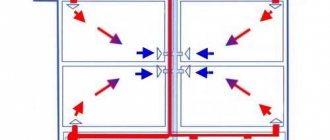
Installation of an expansion tank in an open and closed heating system

In modern heating systems, to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant, expansion tanks of open or closed type are installed, which have special requirements for installation, operating conditions and have various advantages and disadvantages.
In this article, we will consider the main points of choosing and installing an expansion tank in a heating system with forced and natural circulation of the coolant.
The main parameter of the tank is its useful volume, which must exceed the change in the volume of the system liquid as a result of the maximum change in its temperature.
The volume of liquid in the heating system is not constant, since during operation the coolant can expand and contract. Heating the coolant, and, accordingly, an increase in its volume with a constant size of the internal space of the heating system leads to an increase in pressure on the walls of pipelines and heating equipment, which can cause their destruction.
To compensate for the change in fluid volume and stabilize the pressure on the inner walls of the heating system components, an expansion tank (also known as an expansomat, from the English verb “expanse”, which means “to expand”) is introduced into its circuit. When the coolant expands, its amount, which exceeds the volume of the internal space of the system, enters the expander, and after the temperature drops, it returns back.
All about plumbing
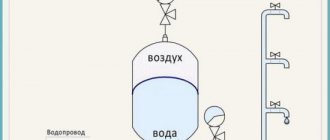
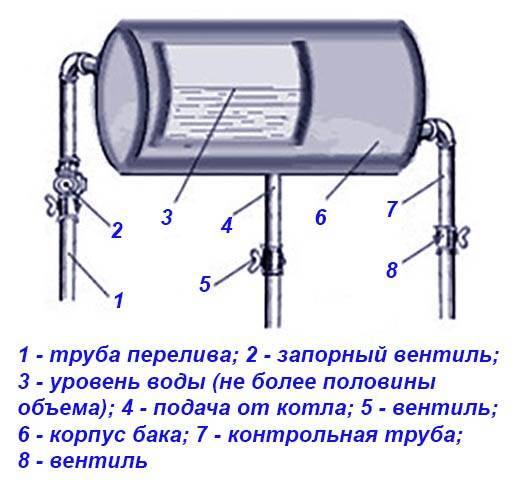
In the systems of individual heating, earlier, mainly, expansion tanks with free overflow of liquid, or open type, were used. They are easy to manufacture and not difficult to construct. Usually, this is a rectangular tank with an open top, or with a closed one. In such a tank, at least two tubes are welded: one for entering the expandable liquid from the heating system into the vessel (located in the lower part of the tank), the second tube serves to enter and remove air, and, if necessary, to discharge excess liquid from the heating system. The second tube is located in the upper part of the tank for excess heated liquid, open type. It also (the upper tube) acts as a "control" of the filling of the heating system, when it is energized, or after energizing.
At the present time, expansion tanks of a closed type are more widespread. Tanks of this type are designed to work under a certain pressure. There is an article on the device of the expansion tank on this site, if you wish, you can familiarize yourself with it. A closed-type tank consists of a container with a rubber membrane or "pear", and a certain air pressure is pumped into it (usually, the factory pressure is 1.5 Bar).
Watch a video demonstrating how the expander works.
But, since the speech in this article is not about their design, but about the principle of action and the calculation of the required volume, we will move on to these concepts. To determine the working volume of the expansion tank, both open and closed, we need some initial data. The article provides an example of calculation for a heating system filled with water. If you have something else, then these calculations will not work.
We need the following data:
- Heating system temperature range
- The volume of liquid in the system
- Water Expansion Coefficient Data
- Static expansion tank height
- Tank volume safety factor (equal to 1.25%)
Let's start calculating.First, it is necessary to determine the expansion coefficient of the water in the heating system. To do this, we need such a table, with the calculated expansion data, for specific temperature ranges.
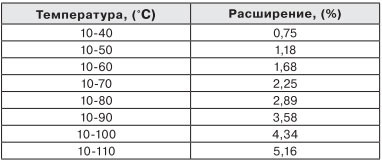

A range from 10 to 90 degrees Celsius is suitable for us, the expansion coefficient for these temperatures is 3.58%.
The volume of fluid in the system is taken as 150 liters (Vsis = 150 liters).
Since the factory pressure inside the expansion tank is equal to 1.5 Bar, we will take it as the preliminary pressure of the expander - Pmin. The maximum working pressure Pmax is taken as 3 Bar (in the example we use the most suitable figures for real projects, suitable for 1 - 2-storey buildings or apartments).
So: The volume of the expandable fluid is Vex = 150 liters. X 3.58% / 100% = 5.37 liters.
Stock volume: 150 X 1.25% / 100% = 1.875 liter.
Total: V = 5.37 + 1.875 = 7.245 liter.
Please note that we have taken the tank volume safety factor, for simplicity, as 1.25%. It can be calculated personally using the formula: Pmax- Pmin / Pmax (our data: 3 - 1.5 / 3 = 0.5%)
The most suitable and reasonable, in our case, is an expansion tank with a volume of 8 liters.
These calculations are also suitable for determining an open-type expansion tank. Visit us again!
All the best.
Specialist recommendations


