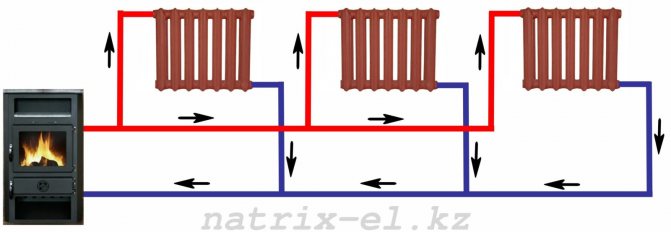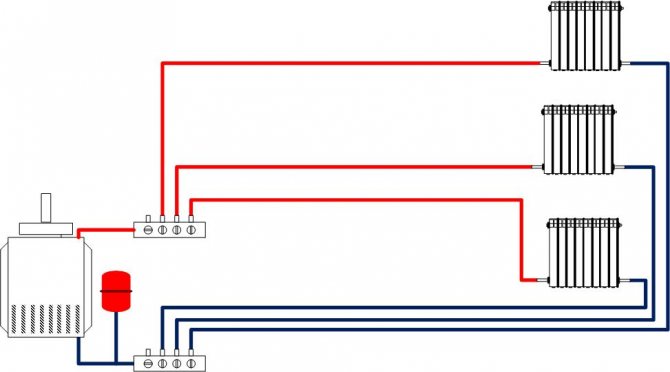
Have you decided to make a private house your permanent residence? Or maybe the summer season lasts in your family all year round and winter weekends outside the city are a common thing for you? Then the question of heating your nest is extremely relevant. Today, perhaps the most popular among all heating systems for private houses is water heating. The principle of its operation is quite simple and straightforward: heat is generated in a special boiler and already from it through a closed circuit, hot water is supplied through pipes to heating devices.
But this is a general principle. Depending on the heating method (gas, electricity, etc.), the circulation method, the heating systems used, as well as other characteristics, water heating is divided into many types. It is this topic that we will cover in detail in our article.
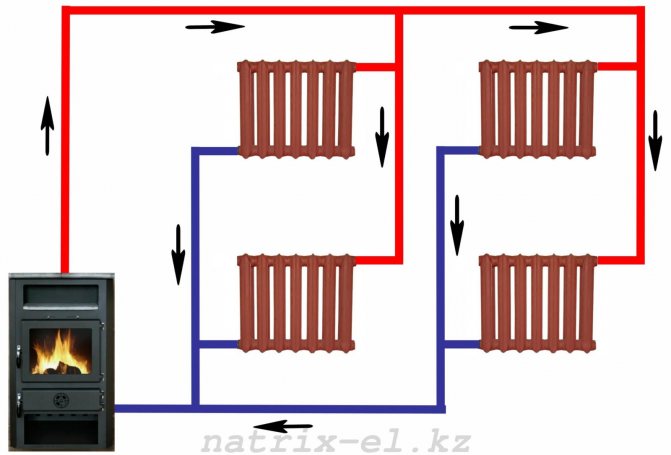
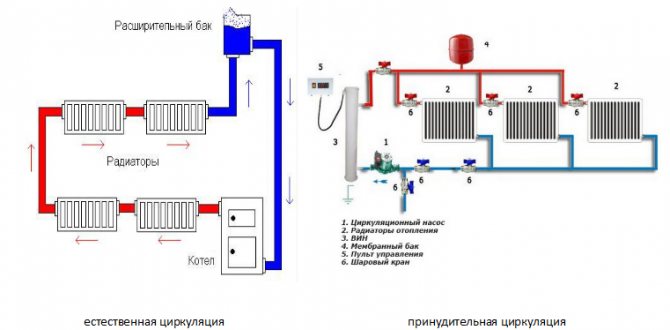
All water heating systems at home can be divided into two groups: using natural or forced circulation of water.
Natural circulation heating
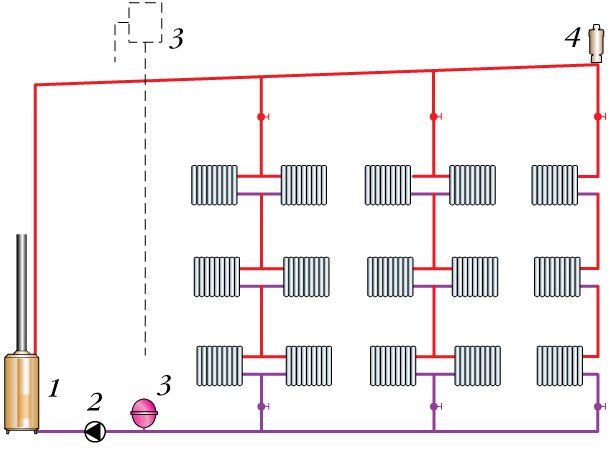

