| Name | Key Features |
| Liquid | The most common. It is used for thermal insulation of various structures, for repairs. Fills cracks and gaps. Can be cooked on site. |
| Granular (thermovata) | It is made by crushing the polymer into fractions of 10-15 mm. Economical during installation. Penoizol in granules in volume is 2 times higher than the amount of sheet polymer obtained during production. They fill the cavities between the walls when laying the floor. |
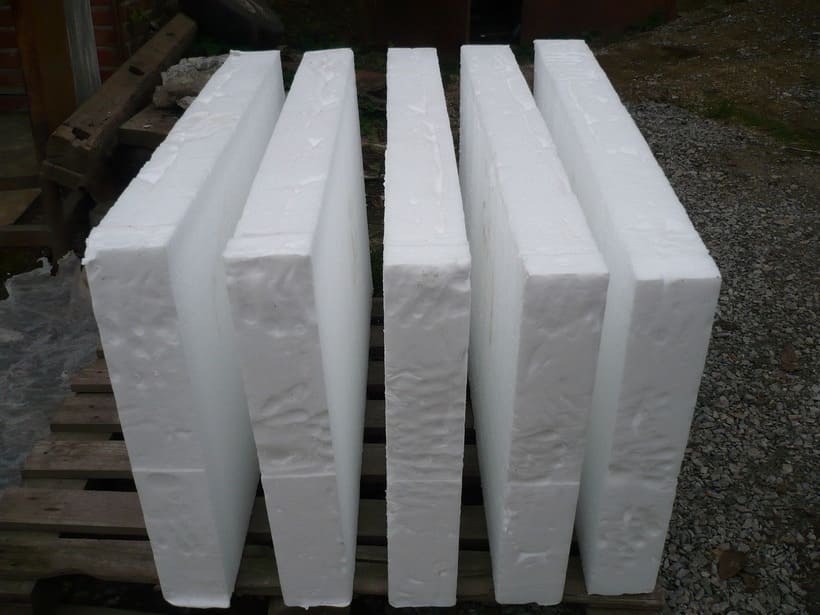
| Sheet | Insulation is poured into a special uniform, cut when ready, dried and further processed. It is mounted on the outside of the walls of houses, fastened with dowels. It can also be laid on the floor (between the joists). |
Indicators and advantages of penoizol
The popularity of urea foam is due to its low price and characteristics:
- Low thermal conductivity (0.041 W / m2 * K). To ensure good thermal insulation, a narrow layer of foam insulation is sufficient (at least 10 cm).
- High noise absorption, up to 65%. Even a narrow layer of building material solves the issue of sound insulation.
- Good fire resistance. The insulation belongs to the G-1 flammability group with the B-2 flammability category. The polymer does not melt, but evaporates without releasing harmful toxins. Smokes weak.
- Hygroscopicity. Air can pass through the foam, the vapor permeability property allows the walls to "breathe".
- Chemical neutrality to various components, including organic solvents.
- Biostability. Fungus and mold do not grow on penoizol, mice / rats do not gnaw it.

disadvantages
Penoizol has the following disadvantages.
First, it absorbs moisture and does not give it away. Penoizol is quite resistant to moisture, but this feature does not allow the use of insulation when screed the foundation.
Secondly, the material gives a sediment in the range of 0.1-5%.
Thirdly, penoizol tears easily - it has low tensile strength.
Fourthly, it is possible to put insulation only at a positive temperature (at least + 5 ° C). Only in this case will you get high-quality foam for filling cavities.
If sheet and granular penoizol does not emit hazardous substances, then in liquid form it can evaporate harmful toxins. Workers are better off having protective equipment.
Penoizol types
The material is supplied in several commercial forms:
Liquid
It is a solution ready for application to insulated surfaces. The shelf life of the solution is limited. Before purchasing, you should make sure that the product is fit and that the packaging is tight.
Granulated
Granules are supplied in bags. Their shelf life is practically unlimited; such raw materials can be stored for future use. Before applying, you will have to take time to dilute the solution and bring it to the required consistency.
