What is Propylene Glycol
This substance is directly related to the class of dihydric alcohols. The reagent is a liquid substance with a subtle smell and taste. In industry, it is obtained in the process of hydration of propylene oxide at a pressure of 16 megapascals and a temperature regime in the range of 160-200 degrees.
The chemical formula of propylene glycol is C3H6 (OH) 2. It is completely safe to use, as it does not contain toxic elements. For heating systems, aqueous solutions are used, which are based on this reagent.
Propylene glycol has a related composition with ethylene glycol - C2H4 (OH) 2. But the last element is not used for heating residential buildings, as it has a fairly high level of toxicity. Moreover, the chemical formula of both substances has a certain similarity.
Propylene glycol technical
Propylene glycol is a colorless viscous liquid with a weak characteristic odor, sweetish taste, and hygroscopic properties. Propylene glycol, unlike ethylene glycol, is practically non-toxic, not dangerous if inhaled or accidentally ingested.
Propylene glycol has preservative, sterilizing and bactericidal properties.
Propylene glycol is a good solvent for various classes of compounds, and most of low molecular weight organic compounds containing oxygen and nitrogen are completely miscible with it: monohydric alcohols, ethylene and propylene glycols and their esters, acids, aldehydes, ketones, esters, amines and other nitrogen-containing compounds.
OOO NPP Spetsavia accepts orders for the manufacture of propylene glycol, its packaging and shipment to the consumer. Detailed information can be found in the "Services" section. The production capacity of the enterprise at maximum load allows producing up to 200 tons of product per day.
Specifications
The density of propylene glycol is lower than that of ethylene glycol and glycerin, but higher than that of ethanol. The viscosity of propylene glycol is higher than that of ethylene glycol and monohydric alcohols, especially at low temperatures.
Comparative characteristics of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
| Indicator | Ethylene glycol | Propylene glycol | Comments (1) |
| Flammability | low | low | |
| Caused degree of skin irritation | low | low | |
| Viscosity | low | higher than ethylene glycol | Propylene glycol causes a large pressure loss in systems. |
| Carcinogenicity | not | not | |
| Biodegradation susceptibility | collapses in 10 - 30 days | takes 20 - 30 days for destruction | |
| Freezing point shift when diluted with water | more efficient | less efficient | A high concentration of propylene glycol is required to achieve the same freezing point as ethylene glycol. |
| Toxicity | High toxicity when ingested | The toxicity level is lower | |
| Chemical oxygen demand | low | higher than ethylene glycol | |
| Heat transfer efficiency | worse than propylene glycol | better than ethylene glycol | Ethylene glycol cannot transfer the same amount of heat as propylene glycol, so more ethylene glycol must circulate in the system to transfer the same amount of energy at the same temperature. |
Application
Low-freezing heat transfer fluids based on an aqueous solution of propylene glycol are widely used in various industries as antifreezes, including in heating, ventilation, air conditioning systems for residential buildings and public buildings, in refrigeration systems for food production, as well as in other heat exchange equipment in the temperature range from -40 ° C to +108 ° C.
The corrosive activity of propylene glycol is lower than that of most known aqueous solutions of salts and alcohols.This circumstance makes it possible to present low requirements for the grade of steel for the equipment, which has a positive effect on its cost.
In the food industry, propylene glycol can act as a food additive (water-retaining, emollient and dispersing agent), it is used in the production of e-cigarette liquids, as well as in small quantities in the production of cosmetics.
Propylene glycol can be one of the components in the process of obtaining drugs. In addition, it is used for the lubrication and preservation of food packaging machines, and is used as a plasticizer in the production of cellophane and PVC films.
Documentation
There is the following set of properly executed permits for propylene glycol:
- TU 6-09-2434-81 "Propylene glycol"
Technical propylene glycol is widely used as a non-freezing environmentally friendly working fluid circulating in the circuits of various heat exchange systems for household and industrial purposes.
As a heat carrier, propylene glycol has excellent performance characteristics, and the price of this product manufactured by NPP Spetsavia LLC is in the range of market expectations of most consumers.