An example of a one-pipe system with natural circulation
Systems with natural circulation, or as they are also called gravity, have been used for a long time. From the name itself, we understand that they work without the help of special devices (pumps), and their work occurs due to natural physical laws.
We all probably remember from school physics lessons that a heated liquid or gas always moves upward. This is the principle behind such heating. Heating up in the boiler, the water begins its movement up the pipes. Having reached the farthest heater, it begins to descend back to the boiler, where it heats up again and circulates upward. When installing a self-circulation system, a slope is necessarily created in the water return section. And at the coolant supply, at the highest point of the system, it is required to install an expansion tank, which will act as a buffer that compensates for the increase in liquid volume.
Benefits of gravity heating
As already noted, gravity water heating systems at home have been used for a long time and have managed to recommend themselves, as they have certain advantages:
- Cheapness. After all, this system does not require the installation of additional equipment.
- Ease of installation and repair (it is even possible to build a heating system in your own house with your own hands).
- Work in the absence of electricity. For a while, until the boiler temperature drops below 50 degrees, the liquid will continue to circulate through the system.
- Almost complete noiseless operation, again due to the absence of a pump.
Disadvantages of gravity heating
But with all the above advantages, self-circulation heating systems have many disadvantages that make it impractical to use this method of heating a house today.
- The inability to use this type of system for large rooms. Even for a two-story private house, the circulation of water will be difficult.
- Temperature difference in heating devices. The farther the room is from the boiler, the colder it will be. Moreover, the difference can sometimes be significant - up to 5 degrees.
- The regulation of heating is complicated. Firstly, the system will start working only when the boiler heats up to 50 degrees, respectively, you will not be able to make the heating power in the house below this mark.Secondly, even when installing heat regulators, the temperature error will be from 3 to 5 degrees, which is quite significant.
Such systems are gradually losing their relevance and every year they are replaced by more modern compulsory systems. We recommend that you do water heating from natural circulation only if you want everything simpler.
Classification
It is clear that, by definition, water or a heat carrier based on it with a lower freezing point is used as a heat carrier. Are there any alternatives?
- Steam heating. The heat carrier is superheated high pressure steam. Temperature allows heating devices to be made more compact or more efficient with the same size.
Please note: the downside of efficiency is a greater risk of accidents (steam heating is not used in residential premises) and faster corrosion of pipes and registers made of non-corrosive steels.
- Air heating system. The heated air is dispersed by heat-insulated air ducts, at the same time performing the functions of ventilation.
- Decentralized heating implies that instead of any coolant a separate heat source is used for each room or even for each zone of the room. This is how electric and gas convectors, infrared panels and oil radiators work.
Let us return, however, to the use of water as a heat carrier. On what grounds is it possible to classify hot water heating systems?
Dependent and independent
In the dependent system, the heat carrier from the outside (as a rule, from the heating main) enters the heating system directly. It can be used exclusively for heating; hot water extraction for households is more often possible. It is according to this scheme that heating works in the vast majority of city houses.
The heating unit of an independent system includes a heat exchanger, through which the water of the heating main gives off thermal energy to the heat carrier in a closed loop. The scheme can be applied if antifreeze is used as a coolant in a private house. In the presence of heat meters, such a connection will allow you to turn off the heating during a long trip without risking defrosting the system.
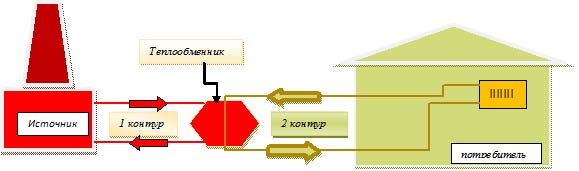

Schematic diagram of independent heating.
Open and closed
An open water heating system operates without overpressure and opens to the atmosphere. At its upper point, an open expansion tank is mounted, where all air locks are displaced.
In a closed system, a constant overpressure is maintained from 1 (in private houses) to 6 (in apartment buildings) atmospheres.
Forced and natural circulation
Systems with natural circulation are used relatively rarely in our time. However, this is an excellent solution for small houses, allowing you to make heating independent of electricity.
The principle of operation of the so-called gravitational systems is based on the fact that when heated, the density of water decreases. In a confined space, colder water displaces heated water masses to the upper part of the circuit. With a certain configuration, it is possible to ensure a continuous flow of the coolant.
The instructions for creating a gravitational system are, in general, relatively simple:
- The boiler is placed as low as possible. In houses without a basement, a recess is often made under it in the floor.
- From the boiler, the filling rises vertically up to the highest point of the circuit, forming the so-called booster manifold.
- At the top point in the case of an open system, an open-type expansion tank is mounted, as already mentioned.In the case of a closed circuit, an air vent is installed there - automatic or manual; the expansion tank of the membrane type can be located in any part of the circuit.
- From the top point, the filling returns to the boiler with a constant slight slope necessary for the cooling water to move by gravity. Along the way, the coolant gives off heat to radiators or other heating devices.
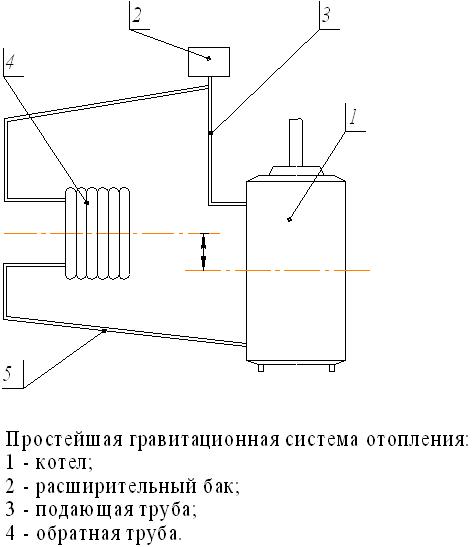