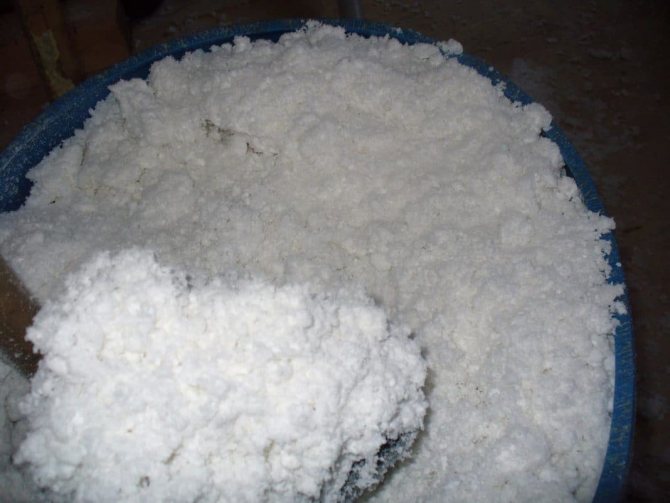


Granular penoizol
Sheet
This is insulation, foamed and molded in production. The sheets have a standard size for insulation 1200 * 600 mm and are convenient for laying in guides or end-to-end on horizontal surfaces. Also available in rolls of various widths.
Penoizol manufacturing technology
- In a separate container, 3 ingredients are mixed: water, a foaming agent and a reaction catalyst. Urea-formaldehyde resin is poured into the second container. Subsequently, it enters the mixture under the influence of compressed air.
- The components are thoroughly mixed until a mixture is formed, similar in consistency to a soufflé.The resulting material is called liquid penoizol, that is, it is already suitable for use on construction sites.
- The liquid mass is poured into molds of various sizes. Curing takes place at room temperature, lasts up to 3 hours (depending on the shape, size and specific recipe), on average - 30-40 minutes.
- The resulting sheets of insulation are cut into separate slabs in accordance with the required dimensions.
- Urea foam is coated with a protective compound that increases strength and fire resistance.
- The finished product is packed and stored.


Our equipment
The main advantage of the Penoizol production technology is an innovative approach and constant work to improve the quality of products. Much attention is paid to the properties of raw materials and the design of production devices. At the moment we are using certified installations made by the Tula Scientific and Production Enterprise "Logrus" POTOK-7 and POTOK-12. The advantage of this equipment is its accurate dosage of the proportions of urea resin and solution, as well as the ability to supply foam under high pressure into difficult-to-pass cavities with a thickness of 2-3 cm. We also improved the STOP-START system, which allows you to stop the feed as needed. The equipment is designed for different production capacities. Distinctive features of the equipment are compact size, reliability and ease of use.
Manufacturing process
Penoizol is based on carbamide resin and a specially prepared solution consisting of water, phosphoric acid and ABSK foaming agent. All components are fed into the mixing unit in strict proportions, after which they are mixed and saturated with compressed air. Further, from the mixer, the components enter a hose having a certain length and section. The mixture, passing through the hose, continuing its thorough mixing, enters the hose of a larger diameter, as a result, a pressure drop occurs in a smaller direction, due to which the mixture boils, thereby forming a liquid foam.
Components used
Urea resin
The main component of urea foam is urea resin. The quality of the resulting material directly depends on the quality of the resin. For manufacturing, we use, as a rule, VPSG resin, which is certified according to TU 2223-003-33000727-2002, or its analogue Karbopen resin (TU 2223-048-26161597-2000). These resins are specially formulated for cold curing foams used as thermal insulation for residential premises. They contain a low percentage of formaldehyde 0.25%, odorless, non-toxic.
It is important to observe the temperature storage conditions of the resin, since the carbamide resin is a perishable product and its shelf life should not exceed 60 days from the date of manufacture.
Orthophosphoric acid
In the production of liquid foam, we use food grade 85% phosphoric acid. It serves as a hardener. The higher the percentage of acid in the solution, the faster the foam hardens. It is important to take into account all the structural features, ambient temperature, water density. Comparing all these parameters, it is necessary to make a solution with the desired concentrate.
Foaming agent ABSK (Alkylbenzenesulfonic acid)
For foaming consistency, alkylbenzenesulfonic acid is used as a foaming agent. Its content depends on the hardness of the water, the harder the water, the greater its percentage in the solution. Usually its concentration is 1%.