By its nature, propylene glycol is a unique chemical compound that makes it possible to expand in practice a whole range of consumer properties of special technical non-freezing (cooling) liquids due to the presence of the following qualities:
- excellent solubility in water in almost any percentage ratio;
- influence on the freezing point of aqueous solutions, depending on their concentration (volume percentage) in them;
- good hygroscopicity, i.e. the ability to absorb moisture, facilitating dehumidification processes;
- the ability to dissolve both hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds.
In the event that a consumer needs to buy propylene glycol as a coolant, he should definitely pay attention to the presence of anti-corrosion and antifoam additives in its composition, since in their absence this coolant can have a negative effect on all metal surfaces with which it will come into contact.
Heat transfer fluids based on propylene glycol with a package of specially selected additives provide stable protection of heat exchange circuits against corrosion and build-up processes for a long time, which, in turn, is directly related to the saving of material and financial resources planned for potential repairs and forced maintenance. ...
A potential buyer should take into account that propylene glycol coolant is made on the basis of raw materials with low toxicity indicators, therefore the selling price for this product differs from the ethylene glycol based coolant.
By purchasing propylene glycol coolant, the price of which, in addition, significantly depends on the volume of purchase, packaging and other technical parameters, the buyer can confidently operate it in heat exchange systems with increased requirements for environmental safety criteria.
You can buy propylene glycol or find out the price of propylene glycol, get detailed information about this product, clarify the terms of cooperation, place an order or choose an acceptable method of feedback in the "Contacts" section.
Main characteristics
Propylene glycol is a hygroscopic substance that is soluble in water, acetone, ethanol, chloroform and diethyl alcohol.Such a colorless liquid containing a carbon atom has a low degree of volatility. It is non-corrosive and completely safe to use.
Among the characteristics of propylene glycol are:
- density - 1037 kg / m³, which is almost 4 percent more than that of water;
- a fairly high boiling point - 188 degrees above zero;
- thermal conductivity - 0.218 W / (m * K);
- the beginning of crystallization - at -60 degrees;
- specific capacity value - 2483 J / (kg * K).

What propylene glycol looks like
The propylene glycol coolant is an aqueous solution that remains liquid at temperatures ranging from -40 to 100 degrees. The finished substance, in addition to the main component dissolved in distilled water, includes dyes, as well as no more than 5 percent of anti-corrosion, stabilizing, softening additives.
The density of the propylene glycol heating medium depends on the concentration of the main component. The higher its percentage, the higher its maximum boiling point. The density index also increases accordingly. Based on this, percentage markings are indicated on the coolants produced.
Propylene glycol properties
Today propylene glycol is one of the most popular types of heat transfer fluids due to its safety and non-toxicity. It is a viscous colorless liquid with a characteristic odor and a sweet taste. It is widely used in the cosmetic, food industry and other sectors of the national economy.
Its solution is able to withstand temperatures from -40 to +100 ° C, and pure propylene glycol works in the range from -60 to +187 ° C. The composition of the substance contains about 5% carboxylate additives, which protect metals from corrosion, cavitation, and increase the service life of the coolant. In addition to carboxylate additives, propylene glycol fluids contain anti-corrosion, stabilizing, anti-scale and other types of additives.
It should be remembered that propylene glycol and its solutions cannot be used in systems where zinc elements are present. But to materials such as plastic, rubber, textiles, etc. such fluids are not corrosive.
One of the important properties of propylene glycol is density. The higher its concentration in the solution, the higher the density of the coolant and the wider the range of operating temperatures in which it will work.
This value can be from 30 to 55%. Sometimes this information is indicated in the name of the liquid: propylene glycol 30, propylene glycol 40, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
Propylene glycol is one of the most demanded ready-made heat carriers for heating systems. Its main function is to protect the heating equipment from ruptures, which occurs due to the ability to practically not change its volume at low temperatures. Therefore, in severe frosts when using it, there is no need to drain the system.
The advantages of using a propylene glycol-based coolant include:
- Safety and environmental friendliness. The substance does not contain components of increased toxicity. The reagent does not have a negative effect when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of the eyes. Its vapors are harmless enough. When the floor finishing material hits the surface, any chemical reactions are excluded.