The simplest gravitational system.
A feature of gravitational systems is stringent requirements for the hydraulic resistance of the circuit. A pipe is used not thinner than DN 32 and a minimum of shut-off valves. Chokes of any type are absolutely not placed on the filling.
For reference: the hydraulic resistance of a modern ball valve is ten times less than that of a cast iron or brass screw valve. Comparison of this and a number of other characteristics leads to a simple thought: it is better to completely forget about screw valves when purchasing materials.
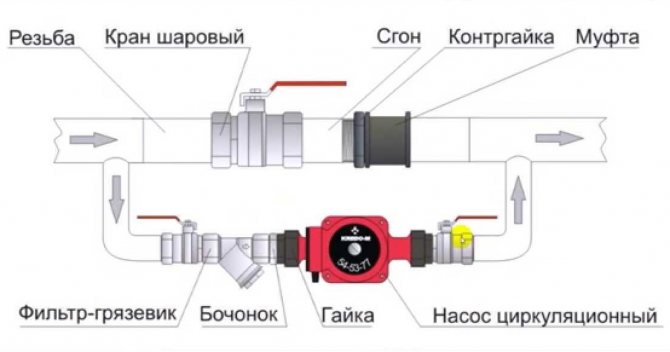
In a system with forced circulation, an external (from the heating main) differential or its own circulation pump is used to create it. Moreover, the pumps can operate in both closed and open systems.
An excellent solution is a circuit with a circulation pump, which, in the absence of electricity, can work as a gravitational one. To ensure this possibility, the filling is carried out with a pipe of large cross-section and at one point it is broken by a valve. Before and after the valve, a pump with a sump cuts in.
What does such a scheme give?
- When the bypass is closed and the pump is on, the system operates with forced circulation. The bypass is closed so that the pump does not circulate water in a circle.
- With an open bypass, the system, due to the minimum hydraulic resistance, is able to operate as a gravity system.


In the photo, instead of a valve, the filling is bursting with a ball check valve. Such an implementation is able to switch to forced circulation when the pump starts up automatically, but is less fail-safe.
Why forced circulation forced gravitational systems to squeeze out? After all, it makes heating more fault-tolerant by definition, doesn't it?
- The circulating heating pump allows you to lay the filling strictly on the level and get by with a pipe of a smaller diameter. Apart from the savings, this greatly affects the aesthetics of the room.
However: in houses with an attic and a basement, the supply and return spouts can be taken out of the residential part of the house.
- Forced circulation ensures faster and more uniform heating of heating devices. In a gravitational system, the radiators farthest from the boiler are always noticeably colder than the close ones.
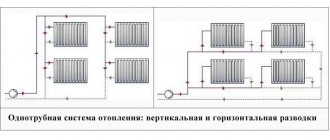
One-pipe and two-pipe
The difference is easier to explain with examples.
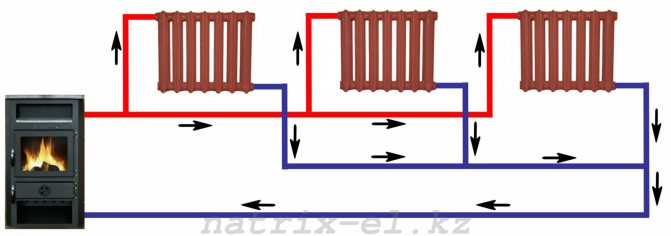
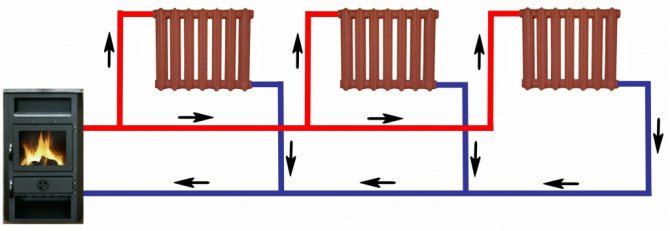
The simplest one-pipe scheme (barrack type, or Leningrad) is arranged as follows:
- A filling ring runs along the contour of the room.
- In parallel to it or by opening it, heating devices are mounted.
Minimum material consumption and maximum fault tolerance are undoubted advantages. The disadvantage is the large temperature spread between the first and last radiators. However, it is easy to level it with a different number of sections or throttling fittings on each radiator (of course, in this case, they should not break the main filling ring).
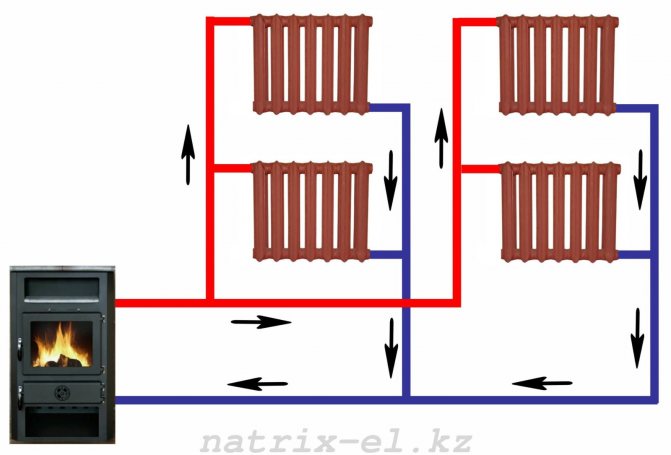
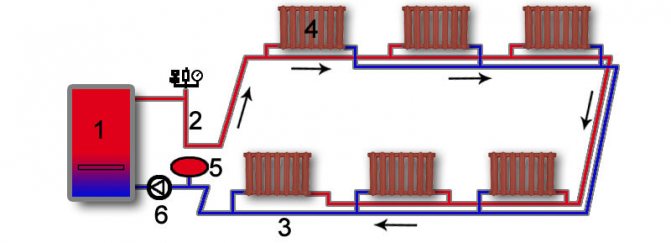
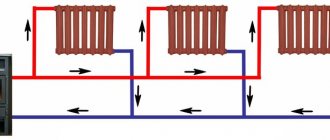
In the case of a two-pipe scheme, which is quite logical, we will need two fillings - supply and return. Each heater is a jumper between them. What is the result?
- No need for a continuous loop around the entire perimeter. You can, for example, not pipe around a door or panoramic window.
- The temperature of the heaters can be the same. In practice, however, there is a scatter.
- Balancing with chokes or thermal heads is MANDATORY.Otherwise, the situation is quite real when the entire mass of the coolant will move along a short circuit - through the nearby heating devices, and the distant part of the filling and batteries in cold weather will simply be defrosted.


