of all energy carriers available in our country - electrical energy.
Direct electric heating systems are used, both to fully cover the required heating and for peak loads and maintain a constant room temperature.
When choosing an electric heating option, it is very important to take into account what building materials the house is made of.
From the ability of the walls of the house to store heat directly, the choice of a heating device will be determined.
If we compare housing heating directly with electricity with other available methods, then many facts speak in its favor.
For example, this method of heating rooms requires only the presence of special heaters in them.
No other equipment is required for this at all.
There is no need to worry about the coolant or the installation of a special kind of ventilation system.
Such heaters independently transform electric current into heat energy.
They do not need various "intermediaries" from boilers, heat carriers and other equipment.
Heating a house with electricity has many significant advantages, among which the following should be highlighted:
- ease, convenience and reliability of system operation;
- possibility of regulation and efficient heat transfer;
- noiselessness of the heating system;
- small dimensions of heating devices that do not require labor-intensive and high-cost special care;
- high environmental safety and hygiene of electric heaters.
Scheme of operation of a dead-end heating system
In most cases, a dead-end heating scheme assumes that the supply of the coolant to the radiators and its removal is carried out through separate lines.
Work cycle:
- Hot water is supplied from the boiler through the supply pipe to the expansion tank.
- The heated coolant is directed along the pipeline outgoing from the tank through pipes connected to the upper branch pipe of each radiator.
- Hot water, passing through the heater and giving off heat to it, flows through the lower pipe to the return line.
- The cooled coolant collected from all radiators is returned to the boiler through the return pipeline.
After heating the water, the working cycle is repeated.
Types of heaters for direct electric home heating
Since heaters are the key elements for any direct electric heating system, it is necessary at least a little to navigate the devices on our market.
This equipment is classified according to several criteria, the main one being the method of heat transfer.
For example, radiant and convective heaters.
Radiant heaters include infrared panels and mirrors that emit heat.
And the devices whose operation is based on convection are electric convectors, air heaters and heat fans.
To the above, the following types of heaters should be added - combined, convective-radiation, as well as electric heaters, whose operation is based on "indirect heating".
Water heating
Among the entire classification of heating systems, water heating is the most popular. The technical advantages of such heating have been identified as a result of many years of practice.
Undoubtedly, when asked what types of heating there are, it is water heating that first comes to mind. Water heating has such advantages as:
- Not very high surface temperature of various devices and pipes;
- Provides the same temperature in all rooms;
- Saves fuel;
- The operational terms have been increased;
- Quiet work;
- Easy to maintain and repair.
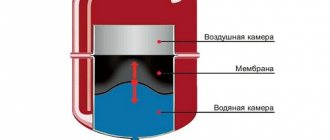
The main component of a hot water heating system is the boiler. Such a device is necessary in order to heat water. Water is a heat carrier in this form of heating. It circulates through closed-type pipes, and then the heat is transferred to various heating components, and from them the entire room is already heated.
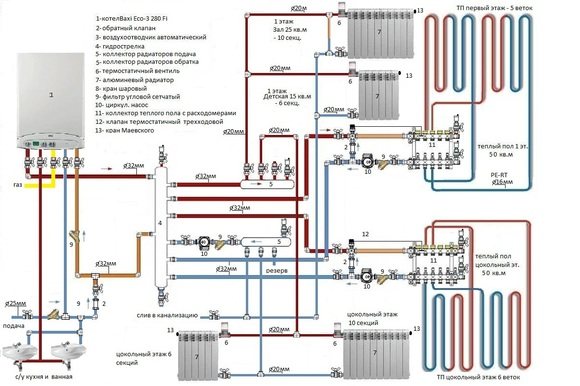