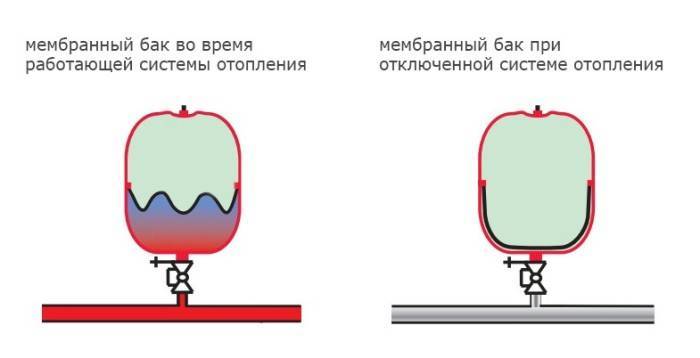
The closed expansion vessel does not need to be installed at the highest point in the system.
The main advantage of membrane expansion joints lies precisely in the possibility of its placement in a place most convenient for installation and operation.
Small tanks with a volume of 20-25 liters are usually installed in systems with a circulation pump, whose power is 1.2 kW. Increasing the capacity to 20-60 liters will increase the pump power to 2.0 kW.
Compensating devices with a volume of 100-200 liters are on sale. In addition to their direct purpose, they can play the role of a storage tank for warm water. True, they can be used in this way only if the main source of hot water supply is turned off for a short time.
Sizes of expansion tanks cover a fairly wide range. Among them, there are models with dimensions so large that standard doorways do not allow them to be brought into the room. In such a situation, it is better to replace one huge container with several small ones. The main thing is that their total volume is equal to the calculated one.
Installation work
Strict adherence to the installation rules when equipped with an open or closed heating system expander will ensure the safety and efficiency of the equipment.
Installation of an open-type expansion tank
It has already been said above that the expansion vessel for an open system is mounted at the highest point. This requirement is due to two factors:
- The rise of the coolant into the expander and its draining back into the heating system should be carried out by gravity, because there is usually no circulation pump in such systems.
- Such an arrangement of the expansion tank makes it possible to effectively carry out its additional function - air removal. Bubbles always rise to the top.
Connection diagram of a membrane tank in an open-type heating system
A feature of installing the expander in an open system is that there is no need to equip the tank with shut-off valves. As a rule, the tank is supplied with only two nozzles, through one of which the coolant enters the tank, and through the other it returns to the system. Even the presence of a cover at the tank is not essential, although its absence can lead to an increase in the loss of water volume from evaporation, as well as the ingress of debris and dust into the system.
Closed tank installation
The installation of an expansion tank for heating in closed-type systems is somewhat more difficult, since it is a completely sealed device. Unlike open expanders, which are often made by users on their own, such units are created only at the factory, so you will have to buy an expansion tank for the heating system if you have it of this type.
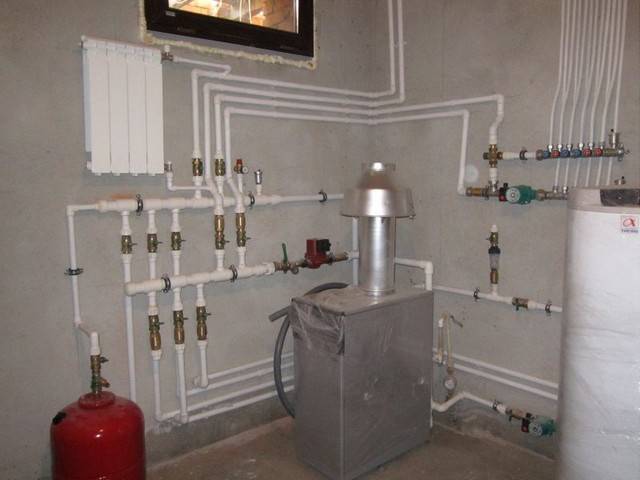
In the photo, an expander in a closed heating system
There are several rules, following which you can install the heating expansion tank competently.
- In most cases, expanders of closed systems are installed on the return line in front of the circulation pump, if we consider the sequence of elements in the direction of movement of the coolant. If for any reason such an installation is not possible, a section is selected where the flow parameters are close to laminar flow. The main and mandatory requirement is the horizontal location and straightness of the piping section.
- The best option would be to purchase and install a tank with a safety valve. This accessory is designed to relieve pressure if the pressure exceeds the maximum allowable value. Thus, the safety of the equipment operation increases, however, you should be aware that if there is an error in the calculations (downward) of the volume of the expansion tank, the safety valve will work too often. The solution to the problem may be to replace the expander with a more capacious one or install an additional tank in parallel.
- For the convenience of monitoring the operation of the system, it is best to equip the expansion tank with a pressure gauge during installation.
Possible problems
First, let's look at the consequences of incorrectly calculating the expansion tank for a closed heating system. Perhaps you also have an unusable reservoir for your system, and you do not even know about it. If the volume of the tank has been calculated correctly, there will always be a stable pressure in the circuit. It doesn't matter if your system is open or closed, the calculation of the volume of the expansion tank for heating both types is similar, since the principle of their operation is approximately the same. The bottom line is that the water in the pipes acts as a heat carrier.
That is, it carries heat around the entire circuit and gives it away through radiators and pipe walls. Thanks to this, the room becomes warm. In this case, the amount of water always changes. After it heats up, there is more of it, and after it cools down - less. It is impossible to squeeze water mechanically, which means that you need to temporarily remove its excess from the circuit. And it is necessary in such quantities that the pressure in the system is always kept at the required level, without drops. So we come to the main thing - these are pressure drops.
If pressure drops occur in the circuit, these are the first bells of malfunction. This may be due to the incorrectly calculated volume of the expansion tank for the heating system.
Useful Tips
It should be remembered that the installation of an expansion tank in the heating system involves the selection, purchase and installation of a model with a red housing. The blue painted models are designed for cold water applications. Structurally, the expanders do not differ from each other, but the red ones are designed for long-term high-temperature exposure. Despite the generally accepted practice of using a circulation pump only for closed systems, the presence of a pumping unit does not change the state of the system. That is, if you put a circulation pump on the heating with an open tank, it will not become closed. It's just that in open systems, there is often no need for such units. The boiling of the coolant in the heating system has nothing to do with the expander operation
Most likely, you should revise the slope of the horizontal pipelines and the diameters of the pipes used. It is not recommended to install the expander in the immediate vicinity of the pump due to the possible pressure drop. When installing, use only special heat-resistant sealants.When installing the expander, take into account the need for maintenance and possible repairs and provide free access to the unit. Some boiler models are already equipped with expansion tanks and then you will not need to buy it additionally.
Open tanks
These tanks are used for an open heating system (otherwise - gravitational, gravity) and represent a metal tank with an open top of arbitrary shape. A branch pipe is welded to the upper part of the side wall for connecting a hose or overflow pipe, the coolant is supplied to the tank from below. The element is installed above the entire system on the supply pipe, usually in the attic of the house.


Any expansion tank for open-type heating performs 2 functions:
- serves to compensate for the expansion of the coolant;
- removes air from the system, since its top communicates with the atmosphere.
This is its advantage, but it is not the only one. An open container can also serve successfully and for a long time in systems with forced circulation, since the design of the tank is very simple, there is nothing to break there. However, it also has a lot of shortcomings:
- a tank installed in the attic requires good insulation;
- during the season, it is necessary to constantly monitor the water level in the tank and replenish it in a timely manner;
- the coolant is constantly saturated with oxygen from the atmosphere, which makes the metal parts of the boiler corrode faster;
- additional consumption of materials and complexity during installation.
Bath water tank: purpose and advantages
As already mentioned, the container is used to heat water, which is subsequently used for bathing and various household needs: washing, washing floors, preparing a broom, etc.
The water in the tank increases the humidity in the room, which is especially beneficial and helps to avoid the problem of dry air.
Of course, today there is a huge selection of gas and electric water heaters, but at the same time, bath tanks do not lose their relevance. This is due to their economy: when using a boiler, gas / electricity is spent, but when the water is heated by a stove for a bath, there is, in fact, no consumption at all, because in any case, in order to go to steam, you need to heat the stove. Also, the tank will be irreplaceable in the event that an accident occurs on the gas main or power line, and the use of the water heater becomes temporarily impossible.
Types of expansion tanks
As you know, for heating private housing, different principles of coolant supply can be applied - natural and forced circulation. For each type of system, its own modifications of the expansion tank are used:
- Open. In infrastructure with natural circulation, the additional tank is installed at the highest point and is in the form of an open tank. The pressure in the pipes is equal to atmospheric, and air bubbles are removed through the tank and, if necessary, water is topped up.
- Closed. If a pump is installed in the heating main to circulate the coolant, a sealed metal cylinder with compressed air acts as an expansion tank. Excess coolant is supplied to the tank when heated, and when the temperature drops, the air pressure displaces the liquid back.
A closed expansion tank offers significant advantages over an open one. Its installation can be carried out in any convenient place, the absence of contact with the atmosphere protects the inner space of pipes and radiators from corrosion and penetration of dirt and small debris. However, the final decision on the choice of the type of expansion tank is usually dictated by the implementation scheme of the heating system as a whole, and not by these important, but not decisive advantages.
Installation
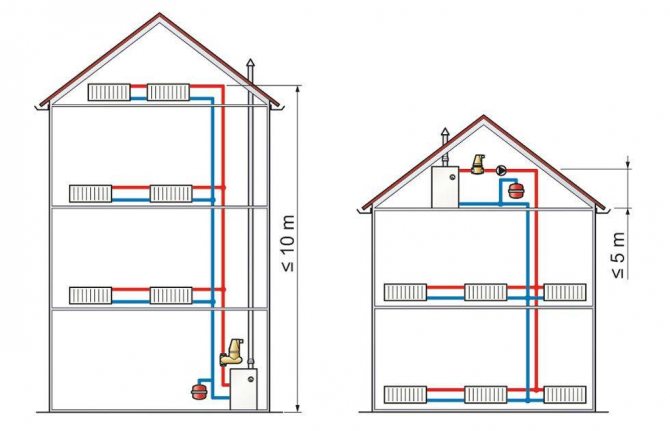