Two-pipe scheme. A balancing throttle is required.
Horizontal and vertical routing
How these diagrams of water heating systems differ is easy to understand intuitively. For example, the notorious Leningrad woman is a typical horizontal scheme, but the heating riser in a modern five-story building is vertical.
In practice, however, it is much more common to see combined schemes that include horizontal and vertical routing sections:
- In the standing system in Soviet-built houses, in addition to risers, there are also horizontally located bottlings.
- In new buildings, an even more complex combination is used: the spouts are connected by vertical risers, from which horizontal wiring inside a single apartment is powered on each floor.
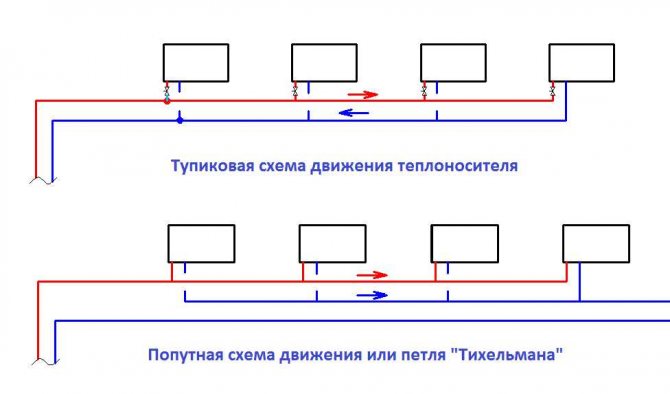
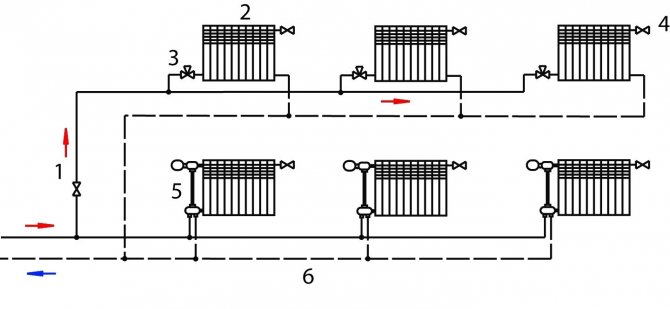
Dead-end and passing schemes
Dead-end water heating systems are two-pipe schemes in which the directions of water in the supply and return flows are opposite. The coolant gets to distant radiators and returns back. But if it continues to move towards the boiler or heating unit, keeping the same direction, our scheme becomes passing.
Note: a passing wiring diagram has very few advantages over a one-pipe wiring in the case of a one-story house. Only a slightly more uniform heating of the radiators speaks in its favor.
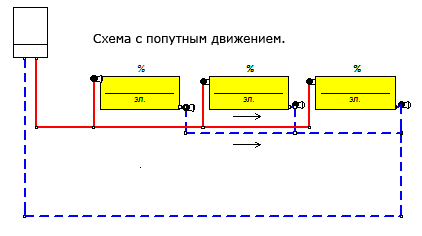

The simplest passing scheme.
Connecting heaters
Different types of connection can be used, above all, for sectional radiators of different types.
Convectors are supplied with connections, and the direction of circulation in them is determined by the manufacturer. What options are possible when connecting batteries?
- Lateral connection is most popular in city apartments. Lines enter two plugs on one side of the radiator. The main advantage of such a scheme is that the length of the connections leading from the riser is minimal. Disadvantages - uneven heating of the far and near sections and, much worse, the inevitable silting up of the end of the battery.
- Diagonal connection (the upper plug is on one side of the radiator and the lower one on the other) will make the radiator heat up as evenly as possible throughout the volume. Under the upper liner, however, the bottom of the sections will silt up in this case too. Periodic flushing will be required.
- Finally, bottom-down connection means both uniform heating along the entire length and absolutely clean sections. The price of this is an air pocket in the heating device: you will need to install a Mayevsky crane or, better, an automatic air vent.
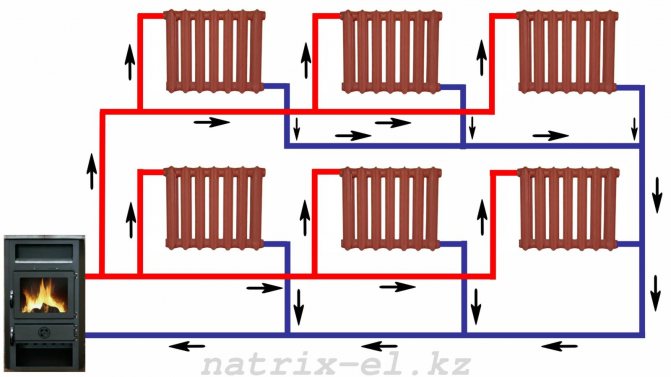
Forced circulation heating
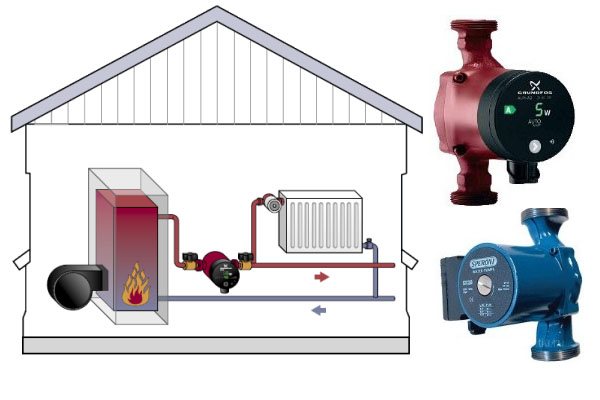