- Lack of corrosive activity. This property allows the use of this coolant for heating systems with various structural materials.
- High level of thermophysical characteristics. The use of an aqueous solution of propylene glycol for heating circuits promotes rapid and uniform heating of the room. In this case, the heat is retained for a long time.
- Lack of limescale. When heated to high temperatures, this antifreeze does not form any hard deposits.At the same time, propylene glycol has bactericidal and cleaning properties. With its help, various deposits are removed on the internal sections of heating equipment.
The ready-made propylene glycol solution is completely fireproof and its use excludes the possibility of an explosion.
This coolant also has some negative operating points:
- High rate of fluidity. Propylene glycol is able to penetrate the smallest crevices. Its fluidity is slightly higher from water, so sometimes leaks occur in places where they should not be. But this property at the same time can be attributed to the positive aspects, since it allows to improve the assembly quality of the heat-conducting structure.
- The possibility of using propylene glycol coolant in the presence of parts containing zinc is excluded. If you do not follow this precaution, then the viscous antifreeze will eventually flake off the zinc, which will lead to blockage of the pipeline.
Also, sometimes the high cost of propylene glycol-based antifreeze is attributed to the negative sides. At the same time, it must be replaced in the heating system at least after five seasons.
Concentration of glycols in antifreeze.
The concentration of glycols in antifreeze solutions should be determined taking into account the minimum expected winter temperature for a given area. It is necessary to take into account all factors in order to provide the required protection against freezing, but at the same time to avoid oversaturation of the solution, as this will lead to an unjustified increase in cost and a decrease in the efficiency of the system.
Typically solutions are prepared with a glycol concentration by volume of 20 to 50%. On average, if there is enough free space for the expansion of the coolant and the concentration of the solution up to 50%, sufficient protection against rupture of pipes in the system is provided. Solutions with a glycol concentration of more than 50% are already less energy efficient and less profitable.
The table below shows the freezing point of the glycol solution depending on its concentration:
Table 1. Freezing temperature
Concentration Ethylene Glycol Propylene Glycol
55% -45C -40C 50% -38C -33C 40% -26C -25C 30% -17C -15C 20% -10C -8C
Please note that the table shows averaged data. The exact concentration of the solution must be calculated by a specialist. At the moment, a large number of antifreezes for heating systems are already on the market, already pre-diluted in the required concentration and do not require adding water. Therefore, most likely you will need the help of a specialist just to buy a ready-made coolant of a certain brand and concentration.
Scope of application
Propylene glycol is in high demand in modern industry. Heat carriers made on its basis are widely used not only for heating systems, but also as antifreeze for ventilation and air conditioning equipment.
The safety of the substance allows it to be used for residential and public buildings. At the same time, antifreeze can be poured into structures made of various materials, including rubber, aluminum, steel, copper or cast iron. An exception is galvanized coating.
The field of application in the industry of propylene glycol is quite extensive:
- pharmaceuticals;
- tobacco production;
- food production;
- automotive and aviation industry;
- Oil and gas industry;
- cosmetology, perfumery;
- medicine.
Propylene glycol uses include livestock and agriculture. It is used to improve the quality of feed, as well as to extend the shelf life of vegetable crops. In the chemical industry, a viscous substance is used in the manufacture of polyurethanes, paint solvents, plastics or polymers.
Criterias of choice
The main point that should be considered when choosing a coolant for space heating systems is the manufacturer's recommendation for heating equipment. The instructions for the boiler often indicate the requirements for the liquid with which the water circuit is filled, and sometimes the brand of antifreeze.
The main factors to consider when choosing a propylene glycol solution for heating systems are:
- Climatic conditions of use. The maximum freezing point is indicated on various brands of the product. This indicator depends on the concentration of the solution, the percentage of which is also indicated in the name of the coolant.
- Manufacturer. The efficiency of the heating system depends on the quality of antifreeze. You can buy good products from trusted manufacturers. Quality products do not contain toxic substances and are completely safe to use.
