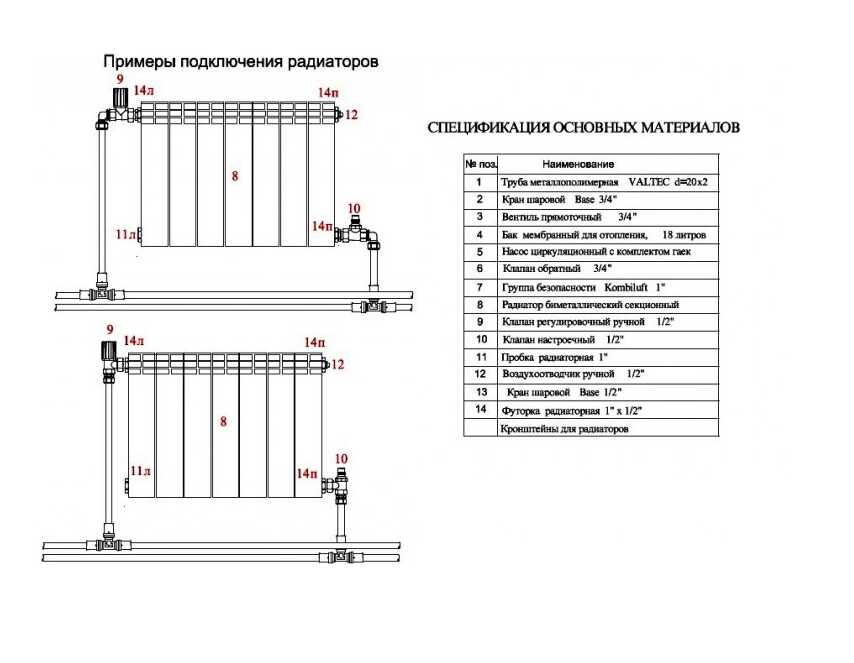
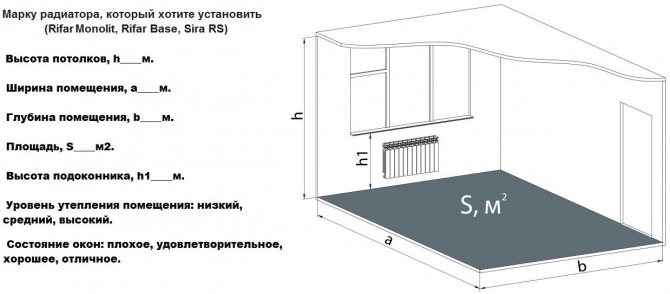
Simple area calculations
You can calculate the size of the heating batteries for a certain room, focusing on its area. This is the easiest way - to use sanitary standards, which prescribe that a heat output of 100 W per hour is needed to heat 1 sq. M. It must be remembered that this method is used for rooms with standard ceilings (2.5-2.7 meters), and the result is somewhat overestimated. In addition, it does not take into account such features as:
- the number of windows and the type of glass units on them;
- the number of external walls in the room;
- the thickness of the walls of the building and what material they are made of;
- the type and thickness of the insulation used;
- temperature range in a given climatic zone.
The heat that radiators must provide to heat the room: the area should be multiplied by the heat output (100 W). For example, for a room of 18 square meters, the following heating battery power is required:
18 m2 x 100 W = 1800 W
That is, 1.8 kW of power is needed per hour to heat 18 square meters. This result must be divided by the amount of heat that the heating radiator section emits per hour. If the data in his passport indicates that this is 170 W, then the next stage of calculations looks like this:
1800W / 170W = 10.59
This number must be rounded to the nearest whole (usually rounded up) - it will turn out to be 11. That is, in order for the room temperature to be optimal during the heating season, it is necessary to install a heating radiator with 11 sections.
This method is only suitable for calculating the size of the battery in rooms with central heating, where the temperature of the coolant is not higher than 70 degrees Celsius.
There is also a simpler method that can be used for the usual conditions of apartments in panel houses. This approximate calculation takes into account that one section is needed to heat 1.8 square meters of area. In other words, the area of the room should be divided by 1.8. For example, with an area of 25 square meters, 14 parts are needed:
25 m2 / 1.8 m2 = 13.89
But this method of calculation is unacceptable for a radiator with reduced or increased power (when the average output of one section varies from 120 to 200 W).