So, we see that systems with natural fluid circulation have a number of rather significant disadvantages. An alternative to them are systems with forced circulation, in which additional equipment is used to increase the supply of coolant in the system. Namely, a circulation pump.
Yes, this type of water heating at home will be more costly and difficult, but you get many advantages:
- The ability to heat a large room. We have already said that natural circulation is not good for large houses. If you are the owner of just this, then your option is only a forced circulation system.
- Complication of the system. By installing a pump, you do not depend on such an indicator as pressure. Therefore, what was an obstacle in a gravity system is not a problem in a forced system. So, for example, you can now increase the number of pipe bends if your home layout requires it.
- Use of smaller pipes. Agree, the neat appearance of the heating system is not the last indicator that you should pay attention to.
- Less dependence of heating quality on the presence of air in the system. With self-circulation, the ingress of air into the system would greatly complicate the transportation of the coolant through the pipes. The forced system solves this problem, but in the case of installing metal pipes, special expansion tanks with air deflectors and fuses should be used in order to avoid system corrosion.
- Possibility of using more durable and lightweight plastic pipes.
- Possibly concealed pipe installation. You can easily hide pipes in the screed and walls
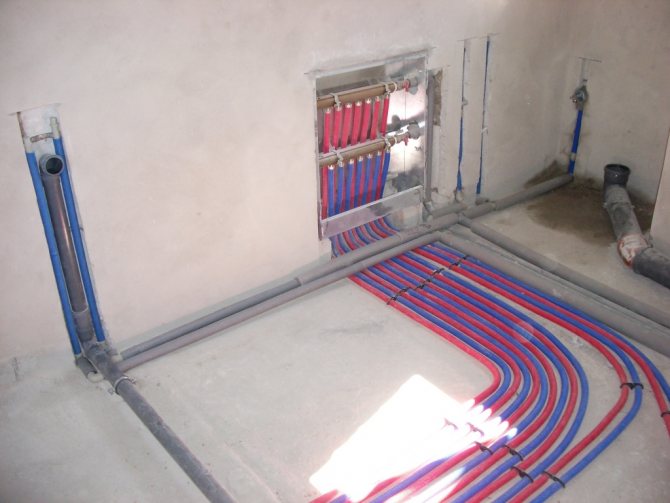
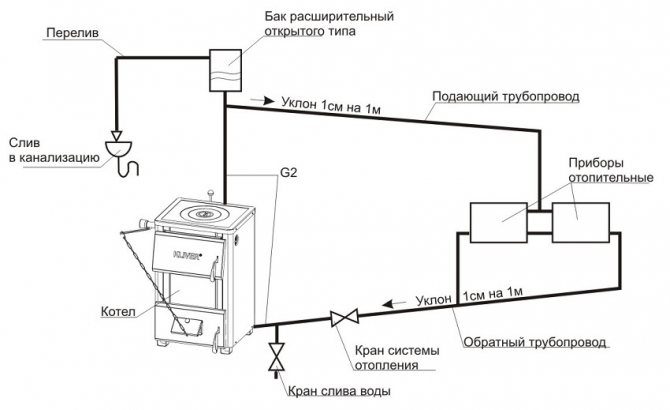
Installation diagram of water heating and its nuances
This process takes place thanks to the laws of physics and thermodynamics. Hot water has a lower volumetric weight than cold water, so it rises up and chilled liquid goes down.
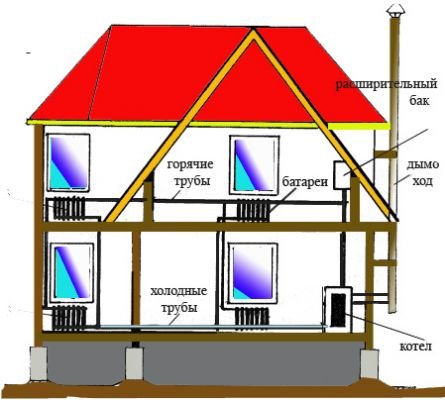