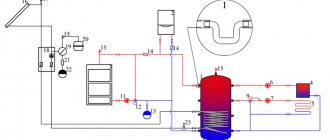
Installation diagram of a tank in a private house system
If you are confident in the calculations and your own strength, the tank and all the materials have been purchased, then you can install the container yourself.
From the tools you will need:
- Step and adjustable wrenches;
- Soldering device for plastic pipes;
- Plastic pipe wrench;
- In some cases, you need a welding machine and angle grinder.
Before installation, you need to de-energize the boiler, close the valves and drain the coolant, if it is already in the pipes.
Installation is carried out taking into account some rules.
- The tank must be assembled and installed so that it can be easily approached for adjustment and maintenance.
- The room temperature should not be below 0.
- A shut-off valve must be installed on the inlet pipe, which will allow the expander to be removed for maintenance and repair.
After installing the tank, you need to start the entire heating system. If boiling is detected in it, then the reason lies in the incorrectly selected pipe diameter. It's not about the tank; the installation of the expansion tank is described in the following video:
Volume calculation
You can calculate the volume of the tank yourself using several online calculators, or by
a fairly simple formula:
Vtank = (Vsystem * k) / (1-Pmin / Rmax), where
Vtank - tank volume;
Vsist - the total volume of the heating system, including all radiators, underfloor heating, boiler, etc .;
k is the coefficient of expansion of the liquid, for water its values depending on heating from 10о to the maximum temperature of the coolant are shown in the table below;
Pmin - initial pressure in the tank;
Pmax is the maximum possible pressure in the tank, which is calculated according to the settings of the safety valve, taking into account the difference in the heights of the location of the tank inlet and the valve.
Table. Expansion coefficient of water depending on heating at an initial temperature of 10aboutFROM.
| Temperature from 10 | K value,% |
| Up to 40 | 0,8 |
| Up to 50 | 1,2 |
| Up to 60 | 1,7 |
| Up to 70 | 2,3 |
| Up to 80 | 2,9 |
| Up to 90 | 3,6 |
| Up to 100 | 4,3 |
| Up to 110 | 5,2 |
Since the quality of the entire heating system depends on the correctness of the calculations, you should not spare money and contact a special organization that will take into account all the parameters, which will allow you to purchase the most suitable tank. Here you can also be given advice on the selection and installation of the tank.
Calculation of the volume of a closed tank
To understand how much of an expansion tank is needed for closed-type heating, several parameters must be taken into account. It is these indicators that will affect further operation:
- the amount of liquid that transfers heat through the system (the more there is, the larger the tank);
- what kind of heat carrier will be used (different liquids increase in volume in different ways);
- the maximum temperature to which the heat carrier will be heated.
Such an expansion tank is a round or oval-shaped container with a diaphragm valve inside, dividing it into two halves. Air is pumped into one of them, and the second serves to receive excess fluid. At the same time, the pressure remains within the normal range. Expansion tanks are usually equipped with a relief valve in case of excess heat carrier.
It is important: installation of a safety group for heating with an expansion tank.
Incorrect calculation of the expansion tank for closed-type heating will entail a lot of problems. For example, if the capacity of the reservoir is too large, then it will not be able to create the required pressure in the system. If a small tank is installed, a constant increase in pressure will be observed, which will lead to a leak in the system.


It is not difficult to calculate the required volume of the tank, it is enough to know a few parameters
To calculate the volume of the expansion tank for heating, you need to know the amount of thermal energy carrier in the mains and radiators. You can find out this value in two ways:
- measure when filling the system;
- calculate mathematically using a formula.
To measure the amount of heat carrier when filling the system, you can use a counter or count the number of liters when manually filling.
For the mathematical calculation of the hydraulic compensator, you will need to read in the boiler characteristics the amount of liquid that will fit in it. You also need to find out from the heat exchanger's passport the amount of liquid that it contains, and calculate the capacity of the pipes using the formula. A formula is suitable for calculating the volume of cylindrical containers V = 3.14 x R2 x H, where:
- V is the required indicator of the internal volume of the pipes;
- 3.14 - constant value;
- R2 is the value of the inner radius of the pipe squared;
- H is the length of the heating main.
The result will be in cubic centimeters and will need to be converted to cubic liters. The resulting number must be multiplied by the coefficient of expansion, depending on the selected type of substance that transfers heat in the pipes. For water, this figure is approximately 0.04%, for liquids based on antifreeze - 0.05%.
To get the desired result, you need to use the formula Vb = Vc x k, in which:
- Vb - tank volume;
- Vc is the amount of coolant in the circuit;
- k is the value of the coefficient used for the type of heat carrier.

With a closed heating system, it is extremely important to make the correct calculations
When calculating the volume of the expansion tank for a closed-type heating system, it is important to take into account the maximum allowable temperature to which the medium will be heated, and the upper limit of the pressure created within the entire circuit. If there is initial data, then you can calculate the expansion tank for heating using a calculator on online resources.
Types of expansion tanks
Depending on what type of heating system the tanks are used in, they are divided into 2 types.
Open type
Such a tank is used for open heating without the use of forced circulation. It is a container without a top. At the bottom of the tank there is a hole, a heating pipeline is connected to it with a thread.
In some houses, you can still find capacity, it copes with its function, while it is quite outdated and has a number of disadvantages:
- the need to place the tank at a height;
- evaporation of liquid from the container;
- acceleration of corrosive processes in different parts of the heating system due to contact of the coolant with air;
- large tank sizes.
In this regard, closed expansion tanks are now becoming more and more popular.
Closed type or membrane
Such tanks are used for heating systems with forced circulation. Capacity
compensates for the pressure jump not only when the coolant is heated, but also when the circulation pump is turned on.
It is also called a membrane-type tank due to its internal structure. It is a spherical or flat reservoir, which is divided inside by a rubber membrane into two cavities:
- one is filled with a coolant through a threaded branch pipe;
- the other with inert gas or air.
The second tank has a nipple that regulates the gas pressure. The bays are not connected to each other.
The principle of a closed tank is simple:
- excess hot coolant enters one of the chambers, the volume of which increases;
- the pressure in the gas compartment rises, which makes it possible to compensate for the voltage in the heating system.
When the coolant cools down, the process in the tank goes along the opposite path.
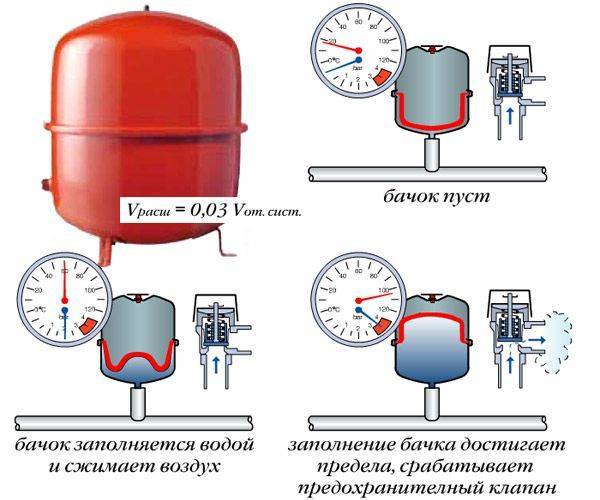