The production technology of components for the manufacture of "Penoizol" is being improved all the time. In particular, by changing the modes of cooking raw materials, it was possible to obtain a larger number of molecules with a branched structure. As part of Penoizol, this resin provides the best mechanical properties.
What you need to get started
Penoizol business can be started without serious investment. The equipment is inexpensive, and the main expenses every month will go to the purchase of raw materials and remuneration of personnel.
Table 1. Initial Costs for the Penoizol Business.
| Consumable item | price, rub. |
| check in | 20 thous. |
| Premises for rent, 90 sq. m | 25 thous. |
| Equipment | 200 thous. |
| Raw materials (for a month at full load) | 230 thous. |
| Salary, 6 people | 190 thous. |
| Additional expenses | 100 thous. |
| Total | 765 thous. |
The calculations are relevant for a city with a population of up to 1-1.5 million people. Additional costs include utility bills, advertising promotion, preparation of premises, etc. The amount of tax deductions is not taken into account in the calculation.
Documentation
First you need to register a form of activity. You can work in the form of an individual (individual entrepreneur) or a legal entity (LLC). It all depends on the plans of the entrepreneur, the scale of production. Each form has its own capabilities and limitations, however, working in the form of an LLC will allow you to cooperate even with large construction companies and wholesale and retail chains.
When registering, OKVED-2 codes are indicated.
23.99.6 "Production of mineral heat and sound insulating materials and products."
22.23 "Manufacture of plastic products used in construction".
22.29 "Manufacture of other plastic products".
32.9 "Manufacture of products not included in other categories".
No certification is required to launch a business project. The polymer is produced in accordance with TU 2254-001-33000727-99 “Heat-insulating foam insulation. Technical conditions ".
THE TRUTH ABOUT PENOISOL SHRINKING
Hello gentlemen!
In this article, I decided to summarize my experience, the experience of my clients in working with penoizol. I will try to honestly talk about such a phenomenon as shrinkage.
So, let's begin.
More than once I heard from customers who bought equipment from us, and we ourselves had to deal with significant shrinkage of penoizol. Some people go to objects 2-3 times and refill what has settled, fill in or manually fill in cracks in the foam-insulating layer. This is a nightmare of a foam insulator and his blue dream of getting a non-shrinking penoizol. Alas, unrealizable! This is due to secondary shrinkage. What is it? Not everyone who deals with penoizol knows this term. And everyone faced the consequences. So what is Penoizol? It is a polymer material consisting of bubbles of urea-formaldehyde polymer. There are channels between the bubbles, the so-called Gibbs capillaries. In the volume of foam, it occupies 3-3.5%. It is these capillaries that contain (or may contain) water. The bubbles of penoizol themselves do not contain water and do not retain. Anyone who has ever poured penoizol will tell you that 30-35 liters of water per 1 cu. m - this is the maximum, after which excess water begins to drain to the floor.
So what happens to the water in the capillaries under normal conditions.
The walls of the bubbles in the foam are moist, soft, the capillaries are swollen, full of water. But the surface area on which evaporation occurs is enormous and the water begins to evaporate. An excess pressure of water vapor is created in the material and they rush outward. In this they are helped by the open-pore structure of the material (or some percentage of open pores with a closed-pore structure).
The soft walls of the bubbles covered with the thinnest water film dry, finally polymerize and acquire their inherent physical properties. If the resin included plasticizers, then the walls of the bubbles will be elastic, if not, then the walls are stiffer and more fragile. Internal stresses are created in them, which lead to rupture of the walls and cracking of the material. The water evaporates from the capillaries until the swollen capillaries become thin.And the capillary forces will not exceed the energy of water molecules striving to break away from the surface.
Has the evaporation stopped? Well no. It was just equilibrium. As many water molecules have evaporated, the same amount has fallen from the ambient air into the capillaries. The result of this process was the past primary shrinkage. On foams made from resins containing plasticizers, shrinkage is usually less, on others it is more. It is the materials after the initial shrinkage that are usually shown to the client.