Effect on the result of the material for the manufacture of the radiator
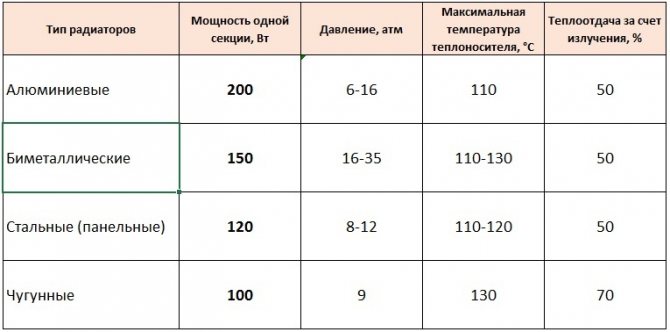
Currently, the following types of radiators are most popular:
- Cast iron... Most often, a cast-iron battery of the MC-140 brand with a heat transfer level of 180 W. This indicator is valid only when using a coolant with a maximum temperature. In practice, this rarely happens, so the actual power of the device is 60-120 watts. It is these figures that are recommended to be used when calculating watts per square meter of heating.
- Steel... They have almost the same area as cast iron. The same applies to the parameters, the exact value of which is indicated in the accompanying documentation. At the same time, the mass of steel products is less, which makes their transportation and installation easier.
- Aluminum... It is problematic to give a general answer to how much one section of an aluminum radiator heats, since similar products are on sale in a large number of modifications. Therefore, in each specific case of calculating the number of sections of aluminum radiators, it is necessary to be guided by the passport data of the model. In general, it is considered that the average indicator of how much one section of an aluminum radiator heats up is 100 W / m2. If the declared power of the device is less, then, most likely, we are talking about a fake.It should also be said that the level of heat transfer from aluminum is higher than that of cast iron and steel. This should also be taken into account before calculating the number of sections of aluminum radiators.
- Bimetallic... These products, which combine the high heat transfer of aluminum and the strength properties of steel, are currently most popular with buyers (the power level of one section of a bimetallic radiator is identical to how many squares one section of an aluminum battery is). Due to good heat dissipation, it is allowed to slightly reduce the number of sections during installation. Correct calculation of bimetallic radiators saves finances, even though bimetallic radiators are considered the most expensive.

It is not recommended to use the maximum heat transfer values of devices when calculating sections of aluminum radiators per square meter - the coolant in the system usually never reaches its extreme values. A more reliable way is to use the minimum values, which will ensure that errors are avoided. The heating system, equipped on the basis of the calculation of sections of aluminum radiators, will provide comfort in the home even in severe frosts.
Consider a calculation method for rooms with high ceilings
However, the calculation of heating by area does not allow you to correctly determine the number of sections for rooms with ceilings above 3 meters. In this case, you must apply a formula that takes into account the volume of the room. To heat each cubic meter of volume, according to the SNIP recommendations, 41 W of heat is required. So, for a room with a ceiling height of 3 m and an area of 24 square meters, the calculation will be as follows:
24 square meters x 3 m = 72 cubic meters (room volume).
72 cubic meters x 41 W = 2952 W (battery power for heating the room).
Now you should find out the number of sections. If the radiator documentation indicates that the heat transfer of one part of it per hour is 180 W, the found battery power must be divided by this number:
2952 W / 180 W = 16.4
This number is rounded to the nearest whole - it turns out, 17 sections to heat a room with a volume of 72 cubic meters.
Using simple calculations, you can easily determine the data you need.
Heat output of 1 section
As a rule, manufacturers indicate average heat transfer rates in the technical characteristics of heaters. So for heaters made of aluminum, it is 1.9-2.0 m2. To calculate how many sections are required, you need to divide the area of the room by this coefficient.
For example, for the same room with an area of 16 m2, 8 sections will be required, since 16/2 = 8.
These calculations are approximate and it is impossible to use them without taking into account heat loss and the actual conditions of placing the battery, since you can get a cold room after installing the structure.
To get the most accurate indicators, you will have to calculate the amount of heat that is needed to heat a specific living area. To do this, you will have to take into account many correction factors. This approach is especially important when the calculation of aluminum heating radiators for a private house is required.
The formula required for this is as follows:
KT = 100W / m2 x S x K1 x K2 x K3 x K4 x K5 x K6 x K7
- CT is the amount of heat that a given room needs.
- S - area.
- K1 - designation of the coefficient for a glazed window. It is 1.27 for standard double glazing, 1.0 for double glazing and 0.85 for triple glazing.
- K2 is the coefficient of the wall insulation level. For a non-insulated panel, it = 1.27, for a brick wall with masonry in one layer = 1.0, and in two bricks = 0.85.
- K3 is the ratio of the area occupied by the window and the floor. When between them:
- 50% - the coefficient is 1.2;
- 40% — 1.1;
- 30% — 1.0;
- 20% — 0.9;
- 10% — 0.8.
- K4 is a coefficient that takes into account the air temperature according to SNiP on the coldest days of the year:
- +35 = 1.5;
- +25 = 1.2;
- +20 = 1.1;
- +15 = 0.9;
- +10 = 0.7.