There are 2 types of closed-type containers, depending on the membrane:
- In some, the membrane is made in the form of a diaphragm that cannot be replaced. Such containers are cheaper.
- In the second type of closed devices, the membrane is removable and looks like a pear.
The choice depends on the capabilities of the buyer.It should be borne in mind that damage to this rubber element occurs quite rarely.
Before buying a tank, you need to decide on its volume.
Expansion tanks of open type
The design feature of open-type expanders is the contact of the coolant with the atmosphere. The circulation in systems with this type of expander is convection. When heated, the volume of liquid increases, its excess is absorbed by the reservoir of the container.
When the temperature indicators drop, the liquid returns back by gravity, under the influence of gravity.
Due to the zero pressure in the tank, the device does not require a solid metal structure, therefore:
- any metal is used in the manufacture of the case;
- a ready-made container made of heat-resistant plastic can be used;
- the shape of the reservoir is not essential.
In country houses, such equipment can be assembled from improvised means. As a container, you can use a plastic canister or barrel equipped with an inlet and outlet for overflow.


Expanders of open type can be made in the form of a rectangular tank with a leaky cover on the upper plane
Outwardly, it is an ordinary metal tank, the upper plane of which is equipped with an opening for servicing and adding liquid. Clogging protection is provided by a leaky cover. Fasteners are provided in the lower part or on the lateral plane.
Image gallery
Photo from
Expansion tank in the heating circuit
Open vessel for collecting excess coolant
The simplest version of the expander
Free evaporation container
Open heating systems are used in low-rise buildings, where the volume of the coolant and the length of heating communications are relatively small.
Installation requirements are simple:
- the expander is placed at the maximum height, on the supply line;
- supply is connected to the tank through a branch pipe;
- to drain excess liquid, an overflow is inserted above the design level.
To ensure circulation by gravity, it is recommended to use pipes with an increased cross-section for installation.