But foams are used in a variety of environmental conditions. Let's look at a specific example. So, the attic is flooded. The filling took place in a rainy autumn, with high air humidity. After initial shrinkage, which occurred quickly (large open surface area, draft), cracks formed in the material. Firstly, the material moved away from all the side surfaces with which it came in contact, and secondly, chaotic cracks formed throughout the entire thickness of the penoizol layer, over the entire area of the attic. Our foam insulator comes to the customer and either fills in the cracks, or binds them with penoizol.
Winter is coming. In winter, the air contains much less moisture than at any other time of the year. In the attic, in any case, it is warmer than outside, therefore, the humidity is even lower. Moisture from the foam slowly begins to pass into the surrounding air and secondary shrinkage begins. Closer to spring, the owner goes upstairs and again rolls out a claim on the quality of the fill.
Eliminating the shortcomings again.
Then summer. In direct sunlight, the roof heats up to 80 ° C. It's stuffy in the attic. Both the insulation and the water contained in it are heated. The water molecules now have enough energy to overcome capillary forces and evaporation, and with it shrinkage continues. And again cracks and again elimination of shortcomings.
For the owner, it turns into a sport, and for a foam insulator, it becomes a nightmare. Three or four such demanding owners and there is no longer a foam insulator, but there is a foam concrete operator or someone else.
Similar embarrassment can occur when pouring into cavities. It all depends on what enclosing structures are installed. Given the physical meaning of what is happening, the enclosing structures not only protect the material from mechanical influences, but also from other types of influences, for example, thermal and humidity. So, for example, embarrassment as with an attic is hardly possible when pouring into brickwork. The brick smooths out the influence of climatic factors on the insulation. But the metal wall of the hangar is not.
Based on the foregoing, a beginner in penoizol should have a good understanding of the physics of the processes that occur after pouring, and not treat enclosing structures as structures that shield penoizol from the eyes of the customer. There will always be a client who will open the inner lining of the hangar, pick out the bricks of the upper row to see why it has become cold.
Are there resins, additives and equipment for the production of penoizol, the use of which guarantees no shrinkage? I can say with full responsibility - NO. And most likely it won't.
Are there ways to minimize or reduce the effects of shrinkage? THERE IS.
Raw materials used.
Resin. There are several brands of resins from which penoizol is made. These are resins "VPS-G", "Carbamet-T", KF-KhTP, KFZh, KFMT-15, KFM-TI.
Resin "VPS-G".
Of all the resins listed above, only the VPS-G resin was originally created for the production of urea foam. The resin is characterized by high reactivity, reduced formaldehyde content. Plasticizers are introduced into the resin at the stage of preparation. The material obtained from the VPS-G resin has passed all the necessary tests, including tests for durability in a climatic chamber. Material made from VPS-G resin is usually sold under the brand name Mattemplast.The developer of the VPS-G resin, Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, Academician of the Academy of Military Sciences of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor, Colonel VP Gerasimenya. The resin is produced at ZAO Uralchimplast in Nizhny Tagil under license and sold by a Nizhny Tagil firm. The VPS-G trademark belongs to the LOGRUS form.
"Carbamet-T".
This resin is produced in Orekhovo-Zuevo. The resin is produced according to the VPS-G resin production technology under license and is sold under the Karbamet-T trademark by agreement with the plant.
The resin is made to order and sold through this firm.
For this resin is really everything that is written about the resin "VPS-G".
Resin KFZH.
This resin is designed for gluing wood. It is characterized by a high formaldehyde content, therefore, highly toxic, and the absence of plasticizers in its composition. Due to the high proportion of formaldehyde, it is highly reactive. Foams made from KFZH resin have a persistent formaldehyde odor and are not recommended for use in residential premises. Due to their low elasticity, they have significant shrinkage.
Resin KFMT-15 (low-toxic).
Due to its low formaldehyde content, it has low reactivity. The absence of plasticizers and a small number of bonds makes the material obtained from this resin loose and fragile. Actually, this resin is intended for gluing wood (fiberboard, chipboard) under hot pressing conditions. Cold curing does not completely cure. The material is more susceptible to shrinkage, cracking, destruction.
Resin VPS-G.
This is an attempt to create an analogue resin "VPS-G". Moreover, the attempt is clearly unsuccessful. The plasticizer introduced into the resin works poorly, the material is stiff and more susceptible to shrinkage than foam from VPS-G. Increased formaldehyde content.
ATTENTION TO CONSUMERS !!!