- Characteristics of additives. Propylene glycol-based products in ready-to-use heat transfer fluids can have anti-corrosion properties while providing protection against metal degradation. Softening components are often added to the composition, which protect the rubber elements from deformation. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze, technical and design features of heating equipment are taken into account.


When choosing a propylene glycol-based heat transfer fluid, take into account the characteristics of the additives
Antifreeze with carboxylate type additives is especially popular. Such a coolant can be used for almost any material included in the design of a thermal device.
Propylene glycol intended for heating systems must meet all technical requirements and comply with the characteristics of the heating equipment used.
Features of use for heating
The propylene glycol coolant is poured into the system in accordance with the technical parameters. Before using antifreeze, a number of preparatory steps should be taken:
- drain the liquid from the system, flush all circuits with caustic soda, remove all deposits and rust;
- seal all connections, including tie-ins and bends;
- remove and replace all zinc-containing parts.
The system can then be filled with a propylene glycol solution. At the same time, it is recommended to keep the trigger valve open at the lowest point. This action will allow you to immediately see when the heat loops are completely filled. After filling, the system is checked for leaks and a test run of the heating equipment is carried out.
Operating moments
Ready-made propylene glycol solution for heating devices has a lower thermal conductivity and heat capacity than water. Therefore, when using a substance, it is often necessary to add the amount of batteries in the room. Replacement of heating equipment may also be required.
In order to productively use polypropylene-based antifreeze for a heating system, some operational recommendations should be taken into account:
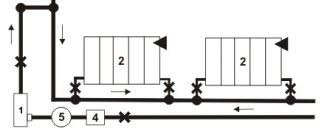
- due to the high viscosity of this coolant, it is necessary to install a pipeline with a diameter of at least 25 millimeters, and also select a sufficiently powerful circulating pump;
- for metal pipes, antifreeze with additives that prevent corrosion should be used;
- use an aerometer annually to check the concentration of the main reagent;
- use an expansion tank of at least 10 liters;
- to provide free access to all connections of heating equipment in case of elimination of leaks;
- replace the propylene glycol coolant every five operating seasons;
- use and regularly monitor heating dirt traps.
- when replacing antifreeze, completely flush the heating equipment.


Change the propylene glycol-based coolant every 5 seasons
If it is necessary to mix this coolant, it must be borne in mind that the solution combines well with a liquid based on glycerin, propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. In this case, the type of additive included in the composition is taken into account, since an incorrect combination of different additives can cause a decrease in the technical characteristics of antifreeze.
Due to its many advantages, propylene glycol is considered one of the best heat transfer fluids for heating equipment. But in order to ensure an effective working process of the heating system for several years in a row, all technical and operational requirements should be observed when using it.
System requirements
Before filling your heating system with antifreeze, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the following requirements for systems operating on glycol heat carriers.
- It is necessary to increase the pump power. Since glycols are more viscous than water, in order to maintain the same heat transfer efficiency, it is necessary to increase the circulation rate of the coolant in the system, which means increase the power of the circulation pump.
- It is necessary to enlarge the expansion tank. The expansion tank for water is selected to a certain size, depending on the volume of water in the system. If antifreeze is used, the volume of the expansion tank must be increased by 1.2 times. Thus, when freezing, expanding, the coolant will be able to fill this additional volume without damaging the pipes.
- Glycol based antifreezes cannot be used on galvanized pipe systems. Zinc can react with glycol to form a precipitate.
- Before pouring antifreeze, a preliminary flush of the system is required.
- Do not use glycol antifreezes in systems where the temperature of the coolant may exceed 140C. Usually these are systems with solid fuel boilers.
- Do not block part of the system, as the coolant will have an obstacle to expansion during cooling, which may result in burst pipes. In other words, you cannot turn off, for example, the second floor or batteries in one of the rooms.
- Do not install or simply disable the make-up valve to prevent the system from automatically filling with water. Otherwise, the antifreeze will be diluted with water, as a result of which it will lose its anti-freezing and anti-corrosion properties.
If you have any questions or need advice from our specialist on the choice of a coolant, call us and we will be happy to help you.