An open structure is placed at the top point, from where the liquid flows by gravity
Usually, they try to mount the tank in a heated room, equipped with an insulated attic, and if this is not possible, then the container will need to be insulated. The presence of a heater will prevent the liquid from freezing and the loss of system performance.
How to calculate the volume of an expansion tank for closed-type heating
The heating system of a private house must be equipped with all the elements necessary for proper operation.
Attempts to do without any "unimportant" devices lead to emergency situations requiring serious repair and restoration.
Moreover, even the complete presence of the necessary parts of the circuit will not provide a regular mode of operation if they are selected incorrectly and do not suit their characteristics.
All units must be carefully calculated and selected according to the data obtained.
The expansion tank is an element of protection of the system against rupture in case of exceeding the permissible pressure.
Staying without heating in winter is a serious problem (read about the repair and diagnostics of plumbing violations in the bathroom here).
Therefore, the reliable and correct operation of the expansion tank is of vital importance.
Volume calculation
And yet, the basis of choice is volume. Let's dwell on the dependence of the volumetric parameter of the device and those indicators that affect its changes:
- The larger the volume of the coolant in a closed heating system. the larger the expansion tank needs to be purchased.
- The higher the temperature of the coolant, the greater the capacity of the device.
- The higher the pressure of the coolant (the permissible value of the indicator is taken), the smaller the container can be purchased.
Three main dependencies.Now you can go directly to the calculation. Let's face it, this is not an easy matter, but it is worth dealing with. Because a small deviation can lead to unpleasant consequences. For example, the relief valve will continuously reset.
So, the formula by which the calculation is carried out:
Vb = (Vc * K) / D, where
Vb is the capacity of the device.
Vc is the volume of the coolant in the heating system.
K is the coefficient of expansion of the coolant. For water, this figure is 4%, so 1.04 is used in the formula.
Formula table
D is the expansion efficiency of the tank itself. Made of metal and under the influence of temperature differences, it can slightly change its dimensional parameters. The following formula can be used to accurately establish "D":
D = (Pmax - Pinit) / (Pmax + 1), where Pmax is the maximum pressure inside the heating system, Pinit is the pressure inside the tank, planned by the factory parameters (usually 1.5 atm.). By the way, according to the maximum indicator, it is planned to adjust the safety valve.
It turns out that the volume of the expansion tank depends on the strength and temperature characteristics of the device itself. Note that all these indicators and characteristics should not exceed the permissible limits. The volume of the expansion device should be equal to or slightly larger than the results obtained.
Calculation of the volume of the accumulator tank
The role of the hydroaccumulator (expansion tank) in the autonomous water supply system at home
3 points of consumption
To begin with, if your home has only a tap for water, a shower and a tap for irrigation, then you don't need to count anything. You need a standard water station with a 24 liter hydraulic accumulator. Feel free to buy it. It is optimal in cases where equipment for a small house (summer cottage) with periodic (irregular) use is considered. Even if in the future it will be necessary to increase the number of water sampling points, it will be possible to simply buy separately and install another 24 liter hydroaccumulator at any point in the water supply system.
More than 3 points of consumption
If the house does not have a sewage system, but with more than three water points, then a 50 liter hydroaccumulator will be enough for you.
Below is a calculation methodology for individual houses equipped with a sewerage (septic tank), with bathrooms and other equipment that consume a significant amount of water.
1. It is necessary to determine the total coefficient of water consumption Su
... To do this, make a list of draw-off points in your home and indicate the amount of each type of equipment. Below is a table of "normal" water consumption for various household appliances.
| Consumers | Normal consumption | |
| l / m | m3 / h | |
| Bath | 23 | 1,38 |
| Shower | 12 | 1,08 |
| Washbasin | 3,5 | 0,21 |
| Kitchen sink | 10 | 0,6 |
| Washing machine or dishwasher | 10 | 0,6 |
| Toilet cistern | 10 | 0,6 |
| TOTAL | 74,5 | 4,47 |
2. To determine the volume of the accumulator, it is necessary to decide how many times per hour the accumulator can be turned on at maximum consumption
... 10-15 times is considered normal. Please note that a large value of this parameter (some companies recommend assigning this parameter at a maximum intensity of up to 45 inclusions per hour) leads to frequent loading of the accumulator membrane in tension-compression, and the total number of such loads is limited by the strength of the membrane. In addition, if 45 starts per hour, this means that the pump runs before shutdown for only about a minute. Typically, the performance of household pumps for individual water supply systems is small, and it is simply impossible to fill a properly selected hydraulic accumulator in a minute. Our recommendation for this parameter is 10.
When checking the possibility of using an existing accumulator in cases where a new source of water consumption is added to the house, this parameter can be taken equal to 15.
It is also required to assign thresholds for the pressure switch of the water supply station (Pmin and Pmax). The lower threshold Pmin for two-storey houses is usually 1.5 bar, and the upper threshold Pmax is 3 bar. Then, to determine the volume of the accumulator, you must use the following formula:
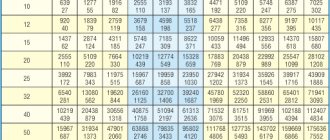
where V is the total volume of the accumulator, l; Omax is the maximum value of the required water flow rate, l / min; A is the number of system starts per hour; Pmin - lower min pressure threshold when the pump is turned on, bar; Pmax-upper pressure threshold when the pump is turned off, bar; Ro is the initial gas pressure in the accumulator, bar.
For example, if Qmax = 36 l / min, A = 15, Pmin = 1.8 bar, Pmax = 3 bar, Po = 1.8 bar, then the total volume of the accumulator is:
The number of such loads is limited by the strength of the membrane. In addition, if 45 starts per hour, this means that the pump runs before shutdown for only about a minute. Typically, the performance of household pumps for individual water supply systems is small, and it is simply impossible to fill a properly selected hydraulic accumulator in a minute. Our recommendation for this parameter is 10.
When checking the possibility of using an existing accumulator in cases where a new source of water consumption is added to the house, this parameter can be taken equal to 15.
The closest in size is a 150 liter hydroaccumulator.
Next, we present our recommendations for setting the thresholds for the pressure switch of the water supply systems of an individual house. The difference in the response thresholds Pmax-Pmin determines the amount of water produced by the hydraulic accumulator of the water supply system. The greater this difference, the more efficient the operation of the accumulator, but the membrane is loaded more heavily in each cycle of operation.
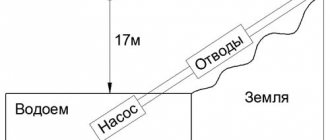
The Pmin value (pump start pressure) is determined based on the hydrostatic pressure (water height) in your home's water supply system. For example, if the height between the lowest and highest parsing points in the system is 10 m, then the water column pressure is 10 m (1 bar). What should be the minimum pressure Pmin? The air pressure in the back pressure chamber of the accumulator must be greater than or equal to the hydrostatic pressure, that is, in our case - 1 bar. The lower response threshold Pmin should then be slightly higher (by 0.2 bar) than the initial air pressure in the accumulator.
However, we need the system to work steadily. The most critical, in terms of operational stability, is the highest parsing point (for example, a faucet or a shower on the top floor). The valve works normally if the pressure drop across it is at least 0.5 bar. Therefore, the pressure must be 0.5 bar plus the hydrostatic pressure of this point. Thus, the minimum value of the gas pressure in the accumulator Po is equal to 0.5 bar plus the value of the reduced hydrostatic pressure at the point where the accumulator is located (the distance in height between the upper point of analysis and the point where the accumulator is located). In our case, if the accumulator is located at the lowest point of the water supply system, the minimum gas value in it is Po = 1 bar + 0.5 bar = = 1.5 bar, and the threshold of operation (switching on) of the pump Pmin = 1.5 + + 0, 2 = 1.7 bar. If the accumulator is located at the upper point of the system, and the pressure sensor is at the bottom, then the gas pressure in the accumulator should be 0.5 bar, and the pump activation threshold should be 1.7 bar.
When assigning the upper threshold for the operation of the automatic water supply system Pmax, it is necessary to take into account several points, first of all, the pressure characteristic of the pump. The pressure generated by the pump, expressed in meters of water column, divided by 10, will show the maximum pressure value. However, it should be borne in mind that:
- in the characteristics of the pump, the maximum parameters are indicated without taking into account the hydraulic resistance of the pipelines;
- the voltage of the electrical network often does not correspond to the nominal value of 220 V, and the real values may be lower;
- manufacturers of domestic pumps often indicate overestimated characteristics;
- at maximum pressure values, the pump flow is minimal and the system will fill up for a very long time;
- with prolonged operation, the pump performance decreases.
With this in mind, we recommend that you set the high threshold value 30% lower than the maximum head of your pump. However, the initial point in determining the upper response threshold is the height of your house, or rather, the height of the water supply system at home. The value of the upper alarm threshold is equal to the height of the water supply system (expressed in meters) plus 20 m, and divided by 10. You will get the pressure expressed in bar.
In domestic water supply systems, the recommended difference between the lower and upper response thresholds is 1.0-1.5 bar. These values are the most acceptable. Thus, to determine the upper threshold of the pump activation pressure, we recommend:
- determine the lower pressure threshold for switching on the pump;
- add 1.5 bar to the value obtained;
- the obtained value is compared with the pressure characteristics of the pump.
It should be 30% below the maximum head of your pump. Thus, it is possible to check the correct selection of the pump and accumulator or the possibility of using existing additional equipment that consumes water when installing.
Buy
hydroaccumulatorin the AQUARIUS online store at a great price. In our store you can get advice on the selection of any type of pumping equipment and additional equipment for the organization of autonomous water supply at home.
We also recommend reading
- How to choose a pumping station?
- Connection diagram of a pumping station with tank No. 1
- Connection diagram of a vortex centrifugal pump for autonomous water supply of a private house No. 5
Tank types
Expansion tanks can be of two types - open and closed. For the tank of the first type, no calculations are required; in fact, it is a bucket half-filled with coolant, installed in the highest part of the heating system, with an opening through which excess air escapes when the coolant expands. Open tanks are considered obsolete and have a number of disadvantages, so it is more advisable to take on the calculation and installation of a closed expansion tank.
A closed expansion tank is installed in systems equipped with a pump, which is responsible for the circulation of water in the heating system. A closed tank is a container divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. In the lower part of the tank there is a coolant, and in the upper part there is air.
When the heating system heats up, the coolant expands and its surplus rises to the lower compartment of the expansion tank. Further, the membrane rises upward, compressing the air chamber and thereby maintaining the system pressure level in the norm. When the temperature of the coolant decreases, the pressure in the system also decreases, which entails a decrease in the level of the coolant in the tank.
After installing the tank, its upper chamber is filled with air using an auto-pump, the pressure in the air chamber should be equal to the initial pressure in the entire system.
Volume selection
Let's consider separately how to calculate an expansion tank for heating sealed and open types. Since the design and principle of operation of such tanks are completely different, although both perform the same function.