Usually, manufacturers of works on pouring penoizol show customers a bunch of test reports, approvals, recommendations for use, certificates, etc.
This is often cheating!
In addition to foams made from VPS-G and Karbamet-T resins, foams from other resins have not been tested for durability. There is not a single recommendation for use issued by a government agency or research institutions.
The technique in this case is simple. Resin "VPS-G" is purchased for certification. Samples of the foam made from this resin are provided by the issuing institutions, and once the certificate is obtained, the facilities use cheaper resins that are not intended for foam production.
Ask the manufacturer of the works for the technical conditions under which they work and check the compliance of the raw materials specified in the technical specifications (invoices, call to the seller). Only this can save you from a big disappointment in penoizol.
Conclusion 1: There is no resin that would make it possible to make the material without shrinkage, but the use of resins containing plasticizers (VPSG and Carbomet-T) will minimize its consequences.
Equipment used.
All my experience in the production of equipment (and dozens of types of equipment for penoizol have been created and tested) and quality control of the foam produced on this equipment suggests that the main thing in the equipment is not productivity, not the ability to play with flows of components, but strict adherence to the proportion between the flows of solution and resin ... This allows you to select the amount of catalyst that you need to obtain the material with the desired properties. This also makes it possible to introduce the required amount of additives. Only dosing pumps can handle this. Among the variety of metering pumps, gear pumps are by far the best. Their main advantages are the ability to create high pressures and the absence of valves.On resin, as the experience of the "Standard" and "Turbojet" installations has shown, these pumps work reliably, but no one was able to use a gear pump for the solution. Adhering to our statement that dosing pumps should be used, we use plunger pumps of the same type for solution and resin in the Potok units. The disadvantages that are inherent in the joint work of different types of pumps, I described in detail in my article "Choosing equipment". As a further perspective, I will say that we are finishing work on the use of a gear pump to supply components, both through the resin line and through the solution line. The operating prototype of the installation is being tested.
The mixing and foaming method plays an important role in the quality of the material. Our experience suggests that mixing and foaming under pressure gives the best results. Moreover, it is in this sequence, first mixing, and then foaming. This scheme is implemented at Potok.
There is a myth and is supported by some equipment manufacturers that the revolution counter helps in the production of foam. Not true. Imagine that during operation your suction hose is clogged with a clot of resin. What will the rev counter show you? That's right, it will show that your pump is spinning normally. It will also show when the suction hose is bent, when the resin runs out, and when the solution supply stops. In all the above cases, you will not receive normal material, and the counter will tell you that everything is fine. It is much more important that a speed stabilizer was installed on the collector engines.
In general, the only device that really and objectively evaluates the process of penoizol production was and remains a manometer on the air line. It shows the pressure in the system. When you change the feed for one of the components, the pressure will immediately change.
Conclusion 2: Installation significantly affects the quality of the foam, and therefore the shrinkage. The equipment must ensure good mixing, foaming and keeping the proportions between the components. The equipment must be free of misleading instrumentation. (The latter is especially important when pouring under pressure, when no foam is visible).
Working methods.
Let's go back to our attic example. If the manufacturer of the work immediately after the end of the pouring took a shovel, for example, and cut the penoizol over the area into even, beautiful, squares (thereby forming future cracks), and even covered the entire surface with plastic wrap (slowing down drying and largely preventing internal stresses), and then, after the initial shrinkage has passed, the cracks formed with a material capable of compressing during filling, and then expanding as the cracks expand, his relationship with the customer would have developed in a completely different scenario. And the fame of his professionalism would go ahead of him. There are many similar methods and those who want to professionally deal with penoizol should, in any case, know them. This knowledge can be obtained on professional forums, where people gather who have associated themselves with this wonderful and complex material.
I am not encouraging you to use only these methods to combat shrinkage. I suggest, before getting down to work, to think under what conditions the material will be used and completely prevent shrinkage.
How to do it?
Consider the example of the same attic.
We can see that in the attic, the foam will work in very harsh temperature conditions. That shrinkage can cause us a lot of trouble.
We decide to lay the attic with bags of crumbs. There will also be shrinkage in the crumb, but it is multidirectional, chaotic and no cracks or gaps are formed that violate the heat-insulating layer. Bags should be breathable.I would recommend making them from polypropylene non-woven fabric (bed cover material). The bags are easy to make according to the pattern and staple with a stapler.