The scheme of water movement in the heating system of a private house. Click to enlarge.
Circulating in a closed system, water initially enters the main riser.
Then it goes from it to the hot pipeline, which is located in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floors of the house, enters the hot riser and then is fed to heating batteries or other heating devices.
Getting into the sections of radiator batteries, cooling down, the water transfers its thermal energy to the heated room, and compensates for its heat loss.
Having given up its heat, the water flows through the return branches into the return riser, and then into the return pipeline, which is laid in the basement, or it is installed in an underground channel.
Through this pipeline, the cooled liquid enters the boiler again, which heats it up again.
During the movement of the coolant in the heating system, insurmountable losses for friction and resistance arise, which must be overcome by the existing circulating pressure.
In order for heating devices, such as a radiator battery, to transfer the required amount of heat, the circulating pressure existing in the system must be equal to the loss during the passage of the calculated amount of coolant along the ring.
For this, a special hydraulic calculation of the heating system is used.
Piping in heating systems is made of gas-water seam pipes made of steel by welding. Risers and connections in heating systems are installed with an open or hidden gasket.
For a more convenient installation of the heating system in multi-storey buildings, pipe billets are used, which are pre-made at pipe procurement factories or special procurement workshops.
Adjustment of the heat output of heating devices installed in heated rooms, or their shutdown, is installed on the hot connection. With the help of special cranes with double adjustment, it is possible to:
- Primary adjustment. Performed during the initial setup of the system.
- Secondary adjustment. Produced directly during operation.
Types of water heating systems
Now let's look at the options for installing water heating. As in the case of the circulation method, we have a simpler and cheaper option, inferior in technical characteristics to the more complicated and costly one.
One-pipe heating systems
The first - simple and cheap - is a one-pipe water heating system at home, in which the liquid will pass sequentially through all pipes, radiators and other heating devices, if they are in the chain, and return to the boiler through the return pipe. This option is better suited, again, for a small room.
The disadvantage of such systems is the impossibility of their competent balancing. The first appliance is always hot, the last one is always warm.
Two-pipe heating systems
For rooms with a larger area, it is better to opt for a more advanced two-pipe system. In this case, the bottom connection of the radiators will be used. But such a heating gasket will become really perfect if you connect a circulation pump. Otherwise, it will be difficult to heat distant rooms.
In addition, it is possible to reduce the rate of liquid cooling in the system by installing special bypasses for each of the batteries, as well as regulators of the liquid supply to a separate radiator.
The difference between a two-pipe water heating system is the laying of a solid pipe to the furthest of the radiators, from which branching is made to intermediate heating devices. Thus, having passed through the entire heating system, the coolant returns to the boiler through a special return pipe, which makes it possible to evenly distribute heat transfer throughout the room.
Of course, the main disadvantage of such heating is its high cost and complexity of installation, but the comfort that you get in return is worth it.
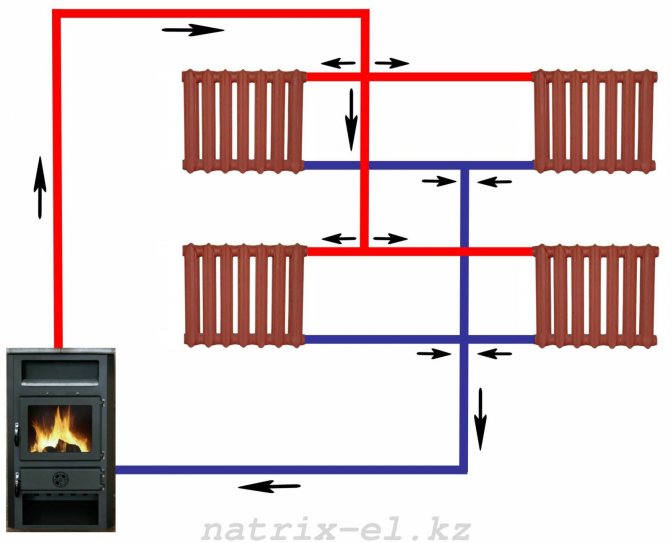
Radiant heating system
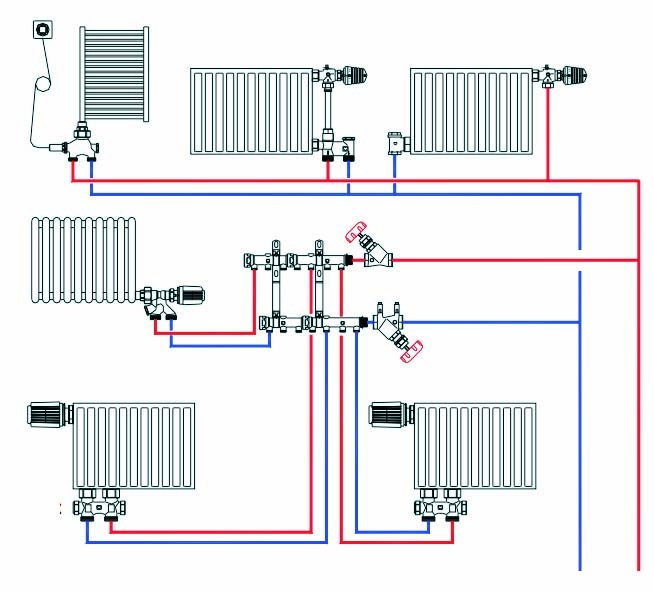