Open tank
The dimensions of the expansion tank for an open heating system, by and large, determine its volume, since the design of such a tank is quite simple. It is made from sheet metal.It has a hole through which the coolant enters the inside and goes back into the pipes. They can also be equipped with an overflow hole through which excess water is discharged into the drain.
It happens that an automatic make-up is brought into the tank. But the main thing is how the expansion tank in the heating system is calculated, or rather, its volume. Let's take the same system with one hundred liters of water. After heating, the liquid will increase by five percent, maybe more, depending on the temperature in the circuit. It turns out that the volume of the expansion tank for this open heating system should be at least five liters, preferably more. And the calculation of the expansion tank for the heating system is reduced to the following algorithm:
- five liters is the expansion of the water;
- a couple of liters should always be in the tank - this is to prevent air from entering the circuit;
- three liters must be made in reserve.
Based on the calculation of the volume of the expansion tank for heating, it receives ten liters. By the way, this is the simplest and most common selection method - ten percent of the amount of water in the circuit.
The easiest way to calculate the volume of an expansion tank for heating is to calculate a tenth of the total amount of coolant. This is a value with the necessary margin, at which everything will work like clockwork.
For closed systems, in addition to the simple, popular, method for calculating the volume of the expansion tank of the heating system, there are more accurate methods. To take advantage of them, you need to know several meanings. These include:
- how much the volume of water (RH) increases when heated. Answer: five percent. The value has been rounded to the nearest whole number without fractions for convenience. If an anti-freeze liquid circulates in your circuit, then this value will be higher;
- how much water is in the circuit (VC). Such data should already be available from the design stage. Since the selection of the heater is based on this value. If it so happens that you do not know how many liters there are, all that remains is to measure. The first thing that comes to mind is to completely drain all the liquid from the circuit and refill it. The number of liters can be measured in buckets, or you can use a special counter that is installed on the stream;
- what is the maximum pressure the circuit and the boiler (DK) are designed for. This value can be read on the heater documents, or on the heater itself. It is unlikely that it will happen that there are neither documents nor information on the boiler body. But if it really happened, then the Internet will help you;
- what is the pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank (DB). This is also indicated in the technical documentation.
To calculate how much volume of the expansion tank is needed for heating, a simple mathematical calculation should be performed:
OV x VK x (DK + 1) / DK - DB
Based on the results of calculating the capacity of the expansion tank for heating, you will receive an accurate value. The question of the expediency of such complex calculations remains open. Undoubtedly, according to the results of this formula for calculating the expansion tank of the heating system, a lower value will be obtained than according to the results of the "folk" method. But a larger margin of error is not an error. If the tank is larger than what you need, it's okay, you just need to set it up correctly.
What is an expansion tank for?
As we know, water tends to expand during heating. As well as any other liquid in general. The coolant in the heating system is no exception. When the liquid expands, its excess needs to be put somewhere. For these purposes, expansion tanks were invented in heating.
First of all, let's recall the basic law of physics: when they heat up, bodies increase, and when they cool down, they decrease. The circulating heat carrier (water) in the system when heated increases in volume by an average of 3-5%.For the prevention of accidents and maintaining the operability of heating equipment, a container is needed, which will smooth out the temperature difference and, as a result, the pressure and volume of water. That is, when heated, the tank will take over the excess liquid, and when cooled, it will lower it back into the system. Thus, the pressure in the boiler remains within the permissible limits. Otherwise, the automatic protection is triggered and the system rises. What can be unsafe in severe frosts.
Calculator for calculating the volume of the expansion tank for the heating system
A closed heating system has many advantages. It is much more compact, since it does not require compliance with the rule of installing the expansion tank at the highest point, it is easier to adjust, it works more economically, and the coolant does not evaporate and does not come into contact with air, that is, it is not saturated with oxygen, which is very important for the durability of the metal elements of the boiler and radiators ...


Calculator for calculating the volume of the expansion tank for the heating system
Compensation of the temperature expansion of water occurs by installing a membrane expansion tank, which can be mounted, for example, on the "return" in the immediate vicinity of the boiler. It is only necessary to correctly determine the parameters of this important element of the system. The calculator for calculating the volume of the expansion tank for the heating system will help us with this.
The necessary explanations for performing the calculations are below the calculator itself.
Calculator for calculating the volume of the expansion tank for the heating system
Go to calculations
Explanations for calculating the volume of the tank
It is clear that when installing a heating system, especially in conditions of a shortage of space, you want to save free space to the maximum. However, the volume of the expansion vessel cannot be less than the calculated value.
The calculation is based on the following formula:
Vb = Vt × Kt / F
Vb - the calculated volume of the expansion tank.
Vt - the volume of the coolant in the system.
How to deal with him?
- A practical way is to detect with a water meter during a trial filling of the system.
- The most accurate way is to sum up the internal volumes of all elements of the system - boiler, pipes, radiators, etc.
- The simplest "theoretical" method - without fear of making a serious mistake, you can take the ratio of 15 liters of coolant for each kilowatt of heating boiler power. It is this dependence that is included in the calculation calculator.
Kt - coefficient taking into account the thermal expansion of the applicable heat transfer medium. This indicator depends on the content of antifreeze additives in the coolant, and changes with the percentage of these additives, and with an increase in temperature, and it is nonlinear. There are special tables, but in our case, these data have already been entered into the calculator - based on the average heating of the coolant up to + 70 ÷ 80 ºС (this is the most optimal mode of operation of an autonomous heating system).
If the system uses water, then this must be noted in the appropriate field of the calculator.
Prices for expansion tanks for the heating system
expansion tank for the heating system
What can be used as a coolant?
For private houses, which can be left by the owners in the winter for a long time with the heating turned off, it is more advisable to use anti-freezing liquids - antifreezes. About diversity heat carriers for heating systems, about their properties, advantages and disadvantages - in a special publication of our portal.
F - the so-called efficiency factor of the diaphragm expansion tank. It is expressed by the following relationship:
F = (Pmax - Pb) / (Pmax + 1)
F Is the calculated efficiency factor of the tank.
Pmax - the maximum pressure in the system, which corresponds to the threshold of the emergency valve actuation in the "safety group".This parameter is necessarily indicated in the passport data of the boiler equipment.
Pb - pumping pressure of the expansion tank air chamber. The product can come already pre-inflated - then this parameter will be indicated in the passport. However, this value can also be changed - the air chamber is pumped, for example, by a car pump, or, conversely, excess air is vented from it - for this there is a special nipple on the tank. As a rule, in autonomous heating systems it is recommended to pump the air chamber to the level of one - one and a half atmospheres.
What other elements are required in a closed heating system?
In order to properly plan and install heating in a house or apartment, you need to know its structure and the relationship of all the main devices and elements. Details about closed heating system tells a special publication of our portal.
Types of tanks
The heating system can be equipped with one of the types of expansion tanks.
How to choose the right element of the heating system in each individual case? This will be discussed further.
Open type
As the name suggests, an open tank is an open-top container into which you can add coolant. It does not require locking parts, a diaphragm seal and a cover. But due to the fact that water evaporates in such a container, and its amount must be constantly monitored (topped up), they began to gradually abandon open-type tanks.
In addition, such heating is characterized by low pressure, and the tank itself is often corroded. Therefore, more modern closed-type tanks are being installed today.
Closed type
Expansion tanks of a closed type (diaphragms) are installed in lines with a circulation pump. The highest quality samples are produced in the form of a sealed red container with a rubber membrane inside. Their diaphragm is made of more durable technical rubber.
Products for hot water supply, the body of which is painted blue, have a lower quality of rubber (it is food grade). Such models withstand pressure worse and wear out faster.
In addition to the main function - compensation of the volume of the coolant when the temperature drops and its intake when expanding from heating, the diaphragm controls the liquid level in the heating main, removes air from the system, drains water into the sewage system with its excess volume and is a buffer zone in the event of a pressure jump.
Useful tips for selection
There are several nuances to consider when buying and installing an expander.
- When choosing a place for mounting the tank, it is necessary to take into account that it cannot be installed immediately behind the circulation pump.
- Commercially available tanks come in two colors: red and blue. In the first, the membrane is stronger, but made of technical rubber. Blue tanks are used for water supply, they have food grade rubber, but it is less strong and durable.
- During installation, you must use a special sealant.
- If you decide to stay on an open system, then the tank must be placed at the highest point, and when installing the pipeline, observe the recommended slope.
- The size of the tank should not be less than the calculated value, a slightly larger volume is allowed. When using forced circulation, the capacity cannot be less than 15 liters.
- Antifreeze can be used as a coolant. For a glycol mixture, it is better to choose an expansion tank, the volume of which is twice the calculated volume.
The main advice is to contact the professionals, because the installation of the tank only seems simple. In addition, you cannot do without a special tool.
How to correctly calculate the volume of the tank for heating systems?