Alternatively, you can lay the attic with pre-made sheets of penoizol. But. Sheets will undergo exactly the same secondary shrinkage as filling foam insulation. Therefore, only heat-dried sheets are suitable for such tasks. Considering that it is quite possible to make them elastic, we will lay the attic without the slightest gap. The sheets that have passed the thermo-dryer have obviously lower humidity than the surrounding air, therefore, during operation, having absorbed moisture from the air, they can change the geometry, but only in the direction of increasing the size. And thanks to their elasticity, they will snuggle closer to each other.
The customer will be satisfied.
Conclusion 3: When carrying out work, it is necessary to take into account the operating conditions of the material and use those types (filling, sheet, crumb) that are most suitable for these conditions. To do this, however, you need to have at least a crusher, a cutter and a small dryer.
General conclusion: None of the above methods work in isolation. If you want to defeat shrinkage, you must work on good raw materials, reliable equipment, flexibly applying all types of foam insulation and methods of its production. Only then can you call yourself a professional.
Alexander Velikanov
Tula, 2009
Equipment for penoizol
For the industrial production of insulation, you need to buy the following equipment:
- compressor and power supply;
- a gas-liquid plant for liquefied gas, including a pumping system for supplying foam and solution;
- collapsible forms for pouring;
- containers for making a mixture;
- large table for packing material.
In this configuration, it is possible to produce sheet and liquid penoizol.
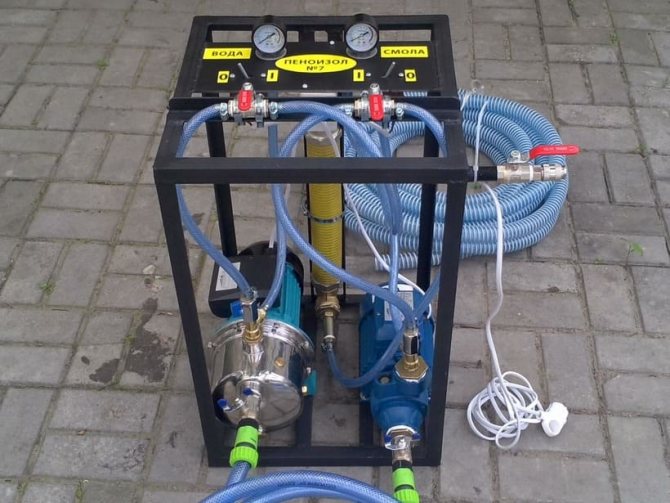


On sale there are equipment of Russian, Ukrainian and foreign production. The models differ from each other in price, technical characteristics - including the degree of process automation. There are mobile and stationary installations.
Equipment and components for the production of penoizol., UPG units, VPS-G resin, ABSK foaming agent, orthophosphoric acid.
Negotiated price Buy
The equipment can be made by yourself - the necessary drawings and diagrams are on sale.
When choosing a technique, it is better to look for a seller who trains the customer's personnel on the installation. The equipment must be guaranteed.
Obtaining urea liquid foam - penoizol.
It is quite simple to obtain liquid foam - penoizol - it is a process consisting of several stages:
- Preparation of components: pouring resin and water into working containers, mixing the foaming agent and hardener with water, heating the water to 40 C;
- Filling the hydraulic system of the unit with resin and mortar;
- Trial pouring into a test container to control the quality of the insulation;
- Direct pouring of insulation into a building structure or mold.
Raw materials
The product is produced by foaming a polymer resin according to a developed recipe. Depending on the formula, additives may be added to the composition, but the main components are the same.
- Synthetic urea-formaldehyde resin.
- Foaming agent. Required for stable foam formation.
- Catalyst (hardener). Accelerates the hardening process.
- Water with a temperature not lower than + 20 ° С.
Finding and buying the necessary raw materials will not be a problem.
There are generally accepted standards regarding the recipe, but a businessman may well create his own insulation formula. It is better to contact a construction expert, although you can find information yourself - there are enough online resources, forums on this topic on the Runet.