Radiation heating system diagram
The two above-described types of laying heating pipes are representatives of the perimeter method. But there is an alternative - ray. With such a laying, pipes are supplied separately to each radiator: one through which the coolant enters the heater, the other is the reverse. Such a system allows you to adjust a comfortable temperature regime in each of the premises of the house. In addition, if one of the radiators or pipes breaks down, there is no need to turn off all heating, it is enough to do this only in the desired area.
In view of the large number of pipes during the installation of the beam system, all communications are mounted directly into the floor or walls, which has a beneficial effect on the interior of the house.
It is most optimal to use the pump circulation of the coolant when radial laying.
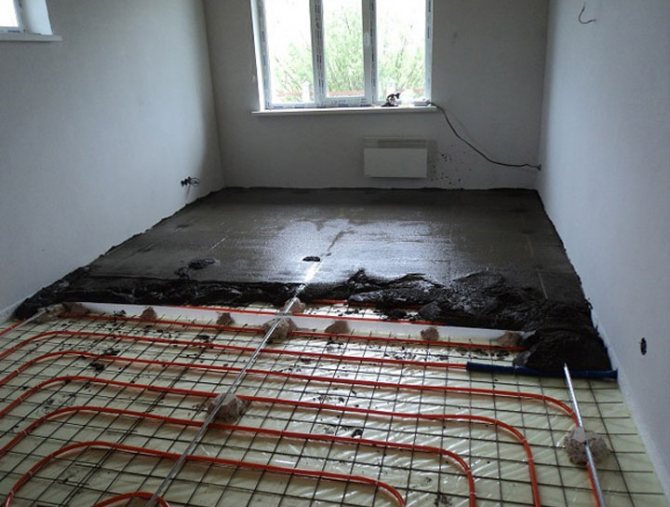
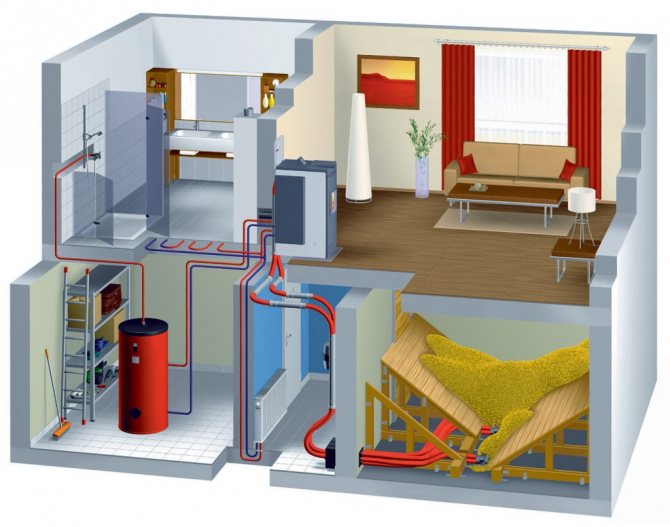
Underfloor heating


The most optimal way to evenly warm up the entire room is to lay water-heated floors in the house. It is possible to use only this system, and it is possible to combine it with other heating devices. For example, when radiators are installed in the rooms, and underfloor heating in the corridors, bathroom and toilet. That is, underfloor heating will be especially relevant for rooms with tiled or marble surfaces.
The use of the "warm floor" system is possible with forced circulation of the coolant.
Of the advantages that water heating gives with underfloor heating, one can single out:
- Uniform heating of the room. The screed, which gives off heat by radiation, gives it off in equal proportions in every square of the room.
- Rational distribution of heat. Heat moves from bottom to top.
- Comfort and microclimate.
- Lack of heating devices on the walls in most cases
How does a water heat-insulated floor work?
Structurally, all types of water heated floors used today are a system of pipelines laid inside the floor building structures. Through them, under the action of a pump, a coolant is pumped, the temperature of which is up to 40 ˚С. As a result, the concrete screed is constantly heated, which in turn gives up its heat to the flooring and to the air.


Among the features of the water floor, it is worth noting that both a centralized water supply system and an individual heating source can be used as an energy source in this case. As a result, a kind of modification of a heating device is formed in the room, emitting heat and heating the room using air convection.
The characteristics of a water-heated floor and its device allow using not only water, but also an anti-freeze liquid as a heat carrier.The second option is optimal for use, for example, in summer cottages, where in winter the house may not be heated for a long time. In addition, it is important to take into account when designing and implementing such systems that all types of warm water floors can be used both as the main and additional heating source in combination with radiators.
Heating pipes
Separately, you should consider the issue of the types of pipes used for heating private houses. Each material definitely has both positive and negative sides. Let's figure out which of the options is the most optimal.
Heating with metal pipes
Metal pipes include steel and copper pipes.
Wiring water heating of a steel house will cost you relatively inexpensively (and this is the main advantage of this material). This metal is quite versatile, suitable for both steam and water heating. Withstands great pressure. The main disadvantage of steel pipes is that they corrode quickly. This is reflected not so much in the quality of heating as in the appearance of your home - rusty pipes are not the best interior decoration.
Copper pipes have more advantages: they are extremely durable, keep temperature well, and do not corrode. Another advantage of copper pipes is the smoothness of their inner surface, which provides a high speed of movement of liquid through the heating system. The main disadvantage of copper is its high price.
It should be noted that both steel and copper pipes are only suitable for open heating systems and cannot be installed in walls or floors. Therefore, as we can see, their universality has a limit.
Heating a house with polypropylene pipes