To correctly calculate the volume of the expansion tank, take into account several factors that affect this indicator:
- The capacity of the expansomat directly depends on the amount of water in the heating system.
- The higher the allowable pressure in the system, the smaller the tank you need.
- The higher the temperature to which the coolant is heated, the larger the volume of the device must be.
Reference. If you choose an expansion tank too much, then it will not provide the required pressure in the system. A small tank will not be able to accommodate all the excess coolant.
Calculation formula
Vb = (Vc * Z) / N, wherein:
Vc - the volume of water in the heating system. To calculate this indicator, multiply the boiler power at 15. For example, if the capacity of the boiler is 30 kW, then the amount of coolant will be 12 * 15 = 450 l. For systems where heat accumulators are used, the capacity of each of them in liters must be added to the obtained figure.
Z Is the rate of expansion of the coolant. This coefficient for water is 4%, accordingly, when calculating, we take the number 0.04.
Attention! If another substance is used as a heat carrier, then the corresponding expansion coefficient is taken. For example, for 10% ethylene glycol it is 4.4%.
N Is an indicator of the efficiency of the expansion of the tank. Since the walls of the device are made of metal, it can slightly increase or decrease in volume under the influence of pressure. To calculate N, you need the following formula:


N = (Nmax — N0) / (Nmax + 1)where:
Nmax - the maximum indicator of the pressure in the system. This number is from 2.5 to 3 atmospheres, to find out the exact figure, look at which threshold value the safety valve in the safety group is set to.
N0 - the initial pressure in the expansion tank. This value is 0.5 atm. for every 5 m the height of the heating system.
Continuing the example with the boiler capacity 30 kWt, let us assume that Nmax - 3 atm., the height of the system does not exceed 5m... Then:
N = (3-0.5) / (3 + 1) = 0.625;
Vb = (450 * 0.04) /0.625 = 28.8 liters.
Important! Commercially available expansion tank volumes meet certain standards. Therefore, it is not always possible to buy a tank with a capacity that exactly matches the calculated value.
In such situation buy a device rounded upbecause if the volume is slightly less than required, it may harm the system.
The principle of operation of the expansion tank
The principle of operation of the compensating device is simple, there are no complicated technical solutions in it. However, the slightest error in the calculation can lead to the failure of the heating system as a whole.
The inner space of the tank is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. The upper cavity is called air - air is pumped into it. The purpose of this operation is to create an initial pressure in the vessel. Water from the system is supplied to the lower cavity. As soon as the membrane takes a stable position - it lies on the surface of the liquid, the system can be considered ready for operation.
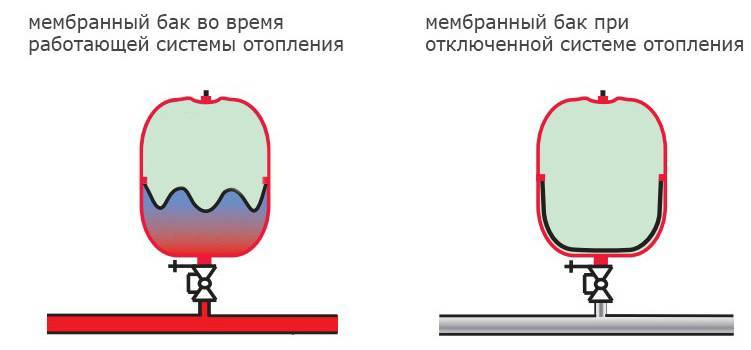

The principle of operation of a closed expansion tank
The heated coolant expands, and its excess enters the tank, displacing the membrane towards the air chamber. As soon as the water begins to cool down, the membrane under air pressure returns to its original position, thereby maintaining the set pressure in the heating system.
An expansion vessel that is too large is not able to create the required pressure in the system. Insufficient capacity of the compensating device will not allow to accept the entire excess of expanded water.
Therefore, it is so important to correctly calculate the optimal volume of this important element of the autonomous heating system.
Final calculation
Having determined the total amount of coolant in the boiler unit and the circuit, you can calculate the volume of the expansion tank.
To do this, you can use the formula Vbaka = Vsyst × k / D, taking into account that:
D is the efficiency parameter of the membrane tank; k is the coefficient of thermal expansion of the liquid that is planned to be used as a heat carrier:
- for water - 4%;
- for ethylene glycol 10% - 4.4%;
- for ethylene glycol 20% - 4.8%.
Vsyst - the volume of fluid in the system.
If parameter D is not indicated in the tank passport, it is calculated using the formula D = (Pmax - Pinit) ⁄ (Pmax + 1), while: Pmax is the maximum allowable pressure in the system (in accordance with this parameter, the factory setting of the safety valve is performed ); Pnach is the pressure in the air chamber of the tank during initial pumping.
When choosing a tank, you should pay attention to the maximum permissible operating parameters.
:
- coolant temperature - up to 120 ° С;
- system pressure - up to 6-10 bar.
It is allowed to install only a membrane tank, the performance of which slightly exceeds the calculated values.
Note! If you expect the possibility of subsequently replacing the water in the system with antifreeze by choosing a suitable type of anti-freeze, you should immediately purchase a tank with an appropriate volume margin, or later mount another tank.
conclusions
In order for the heating system to work correctly, you need to know how to calculate the expansion tank for heating. In addition, the device should be configured according to the manufacturer's instructions or by yourself.
In the second case, air is pumped into the air chamber using a hand pump so that the pressure in this chamber is 0.2 atmospheres lower than the operating pressure of the boiler unit.
Correct calculation and adjustment of the membrane tank will help to ensure a stable pressure in the heating circuit during its operation.
Related videos:
How to put the tank correctly
When installing an open tank in the attic, a number of rules should be observed:
- The container should stand directly above the boiler and be connected to it with a vertical supply pipe.
- The body of the product must be carefully insulated so as not to waste heat by heating the cold attic.
- It is imperative to organize an emergency overflow so that in an emergency situation hot water does not flood the ceiling.
- To simplify the level control and make-up, it is recommended to bring 2 additional pipelines into the boiler room, as shown in the tank connection diagram:

Note. It is customary to direct the emergency overflow pipe to the sewer network. But some homeowners, in order to simplify the task, take it out through the roof directly onto the street.
The installation of a membrane-type expansion tank also has its own characteristics. Considering how this product works, it can be placed vertically or horizontally in any position. Small containers are usually fastened to the wall with a clamp or suspended from a special bracket, large ones - just put on the floor. There is one point here: the performance of the membrane tank does not depend on its orientation in space, which cannot be said about the service life.
A closed vessel will last longer if it is mounted vertically with the air chamber facing up. The fact is that sooner or later the membrane will exhaust its resource, which is why cracks will appear in it. The internal structure of the tank is such that with a horizontal arrangement, air from its half will quickly penetrate through the cracks into the coolant, and that will take its place. We'll have to urgently put a new expansion tank for heating. The same result will quickly appear when the container is hanging upside down on the bracket.