- K5 indicates a correction when there are exterior walls. For example:
- when she is alone, the indicator is 1.1;
- two outer walls - 1.2;
- 3 walls - 1.3;
- all four walls - 1.4.
- K6 takes into account the presence of a room above the room for which calculations are made.
- unheated attic - coefficient 1.0;
- heated attic - 0.9;
- living room - 0.8.
- K7 is a coefficient that indicates the height of the ceiling in the room:
- 2.5 m = 1.0;
- 3.0 m = 1.05;
- 3.5 m = 1.1;
- 4.0 m = 1.15;
- 4.5 m = 1.2.
If you apply this formula, you can foresee and take into account almost all the nuances that can affect the heating of the living space. Having made a calculation on it, you can be sure that the result obtained indicates the optimal number of aluminum radiator sections for a particular room.
If you decide to install aluminum radiators, it is important to know the following:
Whatever calculation principle is undertaken, it is important to make it as a whole, since correctly selected batteries allow you not only to enjoy the heat, but also significantly save on energy costs. The latter is especially important in the context of constantly growing tariffs.
Additional parameters to consider
Having made an approximate calculation of the number of heating radiator sections for your apartment, do not forget to correct it, taking into account the characteristics of the room. They need to be considered as follows:
- for a corner room (two walls facing the street) with one window, the radiator power must be increased by 20%, and with two windows - by 30%;
- if the radiator is mounted in a niche under the window, its heat transfer will decrease, this is compensated by an increase in power by 5%;
- should be increased by 10% if the windows face the north or north-east side;
- the screen, which covers the radiators for beauty, "steals" 15% of their heat transfer, which must also be taken into account when calculating.
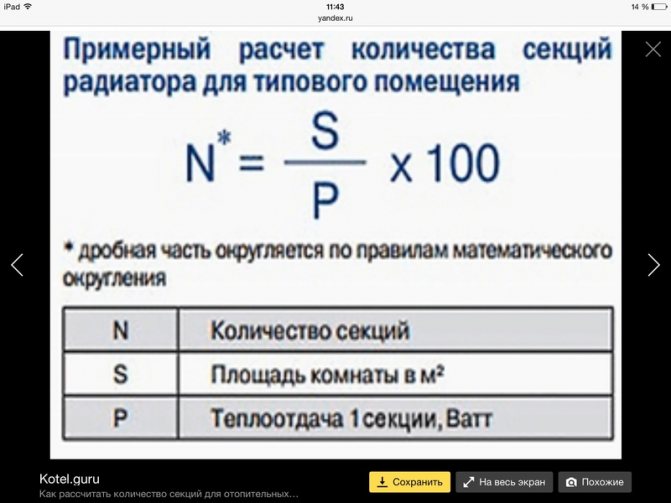
At the very beginning, the total value of the required thermal power for the room should be calculated, taking into account all the available parameters and factors. And only then divide this value by the amount of heat that one section emits per hour. The result with a fractional value, as a rule, is rounded up to the nearest integer.
We make calculations on the volume of the room
For a panel house with a standard ceiling height, as mentioned above, heat is calculated based on the need for 41 watts per 1m3. But if the house is new, brick, double-glazed windows are installed in it, and the outer walls are insulated, then you need 34 watts per 1m3.
The formula for calculating the number of radiator sections looks like this: the volume (area multiplied by the ceiling height) is multiplied by 41 or 34 (depending on the type of house) and divided by the heat transfer of one radiator section specified in the manufacturer's passport.
For example:
Room area 18 m2, ceiling height 2, 6 m. The house is a typical panel building. Heat transfer of one section of the radiator - 170 watts.
18X2.6X41 / 170 = 11.2. So, we need 11 radiator sections. This is provided that the room is not angular and there is no balcony in it, otherwise it is better to install 12 sections.
Specificity and other features
It is also possible that there are other specificities for the premises for which the calculation is made, not all of them are similar and completely identical. These can be indicators such as:
- the temperature of the coolant is less than 70 degrees - the number of parts will have to be increased accordingly;
- the absence of a door in the opening between the two rooms. Then it is required to calculate the total area of both rooms in order to calculate the number of radiators for optimal heating;
- double-glazed windows installed on the windows prevent heat loss, therefore, fewer battery sections can be installed.
When replacing old cast iron batteries, which provided a normal temperature in the room, with new aluminum or bimetallic ones, the calculation is very simple. Multiply the heat dissipation of one cast iron section (150 W on average). Divide the result by the amount of heat of one new part.
Getting ready for winter - calculating the number of heating radiator sections.
There are three methods here, which are based on general principles:
- the standard value of the power of one section can vary from 120 to 220 W, therefore the average value is taken
- to correct errors in calculations when buying a radiator, you should lay a 20% reserve
Now let's turn directly to the methods themselves.