Penoizol production workshop
To organize a business, you will need a room with an area of 70-90 sq.m, divided into a production workshop, a warehouse, a staff room, an administrative office and a bathroom. It should be located away from residential areas. It is necessary to carry out communications on the territory of the mini-plant.
The workshop is equipped with a 220V current supply and a good ventilation system. The latter is necessary, because when drying sheets of insulation, substances harmful to health are released (phenol-formaldehyde is present in the composition of the synthetic resin).
The warehouse will store raw materials and finished goods. It is worth placing metal racks in the room.
The premises should be equipped with a car entrance for unloading and loading operations.
Process technology
Finished penoizol sheets
This type of insulation is very similar to marshmallow and marshmallow. Manufacturing is not difficult and very economical because inexpensive and practical composites are used for raw materials.
If the technology is followed, the result is a semi-liquid foam.
When the resulting mass dries up, it turns out to be quite elastic, and the dents from pressing on it immediately straighten out.
On top of that, the material retains heat very well and has an unlimited service life if used correctly.
Carbide foam is obtained using a foam generator by mixing the following materials:
- plain water;
- foaming agent;
- technical catalyst for obtaining a solid sealant;
- urea-formaldehyde type of resin.
For preparation, take a certain type of urea resin, after which an acid solution and a special foaming agent are added. In a foam generator set with supplied air under pressure, components are put in a certain amount.
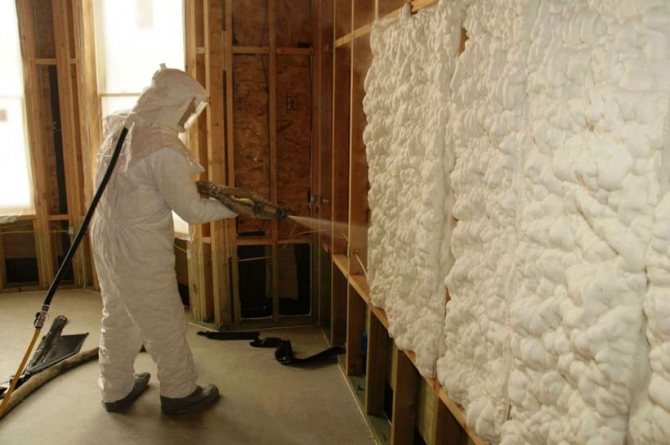
After mixing, a frothy, fluffy mass comes out. It is immediately, until it hardened, is poured into the voids prepared for filling.
The freshly made foam has a consistency very similar to the white jelly. It fills all openings and cracks very well, does not ignite and insulates the room well.
Filling walls with penoizol
The fresh composition does not harden immediately. Within ten, fifteen minutes after exiting the generator, it seizes a little. And after a few hours it hardens, but not yet strong enough.
It gains sufficient strength in 1 - 3 days. During this period, it dries well enough and gains all the due properties.
The insulation comes out excellent, and the cost of insulation is very modest.
In comparison with other materials, the speed of installation of this type of insulation increases several times. The possibility of using it in lightweight structures opens up competition and prospects for penoizol in the future.
You may be interested in an article on how to insulate walls with penoizol.
Read the article on floor insulation with penoizol here.
Staff
To service the production, you need to hire 3 people, one of whom will be the senior in the shop. The latter is responsible for coordinating the rest of the workers, monitoring their activity and training. It is the senior worker who needs to be sent on an internship to the equipment seller.


A sales manager is required to organize sales. He will meet and negotiate supplies with representatives of construction and wholesale and retail companies.
A driver is needed to deliver raw materials to the plant and finished goods to customers.
The accountant will deal with paperwork and preparation of papers for tax authorities. It is better to hire him for outsourcing (contacting an accounting firm).
Who should we sell the finished product to?
3 main groups of urea foam consumers:
- construction companies, repair and construction companies;
- retail stores and wholesale and retail chains selling construction products, construction markets;
- private persons.
At the initial stage, it is important to use all possible distribution channels - it is necessary to attract the attention of potential buyers to the new product.However, the most convenient option is to get a contract for large supplies of insulation. Therefore, great attention should be paid to negotiations with construction companies.
Penoizol business is seasonal. Construction is actively carried out in the warm season. Of course, large construction projects are carried out in winter, but in general, the volume of construction work in the cold drops noticeably.