The main advantage of polypropylene pipes is their resistance to external environmental factors: corrosion, decay, bacteria and chemical compounds.
Also one of the big advantages of this material is its lightness. Hence, other advantages follow: such pipes are easier to install, they are suitable both for use on the support wall and on the interior wall.
Heating made of polypropylene allows you to save fuel consumption (gas or electricity) used to heat the boiler due to the low coefficient of friction, since the coolant easily passes through the heating system. But the difference is insignificant.
In addition, polypropylene pipes are quite plastic, have different modifications with many joints, and are also supplemented by a huge selection of various components, which allows the installation of complex heating systems.
And finally, heating with polypropylene pipes can be done both in open and closed systems, when all pipes are hidden in the floor or walls.
With all the visible pluses, these pipes have minuses. Firstly, with a fairly high resistance to chemical attack, such pipes are easily amenable to mechanical action (you can cut it with an ordinary kitchen knife). Secondly, polypropylene is not suitable for all types of heating systems. It categorically cannot be used in combination with a steam generator, but they are excellent for the water heating we are considering. Also, water heating with polypropylene implies the presence of a large number of joints, which greatly affects the reliability of the system.
Heating with metal-plastic pipes


If we talk about the advantages of metal-plastic pipes, then we can highlight the same advantages as those of polypropylene counterparts. But it is worth highlighting that they are able to keep a higher temperature. And also, and this is their main distinguishing feature, metal-plastic bends perfectly. At the same time, you can not be afraid of damaging it. And this fact makes this type of pipes an ideal option for the "warm floor" system.
Among the disadvantages is a higher price in comparison with polypropylene analogues.
Technical capabilities and advantages of hot water heating
The device of a heating system using underfloor heating technology is never (even in its simplest version) limited to a working pipeline. In this case, each of the used components of the "pie" is important from the base to the topcoat.
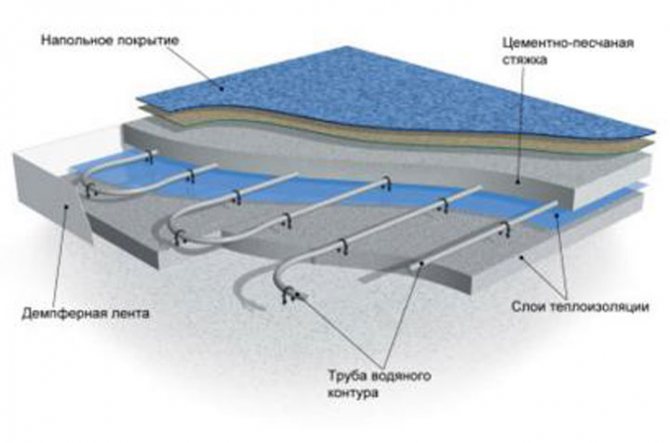

The technology for laying water lines can be radically different depending on its design. The basis can be both a concrete screed and dry structures (prefabricated screeds, frame structures are used with high efficiency). But it is worth noting that the second option is practically not used in practice, since it differs in the complexity of its device with lower operational characteristics of a water-heated floor.
The optimal screed thickness is determined based on the balance of the strength of the resulting structure and the rate of heating of the slab. In this case, the recommended thickness is 5 cm. If there is a likelihood of subsidence, a metal reinforcing mesh is used, but with the installation of rigid insulation, this need disappears.
Heating with water skirting board
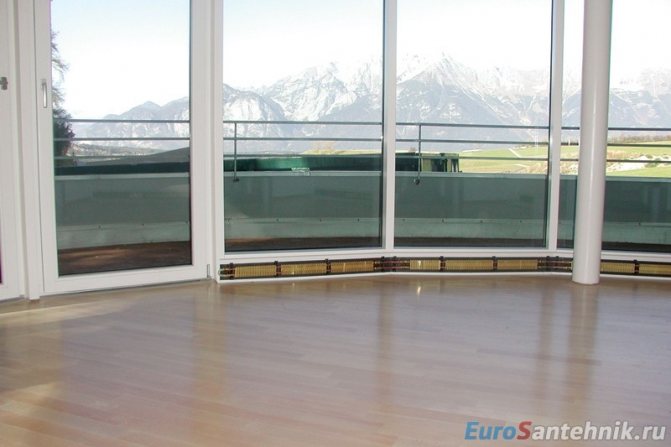


At the end of our article, we want to tell you about the "last word" in the field of water heating systems. If you want to make the heat in your home invisible in the truest sense of the word, then skirting board heating is your option.
Such a heating device is a body that looks like a regular plinth, inside which there is a heating element - special tubes. First they heat up, then the body, then the heat is distributed along the walls.
This type of heating is an ideal solution for our strip, where mold often forms on the walls due to dampness. In addition, as already mentioned, neither pipes nor radiators will spoil your interior.
But this system also has its drawbacks:
- it cannot be used on the walls along which the furniture is installed
- for large rooms, it will be necessary to install 2-3 buildings, since the maximum length of the heating circuit is 15 meters.
Heating with water convectors
You probably managed to collide with electric convectors. There are the same, only water. They are connected in water heating according to the same rules as radiators. And they are essentially the same radiators, only with a different principle of heat transfer.
Water convectors work according to the convection principle. Cold air comes in from below, warm air comes out from above. Due to this, the room heats up very quickly.
The disadvantages of such water heating devices include their high cost, compared to conventional radiators.
If you carefully studied our article, you saw what a variety of solutions for conducting water heating in a private house the modern market of heating equipment is represented. You just have to choose the best option based on the parameters of your own home and material capabilities. Peace and warmth to your home!