In a normal vertical position, air from the upper part will not rush to penetrate through the cracks into the lower one, just as the coolant will reluctantly go up. Until the size and number of cracks increases to a critical level, the heating will work properly. This process sometimes takes a long time, you will not notice the problem immediately.But no matter how you place the vessel, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- The product must be positioned in the boiler room in such a way that it is convenient to service it. Do not install floor standing units close to a wall.
- When wall-mounting the heating expansion vessel, do not place it too high, so that you do not have to reach the shut-off valve or air spool when servicing.
- The load from the supply pipelines and shut-off valves should not fall on the tank branch pipe. Fasten the pipes together with the valves separately, this will make it easier to replace the tank in the event of a breakdown.
- It is not allowed to lay the supply pipe across the floor through the passage or hang it at head height.


How can you beautifully place equipment in a boiler room?
Complete set and principle of operation
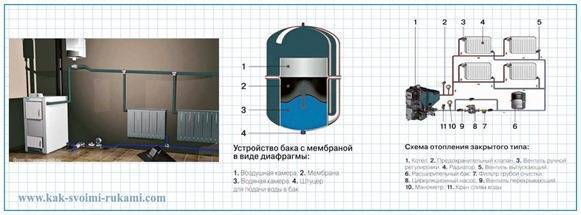
The expansion tank, in addition to the housing, includes a membrane (balloon or diaphragm), the upper part of which is filled with inert gas or air. The lower compartment of the sealed container is intended for the coolant.
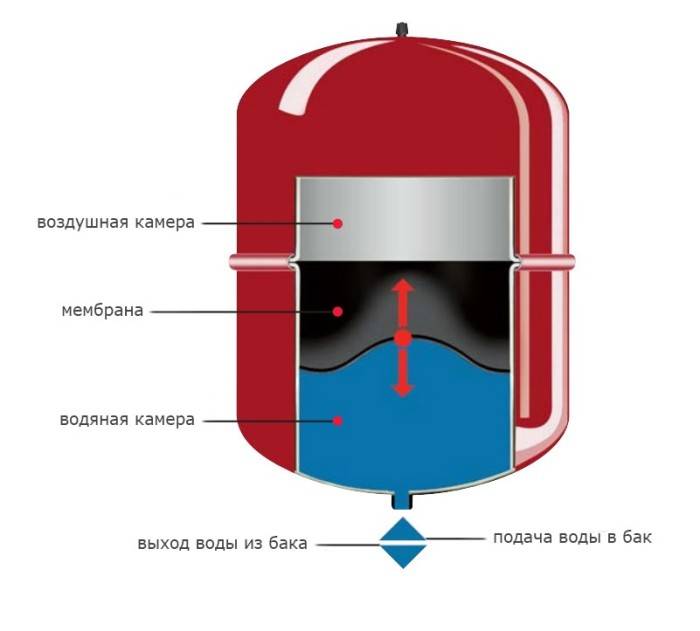

Along with an increase in temperature indicators, the water expands, and the excess mass of the coolant enters the membrane. The volume of the chamber with air decreases, and the pressure in this part of the closed system increases, compensating for the pressure in the line. When the temperature of the coolant decreases, the opposite process is observed.
The expansion tank can be equipped with a replaceable (flanged) or permanent diaphragm. The second type of product is cheaper.
The membrane in the tank is tightly pressed against the inner wall, since its entire volume is filled with gas.
When water gets inside, the pressure increases. At the time of starting the heating, there is a risk of damage to the diaphragm from a pressure surge, and then the pressure gauge gradually changes the readings and the integrity of the part is out of danger.

To avoid damage to the diaphragm, it is necessary to install a pressure gauge safety valve that reacts to the increased pressure (for private houses, the norm is from 3.5 to 4 bar).
Flanged model advantages
The advantages of flanged devices include the following characteristics:
- withstands more pressure inside the system than a device with a constant diaphragm;
- it is possible to replace the membrane if it is damaged;
- horizontal and vertical installation of the device.
What is an expansion tank for?
Depending on the weather conditions and the climatic regime in the room, the coolant that circulates through the heating pipes heats up to a greater or lesser extent. With intensive heating, it expands and forms an excess volume, which can create pressure exceeding the maximum allowable for the operation of the system. The installation of an expansion tank in the heating main is just needed to temporarily remove these excess liquid.
Closed heating system with an installed expander
A double-circuit boiler usually has its own tank for removing the coolant, the capacity of which is quite enough for average operating conditions.
But if your house has a lot of heated rooms, and at least some of them use metal pipes as batteries, then much more fluid is required in normal mode, which means that the increase in volume during expansion will be more noticeable. Therefore, the built-in expansion tank may not be enough, and then an additional tank will need to be installed.
How to install and connect the tank correctly
Depending on the conditions in the bath, the tank connection diagrams may be different. For example, if there is a water supply to the washing room, i.e. water will be supplied under constant pressure, then a closed water supply system is needed.
In this case, the ideal option is a stove with a coil inside, which is connected to the tank. You can, of course, implement another method - hang the container on the oven itself.For this, the simplest design of a 50-120 liter tank is suitable, which can be welded on your own, in which case the price of the product will be formed solely by the cost of the material.
If the connection was made correctly, then the water heating scheme looks as follows - the water is heated in the register and, according to the law of physics, rises up. There it gradually cools down and again descends into the register. Thus, natural circulation is obtained
Why do you need an expansion tank for heating
For the normal functioning of the heating system and stable circulation of the coolant through all its elements, a stable pressure is required. Its sharp jumps lead to a violation of the hydraulic regime and malfunctioning of individual units. To avoid this, an expansion tank is provided in the system. Its task is to compensate for the change in the volume of the coolant (water or antifreeze) caused by a change in its temperature, and to reduce the possibility of water hammer. The change in the volume of the coolant is also affected by its composition and, accordingly, the temperature coefficient. When using water, the value of this coefficient is on average 4%, in the case of antifreeze, for example ethylene glycol, from 4.4 to 4.8% (depending on the concentration of glycol in the antifreeze). It is the expansion tank that is the very container where the excess coolant is dumped in order to maintain the required pressure in the network.
Depending on the type of heating system (open or closed), different expansion tanks are used. Immediately, we note that an open system (it is also called a system with natural circulation - self-flowing) is rarely used in new houses, it can be found mainly in old buildings.

(no votes yet)