Method one - standard
Based on building rules, 100 watts of radiator power is required for high-quality heating of one square meter. Let's do the calculations.
Suppose the area of the room is 30 m², the power of one section is taken equal to 180 watts, then 30 * 100/180 = 16.6. Let's round the value up and get that 17 sections of a heating radiator are needed for a room of 30 square meters.
However, if the room is angular, then the resulting value should be multiplied by a factor of 1.2. In this case, the number of required radiator sections will be 20
Method two - approximate
This method differs from the previous one in that it is based not only on the area of the room, but also on its height. Please note that this method only works for medium to high power appliances.
At low power (50 watts or less), such calculations will be ineffective due to too large an error.
So, if we take into account that the average height of the room is 2.5 meters (the standard height of the ceilings of most apartments), then one section of a standard radiator is capable of heating an area of 1.8 m².
The calculation of sections for a room of 30 "squares" will be as follows: 30 / 1.8 = 16. Rounding up again, we find that 17 radiator sections are needed to heat this room.
Method three - volumetric
As the name implies, the calculations in this method are based on the volume of the room.
It is conventionally assumed that to heat 5 cubic meters of a room, 1 section with a capacity of 200 watts is needed. With a length of 6 m, a width of 5 and a height of 2.5 m, the formula for the calculation will be as follows: (6 * 5 * 2.5) / 5 = 15. Therefore, for a room with such parameters, you need 15 sections of a heating radiator with a capacity of 200 watts each.
If the radiator is planned to be located in a deep open niche, then the number of sections must be increased by 5%.
If the radiator is planned to be completely covered with a panel, then the increase should be made by 15%. Otherwise, it will be impossible to achieve optimal heat dissipation.
Read the article and find out how to build a water heating scheme for a private house.
Here - everything about how to choose a heating radiator
Climatic zones are important too
It's no secret that in different climatic zones there is a different need for heating, therefore, when designing a project, it is necessary to take these indicators into account.
Climatic zones also have their own coefficients:
- the middle strip of Russia has a coefficient of 1.00, so it is not used;
- northern and eastern regions: 1.6;
- southern stripes: 0.7-0.9 (minimum and average annual temperatures in the region are taken into account).
This coefficient must be multiplied by the total thermal power, and the result obtained must be divided by the heat transfer of one part.
conclusions
Thus, the calculation of heating by area does not present any particular difficulties. It is enough to sit a little, figure it out and calmly calculate. With its help, every owner of an apartment or house can easily determine the size of the radiator that should be installed in a room, kitchen, bathroom or anywhere else.
If you doubt your skills and knowledge, entrust the installation of the system to professionals. It is better to pay one time to the professionals than do it wrong, dismantle and re-start. Or do nothing at all.
Continuing the theme: high-quality interior doors www.dveri-tmk.ru will help keep warm in your house or apartment. And to simplify the calculations for the heating area.
Why is it needed
The motives for performing the calculations are quite obvious: when designing a heating system, it is necessary to know the amount of energy that the room must receive during the peak of cold weather to stabilize the internal temperature.
Depending on the calculation result, the following is selected:
- In all, without exception, water heating systems - the total capacity of the batteries for a separate room and for a house or apartment as a whole.
- In autonomous heating systems - boiler power.
Note: when buying a solid fuel boiler, an excess of power is desirable, since its kindling will be periodic, once every few hours. Excess heat energy is accumulated by the heat carrier and massive heating devices; sometimes for this purpose a massive heat-insulated water tank is included in the circuit - a heat accumulator.
Heat loss compensation
In order for the battery power to be enough to heat the room, you need to make some adjustments:
- Round up fractional values... It is better to let some power reserve remain, and the desired temperature level is adjusted using a thermostat.
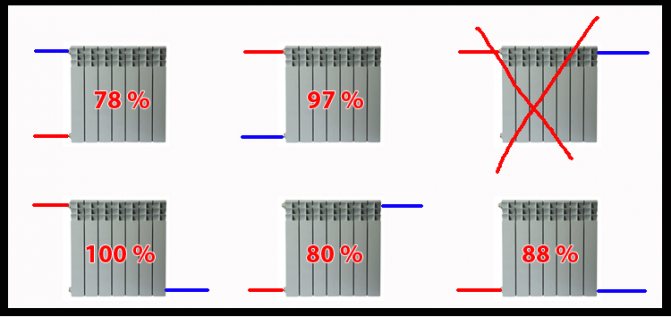
- If there are two windows in the room, then you need to divide the calculated number of sections by two and install them under each of the windows... Heat will rise, creating a heat curtain for cold air entering the apartment through the glass unit.
- Multiple sections need to be added if two walls in the room face the street, or the ceiling height reaches more than 3 m.