Components of hot water heating
The simplest option is natural circulation. Such circulation is achieved due to the fact that different pressures are observed in the circuit. However, such circulation can also be of a forced nature. For such a circulation, water heating options must be equipped with one or more pumps.
After the coolant passes through the entire heating circuit, it is completely cooled and returned back to the boiler. Here it heats up again and thus allows the heating devices to generate heat again.
Classification of hot water heating systems
The water type of heating can differ according to such criteria as:
- water circulation method;
- the location of the distribution type highways;
- structural features of risers and the scheme by which all heating devices are connected.
The most popular is the heating system, where water is circulated by means of a pump. Heating with circulation of natural water has recently been used extremely rarely.
In a pumped heating system, heating of the coolant can also take place thanks to a hot-water boiler house, or thermal water that comes from a CHP. In a heating system, water can be heated even by steam.
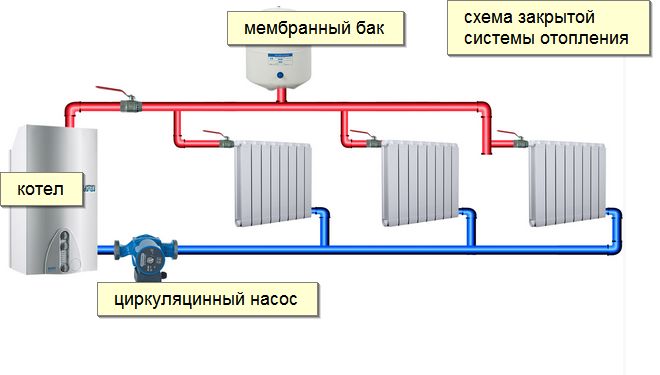

Water heating with circulation pump
A straight-through connection is used when a very high temperature water supply is acceptable in the system. Such a system will not cost so much, the metal consumption will be somewhat less.
The disadvantage of direct-flow connection is the dependence of the thermal regime on the "impersonal" temperature of the coolant in the supplying heat conduit of the external type.
Installation of heating systems
Fan heaters
Another effective device for heating a room are fan heaters, which not only maintain a given temperature, but are also able to raise it in a minimum time.
In addition, they can create a thermal air curtain.
Their undoubted advantage is minimal heat loss and high efficiency.
Today on sale you can see a huge number of fan heaters of various power and quality.
Sometimes they are equipped with air filtration equipment.
Electric "warm floor"
The source of heat in such a field is a special cable built into it.
As a result, the floor turns into a large heating panel that distributes heat evenly throughout the room.
"Warm floor" allows you to create and maintain the optimum air temperature.
In addition, such a home heating system does not require additional equipment in the form of radiators, which greatly facilitates the arrangement of furniture and can be used with any floor covering.
Types of dead-end systems
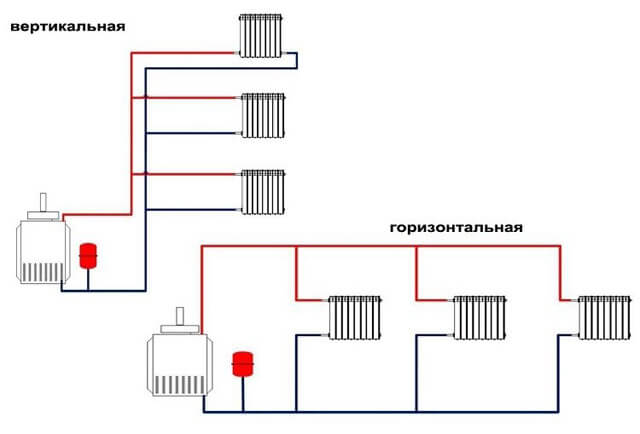

In both schemes, the cooled coolant flows in the opposite direction relative to the hot
Depending on the features of the structure, a dead-end heating system can be mounted horizontally or vertically.
Horizontal
This type of dead-end system assumes a horizontal arrangement of radiators, united by a supply line and a return line in a common scheme. The entire line consists of pipes of the same diameter, so the wiring is easy to install and more economical, especially for houses of a small area, where it successfully works with the natural circulation of the coolant. In houses with an area of 100 m2 or more, the use of horizontal wiring requires the organization of forced movement of the coolant through the system. Dead-end heating of horizontal type allows installation of wiring into the floor, which successfully hides it from sight. In this case, it is better to choose reinforced polymer pipes and connect them with sliding sleeves.
Vertical
Vertical type dead-end heating includes two or three horizontal circuits connected to a vertical riser. Such a wiring diagram is used in two or three-story houses to create pressure in the pipeline and accelerate the movement of the coolant. Each of its circuits is responsible for heating one floor of the house. Such a wiring scheme has limitations on the number of radiators that make up one branch. For efficient space heating, the number of appliances on a floor should not exceed 10 pieces. For a larger number of them, the installation of automatic pressure regulators will be required to balance the supply of the heated coolant.
Dead-end heating with vertical wiring cannot be laid without the use of various fittings, which complicates the installation of the system.